Non-numeric data represents text strings and Boolean values. If the input range contains non-numerical data, we cannot calculate descriptive statistics. This article will help you overcome the problem of Descriptive Statistics: Input range contains non-numeric data.
➤ The “Input range contains non-numeric data” error occurs due to non-numeric data and descriptive statistics can calculated for numeric data only.
➤ Error Checking: Click the green triangle >> Convert to Number.
➤ Text to Columns: Data >> Text to Columns >> General number format.
In this article, we’ll provide solutions for the “Input range contains non-numeric data” error using Error Checking, Number Format, Text to Columns, Paste Special, and the VALUE function.
To calculate descriptive statistics, you need to enable the Data Analysis ToolPak. Once enabled, follow these steps to get the descriptive statistics and understand the results.
Using Error Checking to Convert to Numbers
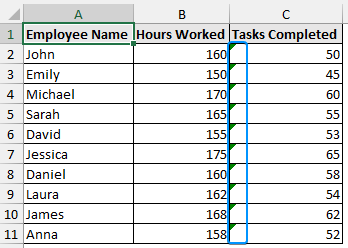
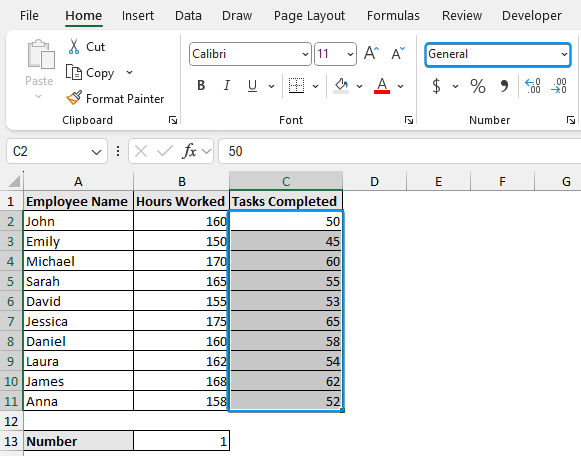
In this dataset, we have the employee name in Column A, the hours worked in Column B, and the tasks completed in Column C. Error checking is the simplest way to convert non-numeric data to numeric data. Follow the steps:
Steps:
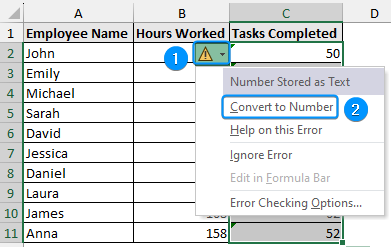
➤ The small green triangle is Excel’s way of telling us that the values look like numbers but they are text.
➤ Select the cell range (C2:C11) >> Click on the triangle >> Select Convert to Number.
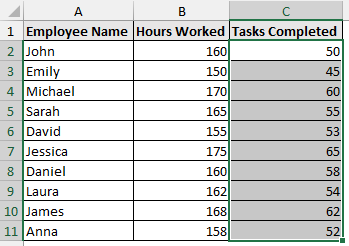
➤ The non-numeric data are now formatted as numbers.
Convert Text to Numbers with Number Format
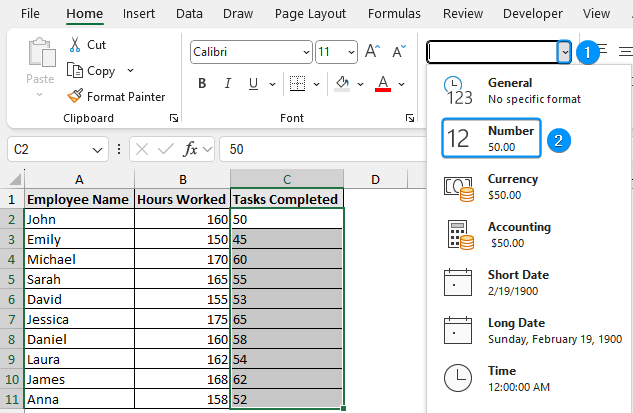
Another simple fix is checking the number formatting from the Home tab. This is useful when numeric data is wrongly formatted as text.
