When we are working with dates in Excel, it is a common task to compare two dates to determine if one is greater than the other. This is good in managing deadlines, tracking due dates, or automating time-sensitive workflows. We know several methods that can do the same which are very easy to apply.
To find out if one date is greater than another, follow these steps:
➤ Click on the cell where you want the result.
➤ Enter the formula: =IF(A1 > B1, “Yes”, “No”)
➤ Press Enter to apply the formula.
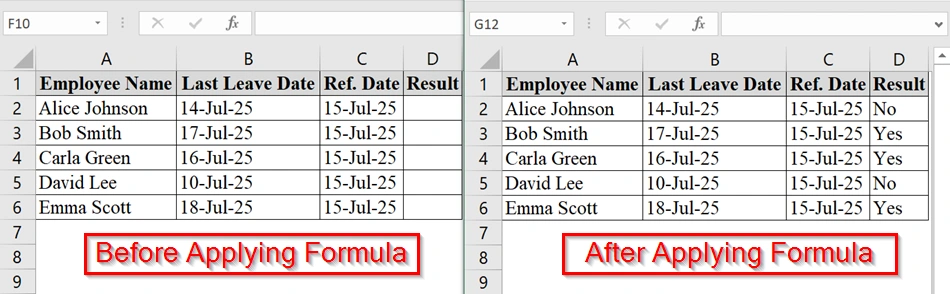
In this article, we will guide you through how to determine if a date is greater than another date or not along with conditional formatting and VBR method.
Using Formula to Compare Dates in Excel
We will use the =A1>B1 formula that will allow us to check if one date is greater than another in Excel. This formula is good when we need to track overdue deadlines, delayed submissions, or chronological errors in the dataset.
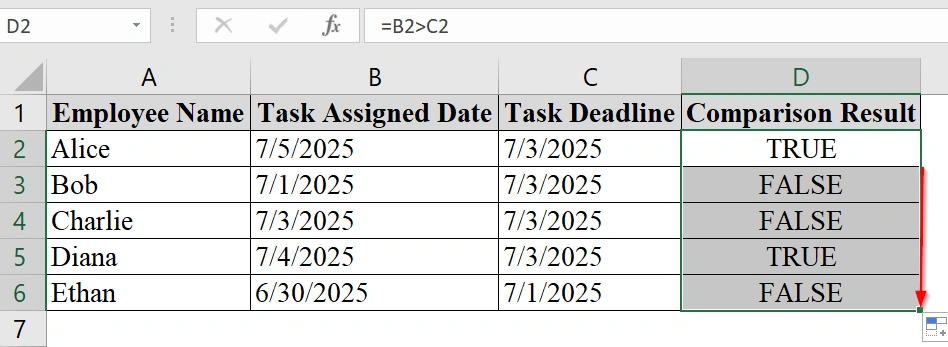
We have a table that tracks the tasks that were assigned after the deadlines. We will check if the assigned date is greater than the deadline. We will use a simple Excel formula to compare two dates, helping in quick task performance audits.
Steps:
➤ You can open your dataset and work there, or download our demo dataset. In our dataset we have Name in Column A, Assigned Dates in Column B,and Deadline Dates in Column C.
