When working with Excel datasets, you often need to delete unwanted rows to keep your data clean and organized. However, manually deleting them takes time and increases the chances of errors. That’s especially true for the large datasets.
In such cases, using VBA macros to delete rows helps to automate the process and make the task faster and more accurate. That is why in today’s article, we will walk you through eight practical methods to delete rows in Excel using VBA. It includes deleting single rows, multiple rows, selected rows, rows based on conditions, blank rows, alternate rows, duplicates, and rows inside Excel tables.
➤ Press Alt + F11 and open the VBA editor
➤ Right click on your sheet name >> Select Insert >> Module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code.
Sub DeleteSingleRowByNumber()
Rows(3).EntireRow.Delete
End Sub➤ Run the code.
➤ The VBA code will delete the row entirely that you have specified [Rows(3)] from the worksheet entirely.
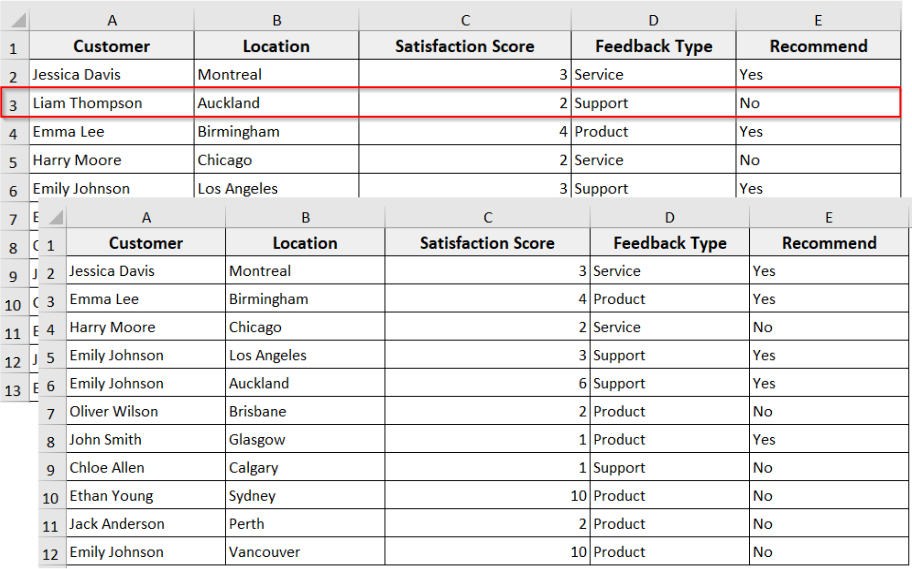
Delete an Entire Row by Row Number
In the Excel dataset, if you want to delete a specific row entirely without manually selecting it, you can use this VBA code. The following Excel VBA selects the row you specify and deletes the row completely. All the other rows below it shifted upward.
