Working with large Excel files can be frustrating when it leads to slow calculations, constant lag, and even crashes. Whether you’re handling thousands of rows, complex formulas, or linked workbooks, Excel can quickly become sluggish.
In this article, you’ll learn how to make Excel run faster with lots of data using proven methods. Each method is easy to follow and designed to improve performance without compromising your work. Let’s speed up your Excel file, step by step.
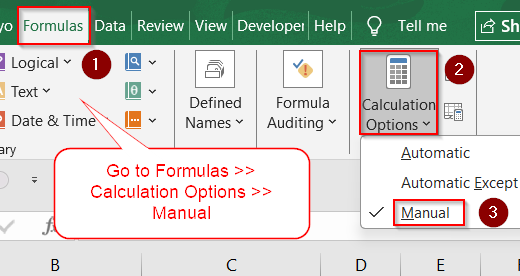
➤ Go to Formulas tab.
➤ Click Calculation Options in the ribbon.
➤ Select Manual.
➤ Press F9 to calculate manually when needed.
Disable Automatic Calculations
Excel recalculates formulas every time you make a change. With large datasets, this can cause delays.
Steps:
➤ Click the Formulas tab.
➤ Click Calculation Options in the ribbon.
➤ Select Manual.
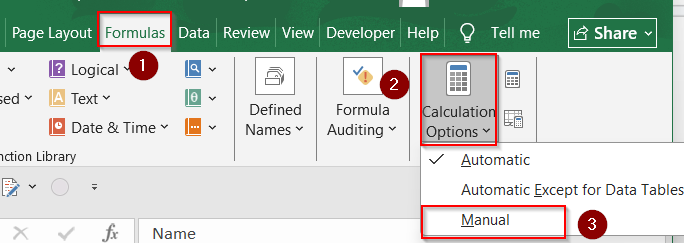
➤ Now, press F9 to calculate manually when needed.
This drastically reduces lag when editing or navigating large files.
Convert Formulas to Values
Complex formulas, especially array formulas and volatile functions like NOW, RAND, or INDIRECT can slow down Excel.
Steps:
➤ Select the range containing formulas.
➤ Press Ctrl + C to copy.
➤ Right-click and choose Paste Values.
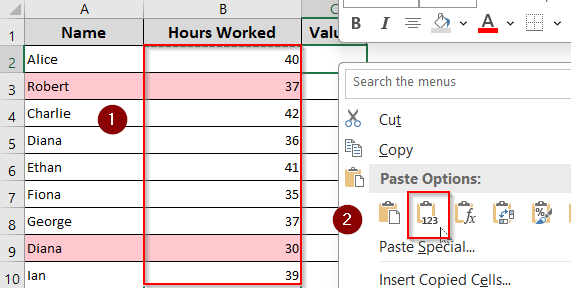
This is ideal for finalized data where you no longer need live calculations.
Use Excel Tables and Structured References Wisely
Tables are powerful but too many of them, especially nested or dynamic ones can slow things down.
Steps:
➤ Use tables for clean structure but avoid overusing calculated columns.
➤ Don’t apply entire column references like =SUM(Table1[Column1]) if not needed.
➤ Turn off table styles if not required.
➤ Convert table to range by right-clicking inside the table.
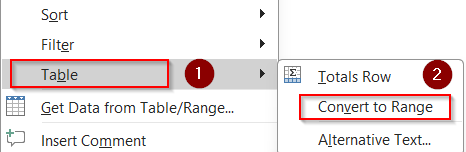
Smart use of tables improves structure without sacrificing speed.
Avoid Array Formulas and Volatile Functions
Array formulas and volatile functions force Excel to recalculate more often than needed.
Steps:
➤ Replace OFFSET, INDIRECT, or CELL with non-volatile alternatives like INDEX.
➤ Minimize use of ARRAYFORMULA and large nested IF statements.
➤ Use helper columns instead of arrays where possible.
Simplifying formulas lightens Excel’s processing load significantly.
Remove Unused Named Ranges and Styles
Over time, Excel workbooks can accumulate thousands of hidden named ranges and styles that slow everything down.
Steps to clean named ranges:
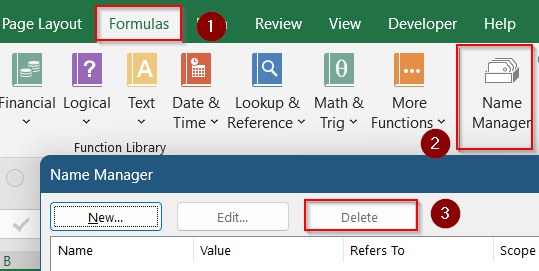
➤ Press Ctrl + F3 to open the Name Manager.
➤ You can also access this using the Formulas tab >> Name Manager.
➤ Delete any unused names.
Steps to clean styles:
➤ Go to Home >> Cell Styles.
➤ Right-click unused styles and select Delete.
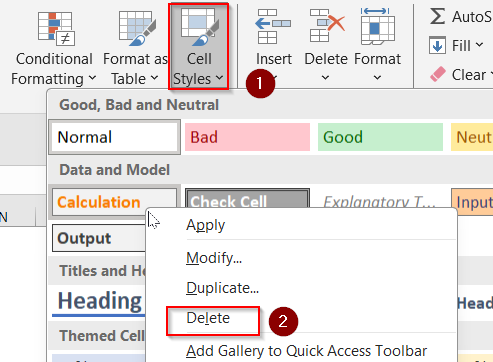
This cleans up background clutter and boosts workbook speed.