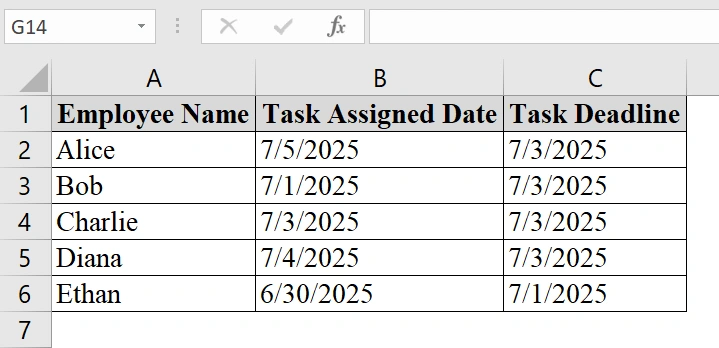
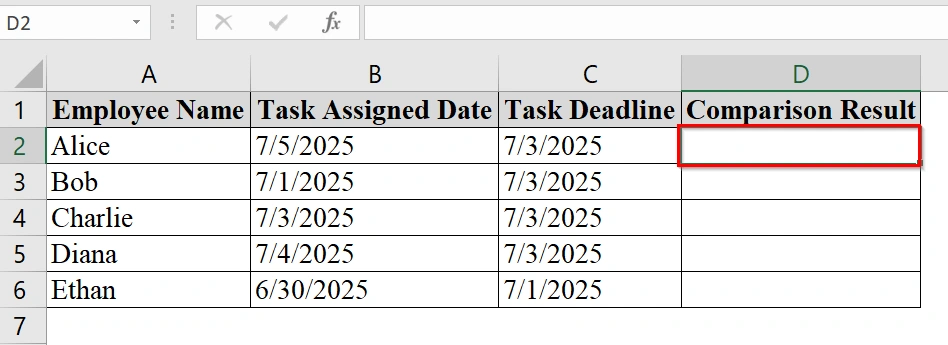
➤ Select the first cell where the comparison result should appear. In our example, click on cell D2 to input the comparison formula.
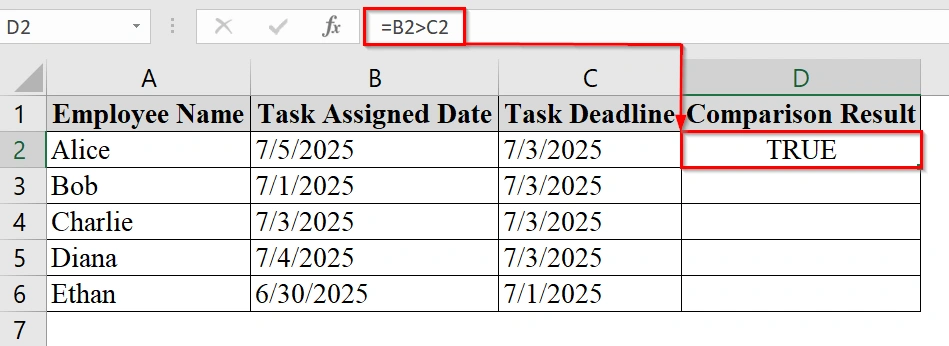
➤ Type =B2>C2 into the formula bar. This will return TRUE if the assigned date is after the deadline, otherwise FALSE.
➤ Use the fill handle (bottom-right corner of cell D2) and drag it down to apply the formula to the rest of the rows.
Note:
➥ Ensure that the date cells are formatted properly as dates. Mismatched formats may lead to incorrect results.
➥ This method works with any valid Excel date format including dd/mm/yyyy, mm/dd/yyyy, or custom formats.
Using IF Function to Check if One Date is Greater than Another in Excel
We can use the IF function to compare two date cells and return a value based on if the first date is greater than the second. This is very useful in scenarios such as HR leave tracking, task deadlines, or event scheduling.
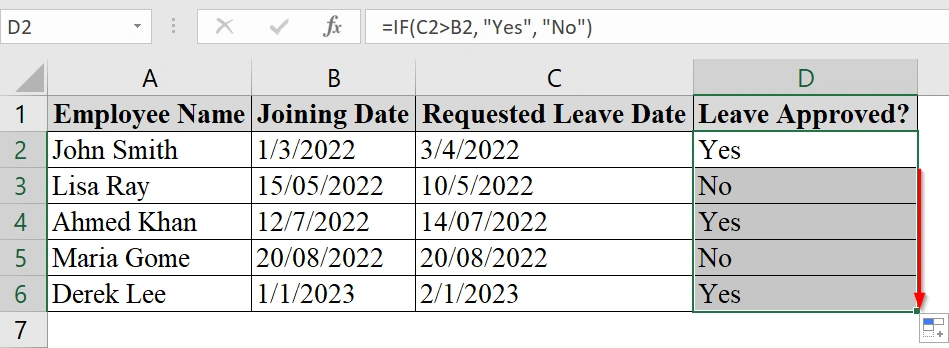
We have an Excel dataset that contains information about Employee joining and leave date. This table explains if the leave requests by employees are made for dates after their joining date. We will use Excel’s IF formula to compare the two dates and return “Yes” for approved requests and “No” for rejected ones.