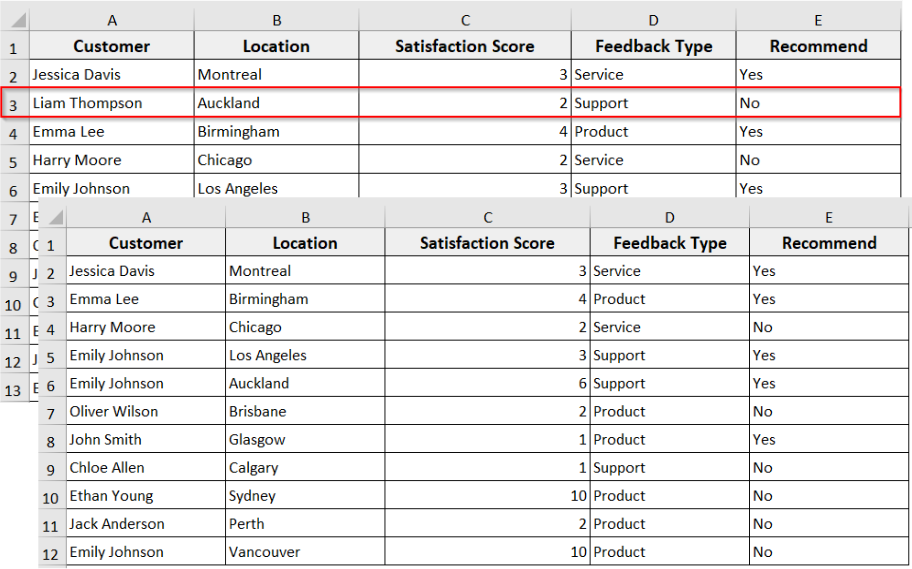
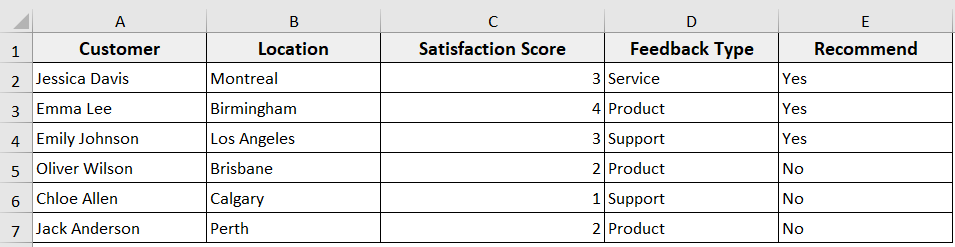
In the following dataset, we have Customer Feedback information. Now we are going to delete entire rows from this dataset in different scenarios.
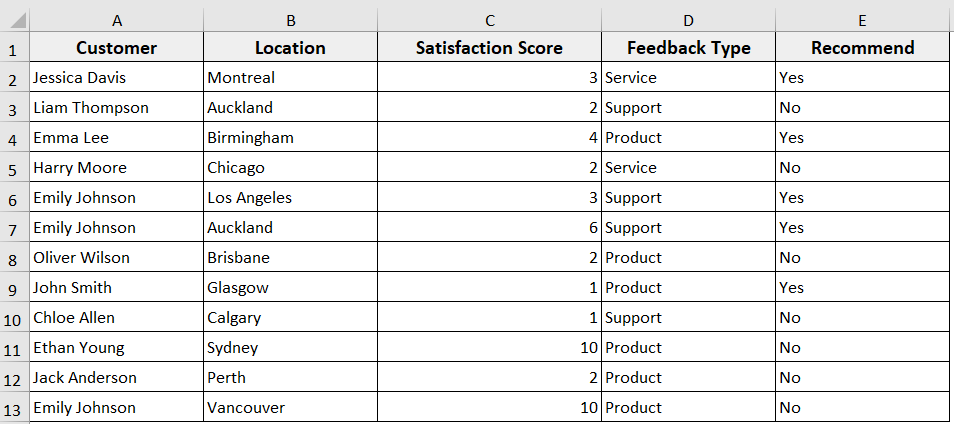
In the first case scenario, let’s say you want to delete a single entire row from the sheet. To do so, follow the steps below.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA Editor.
➤ Right click on your sheet name >> Select Insert >> Module.
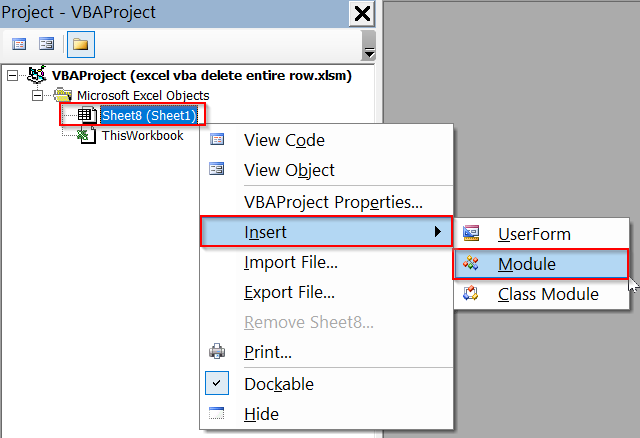
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code.