Steps:
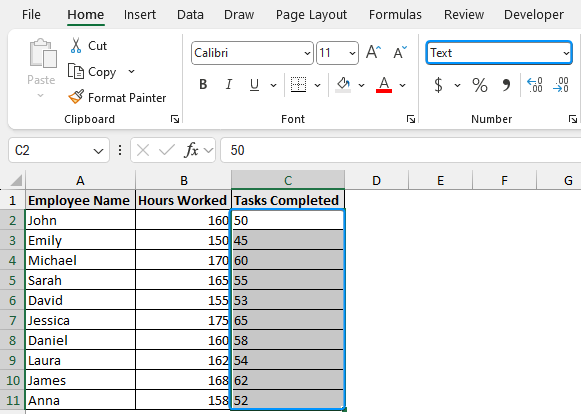
➤ Select cell range (C2:C11) >> In the Number Format box we can see text.
➤ Click the drop-down arrow >> Choose Number.
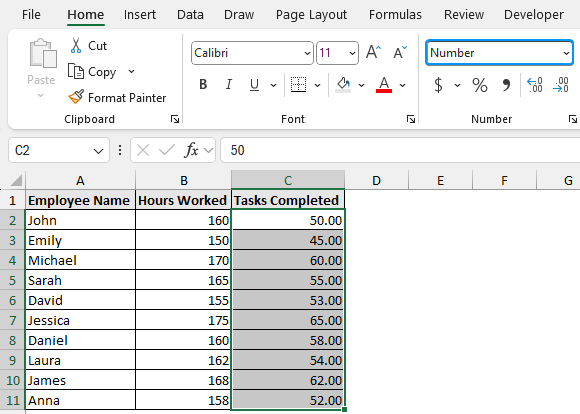
➤ The data will be formatted as numbers. If you observe closely, the alignment has changed. In Excel, texts are left-aligned while numbers are right-aligned.
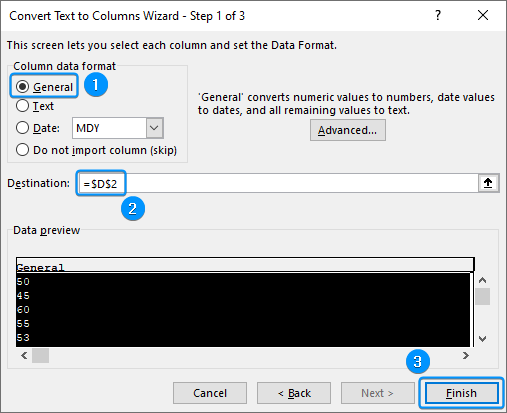
Applying Text to Columns
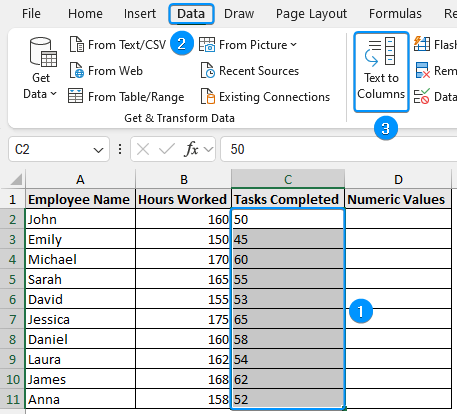
You can use the Text to Columns wizard to transform texts into numbers. In the image below, I have added an empty column for storing the numeric values.
Steps:
➤ Select cell range containing text data >> Go to the Data tab >> Select Text to Columns.
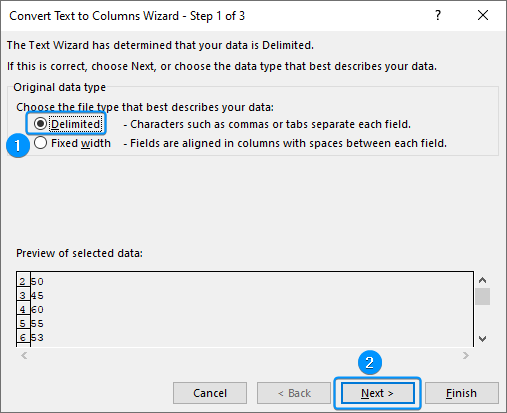
➤ Select Delimited >> Next.
➤ Keep the default selections and click on Next.
➤ Choose General >> Set the destination (D2) >> Finish.