Steps:
➤ Open the Excel sheet. We have three columns: Employee Name, Joining Date, and Requested Leave Date.
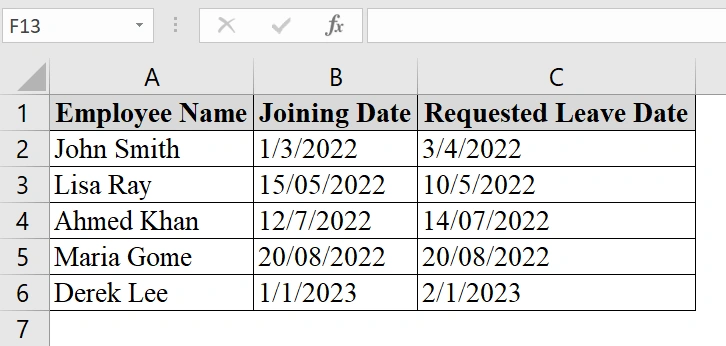
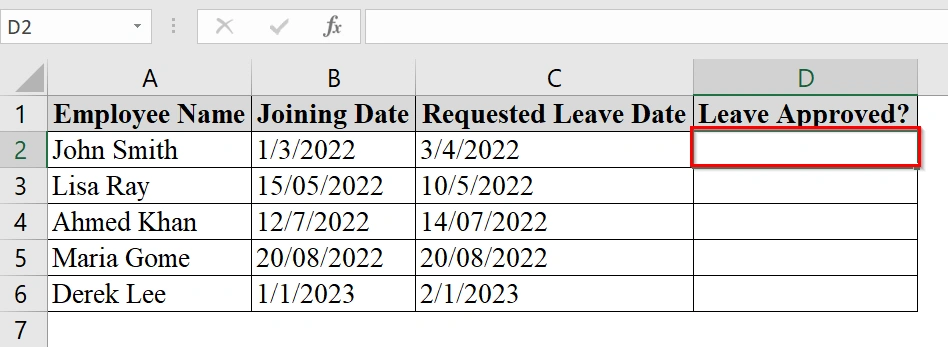
➤ Click in the first empty cell in a new column (e.g., D2 under Leave Approved?).
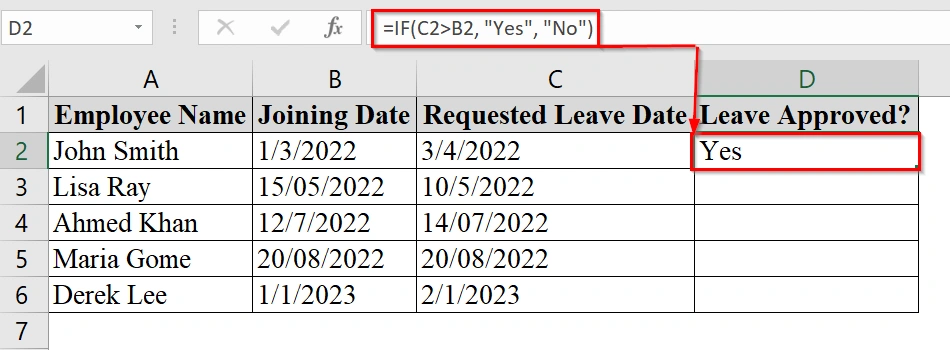
➤ Enter the formula:
=IF(C2>B2, "Yes", "No")
This checks if the value in Requested Leave Date (C2) is greater than Joining Date (B2). If it is, it returns “Yes“; otherwise, “No“.
➤ Drag the fill handle down to apply the formula to other rows.
Combine IF Function with Hardcoded Date
IF with Hardcoded Date uses the IF function in Excel combined with a hardcoded date via DATEVALUE to check if one date is greater than another. We use this when we are tracking deadlines, launch dates, or project timelines and need to display a status based on comparison with a fixed date.