➤ You can copy and paste this VBA with a change in the number of Rows(3) to the number you want to delete the entire row.
Sub DeleteSingleRowByNumber()
Rows(3).EntireRow.Delete
End Sub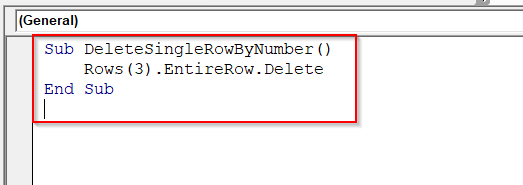
➤ Run the code.
➤ The code will delete row 3 entirely from the active sheet, and all the remaining data will move up one row.
Delete Multiple Rows
The following VBA code can be used when you want to delete multiple consecutive rows at once. It helps you to save time and effort compared to deleting each row manually. The VBA code deletes your specified rows entirely from the dataset.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA Editor.
➤ Insert new module.
➤ Insert the following VBA code in the new module.
Sub DeleteMultipleRows()
Rows("4:7").EntireRow.Delete
End SubNote:
In this VBA code,
➥ Change “4:7” to the range of rows you want to delete for adjacent rows.
➥ For non-adjacent rows, change 4:7 to the “2:2,5:5,8:8” where you need to list each row separated by commas.
For example: Rows(“2:2,5:5,8:8”).EntireRow.Delete
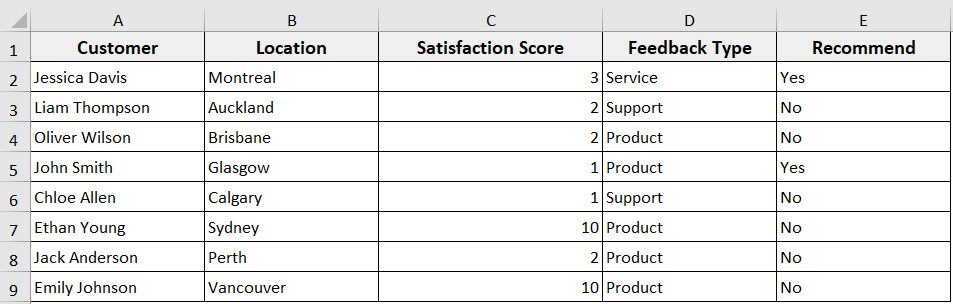
➤ Run the code.
➤ It will delete 4 to 7 rows entirely from the active sheet.
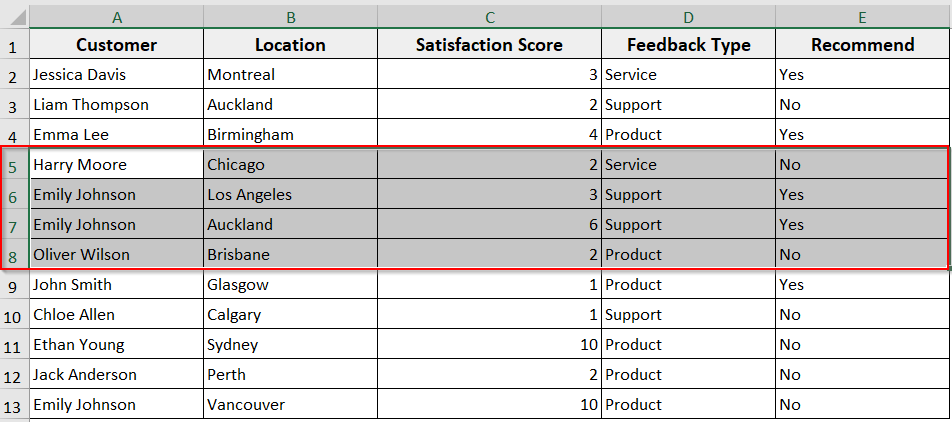
Delete Selected Rows
You can use this code when you want to delete manually selected rows in the worksheet, but with the help of Excel VBA. It’s a useful method as it offers you more control to choose which rows to remove before running a macro. Here, in this method, you need to select the rows manually, and VBA will delete them after running as a result.