Keep Data on Fewer Worksheets
Having too many sheets with separate datasets, calculations, or pivot tables can impact performance.
Steps:
➤ Consolidate related data into one sheet if possible.
➤ Avoid using entire columns (e.g., A:A) in formulas. Use defined ranges instead.
➤ Delete blank or unused sheets.
Fewer sheets and focused ranges make Excel run more efficiently.
Optimize File Format and Features
Large Excel files often contain unnecessary objects, formatting, or older file formats that weigh them down.
Steps:
➤ Save the file as .xlsx instead of .xls
➤ Go to File >> Save As >> Choose location >> Excel Workbook (*.xlsx).
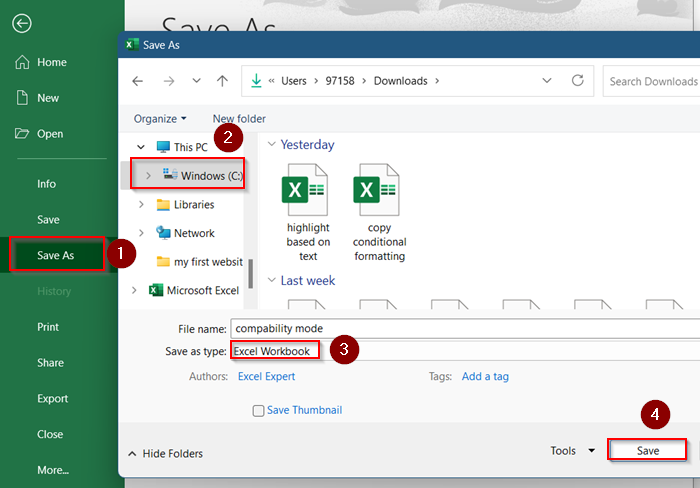
➤ Remove excessive formatting.
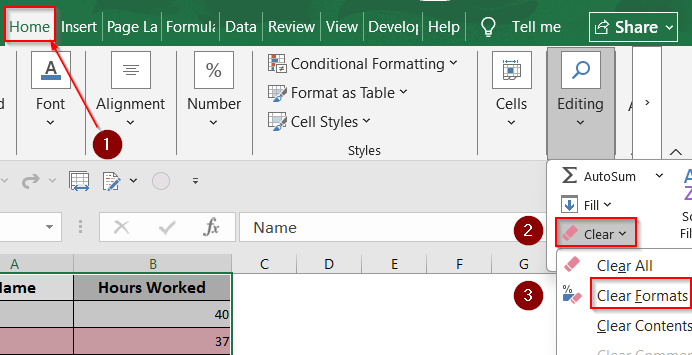
➤ Select all (Ctrl + A) >> Home >> Clear in the Editing group >> Clear Formats.
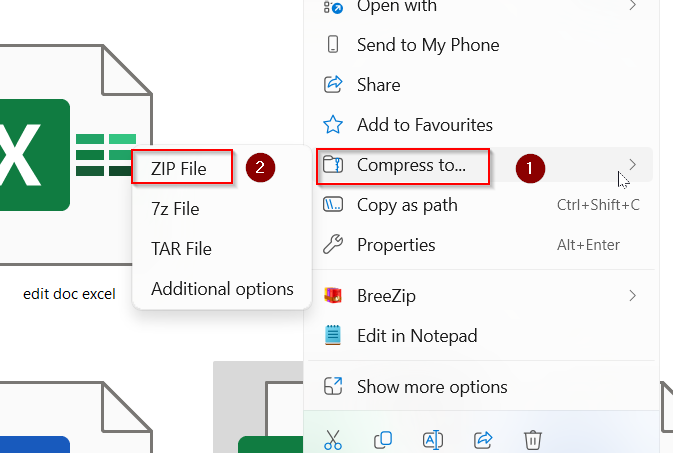
➤ Compress the file.
➤ Right-click the file >> Choose Compressed to >> ZIP file.
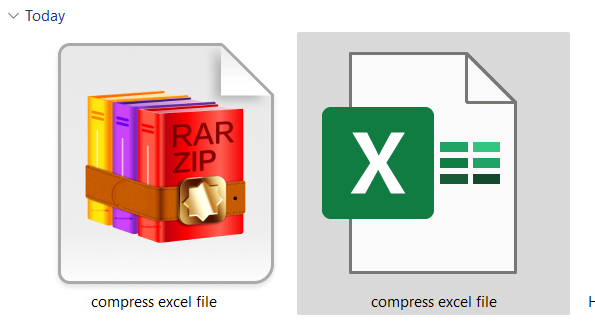
➤ A new ZIP file will appear next to the original.
A cleaner file format helps Excel open, calculate, and save faster.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Excel lagging with large datasets?
Because each formula, formatting, and feature adds processing overhead. The more Excel needs to calculate, format, or load, the slower it gets.
Will using Pivot Tables slow Excel down?
Pivot Tables themselves are efficient, but multiple pivot tables with overlapping caches or data from large ranges can reduce performance.
Does filtering or hiding rows improve speed?
No, hidden or filtered rows still exist in memory. Deleting unused rows is more effective for improving speed.
Wrapping Up
In this tutorial, we learned multiple ways to make Excel run faster with large amounts of data, from using manual calculation mode and optimizing formulas to clearing excess formatting and reducing workbook size. These small adjustments can lead to a significant improvement in performance. Feel free to download the practice file and share your feedback.