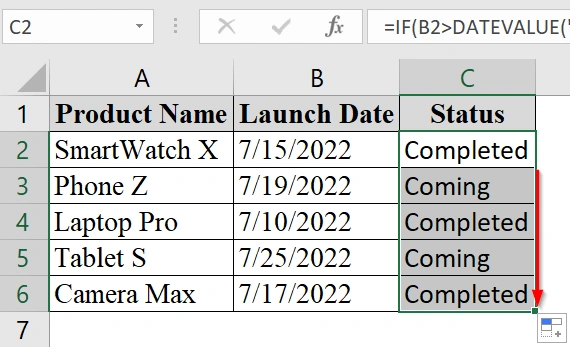
We have taken a worksheet that contains a manager who is managing a product launch calendar and tracking the release status of different products. We want to automatically check if a product is already released or is still “Coming soon” based on if the launch date is greater than a set date (e.g., July 18, 2022).
Steps:
➤ Create an Excel sheet with three columns. Enter the product names in column A and their launch dates in column B.
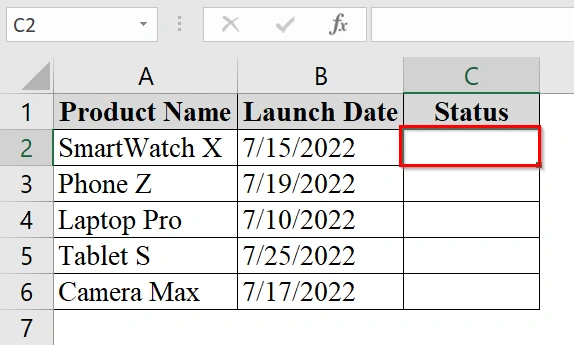
➤ Select the first cell in the “Status” column.
➤ Enter the formula:
=IF(B2>DATEVALUE("7/18/2022"), "Coming soon", "Completed")
This formula checks if the date in B2 is after July 18, 2022. If yes, it shows “Coming soon”; otherwise, it shows “Completed”.
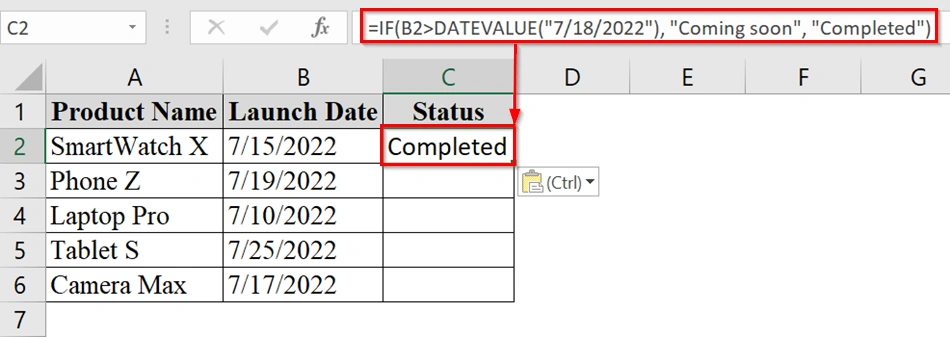
➤ Drag the fill handle down to apply the same formula to the rest of the rows in the Status column.
Note:
➥ DATEVALUE(“7/18/2022”) is used to convert the string into a date Excel can compare.
➥ We can replace “7/18/2022” with any relevant reference or date as needed.
➥ Ensure the dates in column B are formatted properly as actual Excel dates, not text.
Determine If a Date is Greater Than Today’s Date
Using IF and Today Function in Excel is very much used when we want to manage deadlines, schedules, or events.
We have taken a table about how a project manager is tracking various project milestones in Excel. Each milestone has a target completion date. The manager wants to know which milestones are still upcoming and which ones have been completed based on today’s date. We will use IF and Today Function to do this.
Steps:
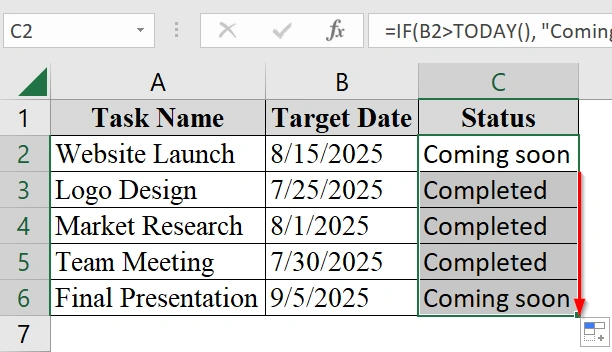
➤ Make sure the dataset has a column with dates as we want to compare it like “Target Date”). We have added a “Status” column in column C for the result.