➤ The text data will be converted to numbers.
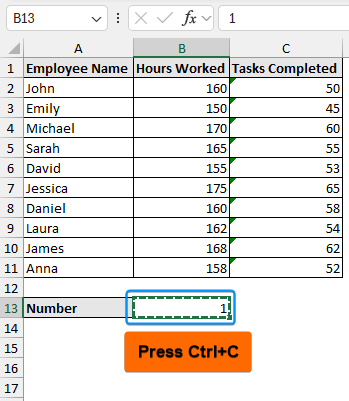
Paste Special to Change from Non-Numeric to Numeric Data
The Paste Special option offers another quick and effective solution. If we multiply a number with text, it gets converted to a numeric value.
Steps:
➤ Enter 1 in any cell (B13) >> Press Ctrl+C to copy it.
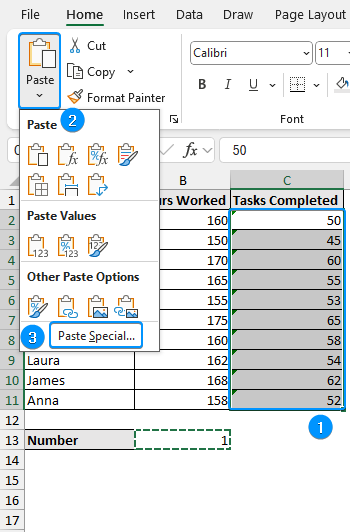
➤ Select the range containing text (C2:C11) >> Click Paste >> Paste Special.
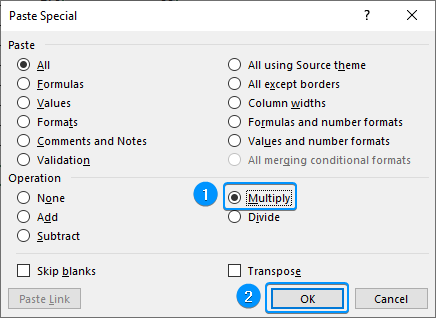
➤ Check the Multiply option and press OK.
➤ The text data will be changed to numbers.
Using the VALUE function to Convert to Numbers
You can use the VALUE function to convert text strings to numbers.
Steps:
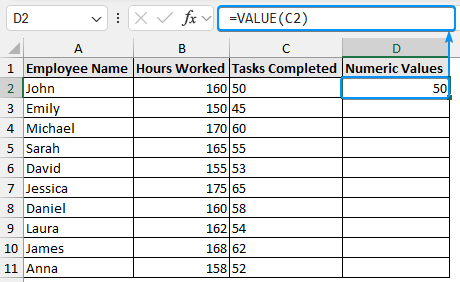
➤ Select output cell (D2) and type the formula:
=VALUE(C2)
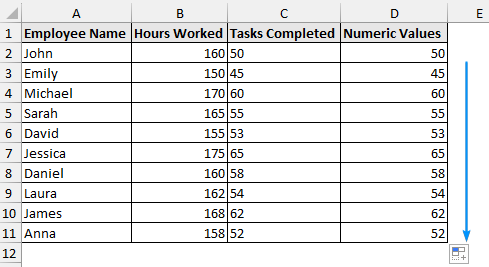
➤ Use the Fill Handle tool to autofill the rest of the cells as shown below.
FAQ
What does it mean when the input range contains non-numeric data?
It means that a column or a cell contains non-numeric (text) data even though it looks like a number.
What are two non-numeric data types?
The two non-numeric data types are:
➤ char which represents alphabets, numbers, and special symbols.
➤ Boolean which represents the true and false values
What is the input range in Descriptive Statistics?
When calculating descriptive statistics with the Data Analysis add-in, the input range represents the range you want to analyze. The selection of the input range usually includes the column headers or labels. In that case, you must check the labels in first row option.
How can you tell apart a number from text in Excel?
In Excel, texts are by default left-aligned and numbers are right-aligned.
Wrapping Up
In this tutorial, we’ve learned to fix the “Descriptive Statistics – Input range contains non-numeric data” error. We’ve discussed the reason for this error and shown several methods like Error Checking, Number Format, Text to Columns, Paste Special, and the VALUE function to resolve this issue. Feel free to download the practice file and let us know which solution you like the most.