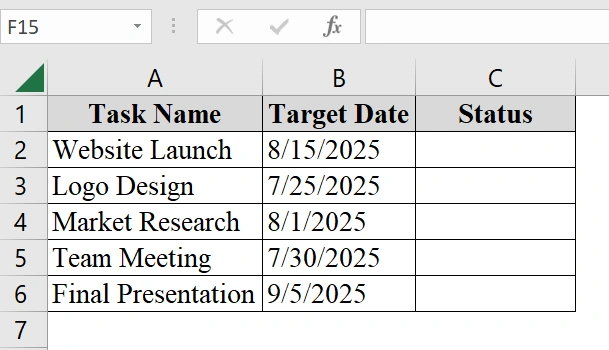
➤ Click on the first cell in the Status column (e.g., cell C2).
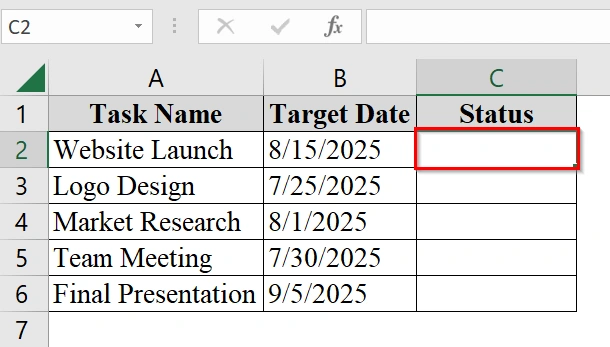
➤ Enter the formula in cell C2:
=IF(B2>TODAY(), "Coming soon", "Completed")
This formula checks if the date in cell B2 is later than today’s date. If it is, the result is “Coming soon“. Otherwise, it is “Completed“.
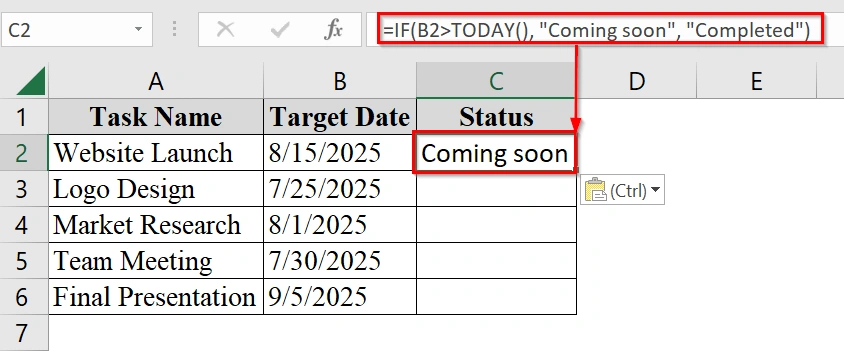
➤ Click and drag the fill handle down to fill the formula for all rows.
Note:
➥ This formula updates automatically every day because it uses the TODAY() function.
➥ Ensure all date values in column B are formatted properly as date types to avoid formula errors.
➥ We can customize the output text, for example: change “Coming soon” to “Pending” or “Upcoming Deadline”.
Highlight Cells If Date is Greater Than Another Date
We can use Conditional Formatting to show how to use an Excel formula to highlight dates in a column that are greater than another date. This is good for deadline tracking, upcoming events, and any time-sensitive records.
We have a table in which we want to track project task deadlines for team members. We want to highlight tasks that are past due compared to today’s date using an Excel formula and conditional formatting.
Steps:
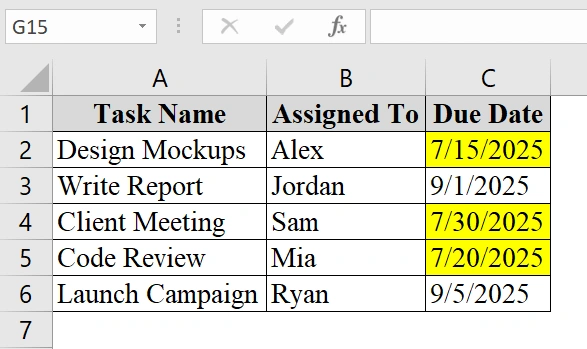
➤ We have taken a table that contains Task Name in Column A, “Assigned To” in Column B, and Due Date in Column C.
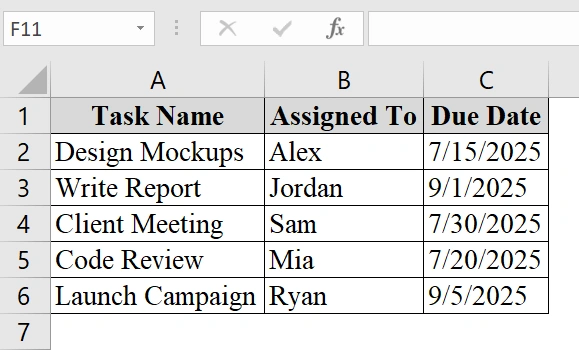
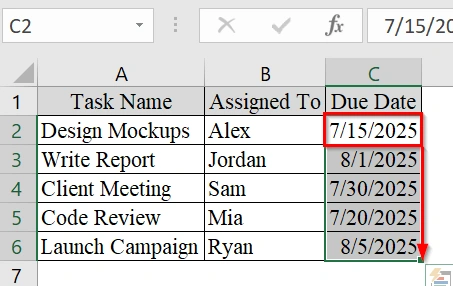
➤ Click and drag to select the cells in column C that you want to check against today’s date. For example, select cells C2 to C6.
➤ Click on Conditional Formatting > New Rule.
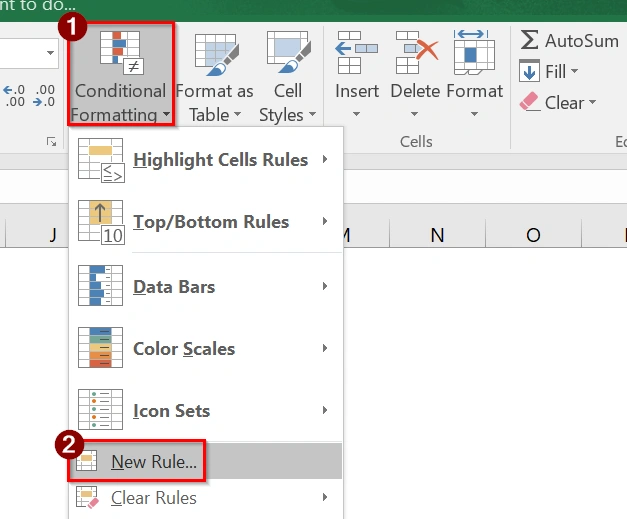
➤ Choose “Use a Formula to Determine Which Cells to Format”. Enter the Formula to Compare Dates:
=C2<TODAY()
This checks if the due date in cell C2 is before today.
➤ Click the “Format” button.
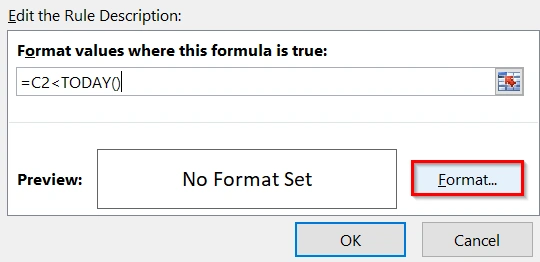
➤ Choose a fill color (e.g., yellow) to highlight overdue tasks. Press OK.
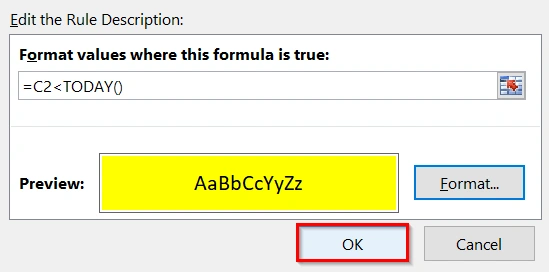
➤ Click OK again to close the rule dialog.
➤ All dates in column C that are before today’s date are highlighted with our chosen color.
Using VBA UDF in Excel to Compare Dates
VBA UDF (User Defined FUnctions) in Excel explains how to use a custom VBA function to compare two dates and return a result like “Late” or “On Time”. This is good when we want dynamic, reusable logic across large datasets such as delivery tracking or project deadlines.
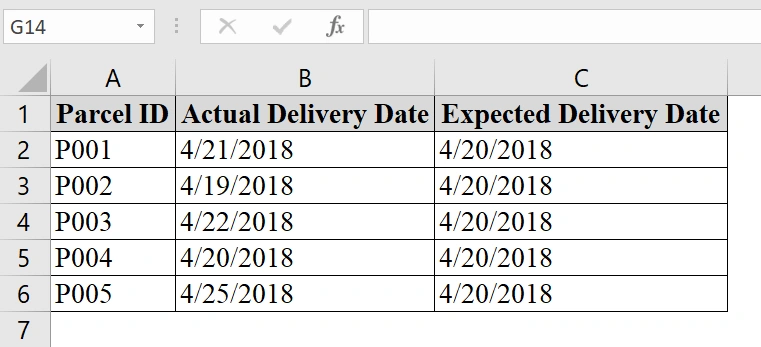
We have a table in which we are tracking the expected delivery date of parcels against the actual delivery date. We want to flag parcels that arrived late. VBA UDF in Excel is good to use in evaluating courier performance.
Steps:
➤ Open the workbook.
➤ Press Alt + F11 in Excel to open the VBA Editor.
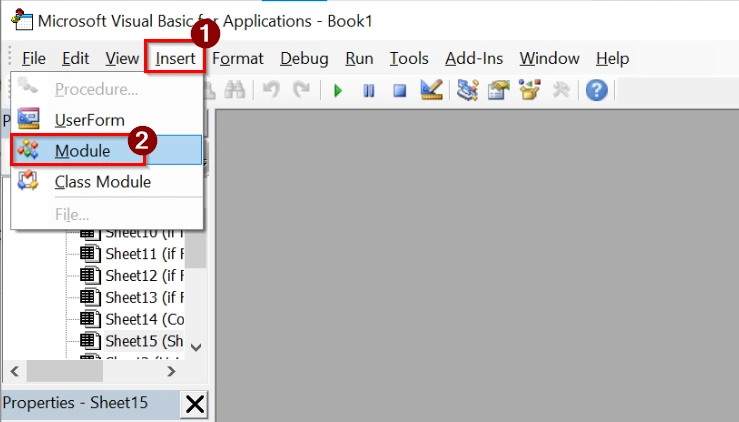
➤ In the VBA Editor, click Insert > Module. This creates a blank module for the function.
➤ Copy and paste the following code into the module:
Function CompareDates(date1 As Date, date2 As Date) As String
If date1 > date2 Then
CompareDates = "Late"
Else
CompareDates = "On Time"
End If
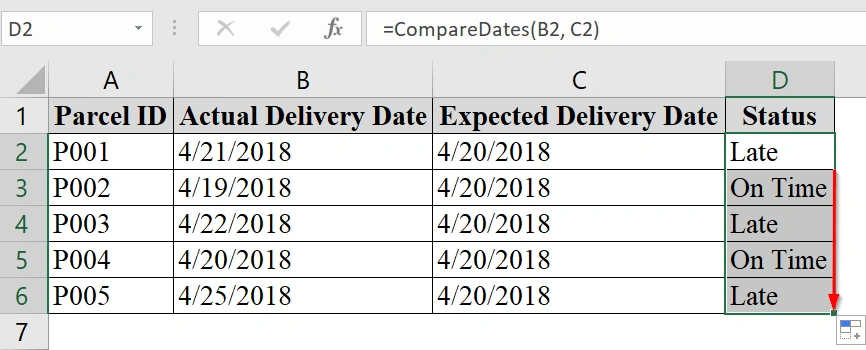
End FunctionThis function checks if date1 (Actual Delivery Date) is later than date2 (Expected Delivery Date), and returns “Late” if true, otherwise “On Time“.
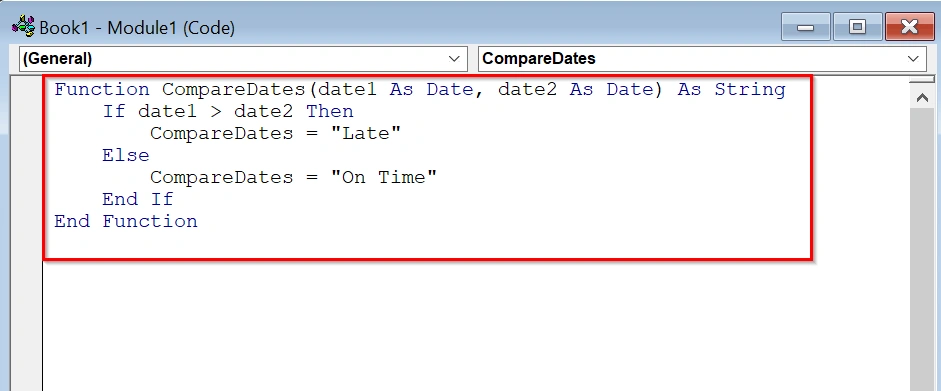
➤ Click “Run”.
➤ Save the file as a macro-enabled workbook (.xlsm).
➤ In the worksheet, create a new column named Status.
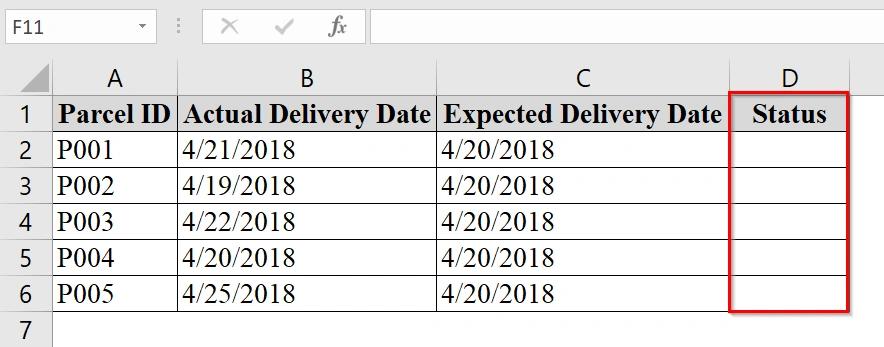
➤ In the first cell under Status (e.g., cell D2), use the formula:
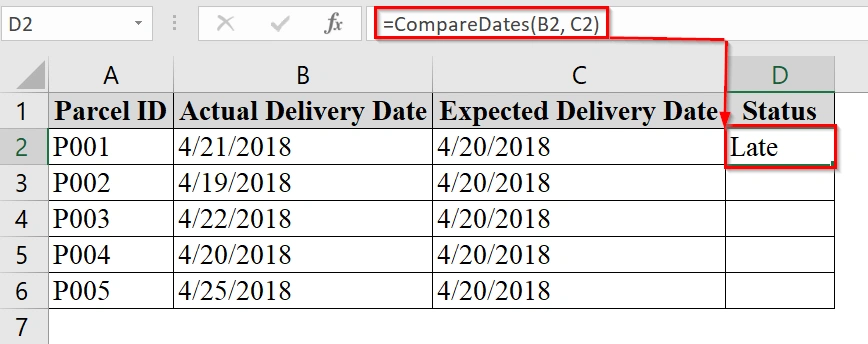
=CompareDates(B2, C2)
This compares the actual delivery date in B2 to the expected date in C2.
➤ Use the fill handle to drag the formula down to apply it to the entire dataset.
Note:
Make sure macros are enabled in the workbook, or the function would not work.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use the IF formula with TODAY?
Yes. You can use =IF(A1 > TODAY(), “Future”, “Past”) to check if a date is in the future or past.
What happens if the cells are blank?
If a date cell is blank, Excel treats it as zero. This may lead to unexpected results unless handled with additional logic.
Can I use conditional formatting with this formula?
Yes. You can apply conditional formatting using a similar formula to highlight cells where dates exceed a specific threshold.
Concluding Words
In this article, we have shown a few methods to compare two dates in Excel and return a value based on if one is greater than the other. These simple methods are good for flagging overdue items, setting alerts, and organizing time-sensitive data efficiently.