Steps:
➤ First, select the range of rows you want to delete from the worksheet.
➤ Open the VBA editor and insert a new module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code. You can just copy and paste the code; no changes are required.
Sub DeleteSelectedRows()
Selection.EntireRow.Delete
End Sub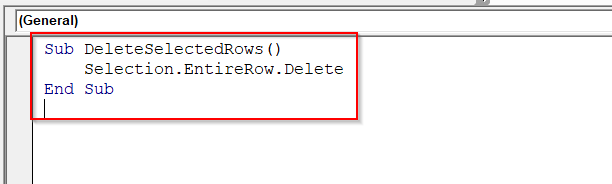
➤ Run the code.
➤ The Excel VBA will delete your selected rows completely from the worksheet. The rows below will move up accordingly.
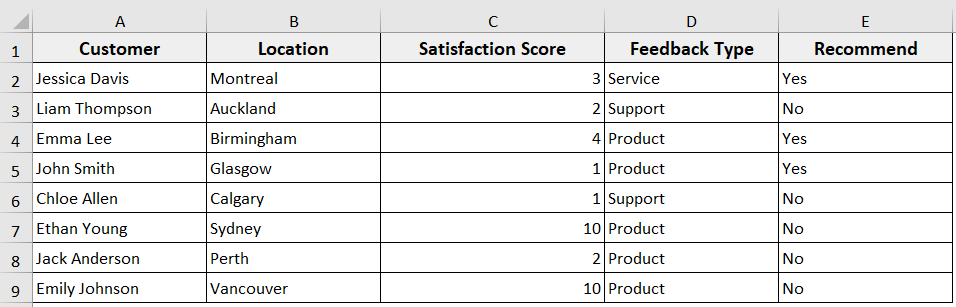
Delete Rows Based on Condition
If you want to delete rows entirely based on specific criteria, this method can help you out. It deletes rows with certain text, blanks in a particular column, errors, or any custom condition. The code loops through rows from bottom to top. When the condition is met, it deletes the entire row.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor by pressing Alt + F11 .
➤ Insert a new module in the VBA editor.
➤ Insert the following VBA code in the module.
Sub DeleteRowsWithSpecificText()
Dim i As Long, lastRow As Long
lastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, "C").End(xlUp).Row
For i = lastRow To 1 Step -1
If Cells(i, "A").Value = "Emily Johnson" Then
Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next i
End SubNote:
In the code, If Cells(i, “A”).Value = “Emily Johnson” Then
➥ Change “A” with the column you want to check
➥ Change “Emily Johnson” to the specific text or value you want to match.
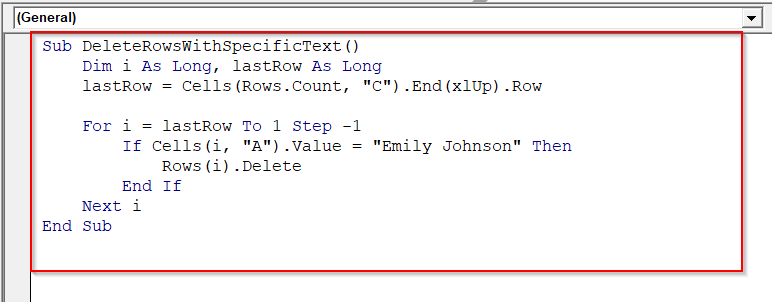
➤ The VBA deletes where column A contains the word “Emily Johnson”
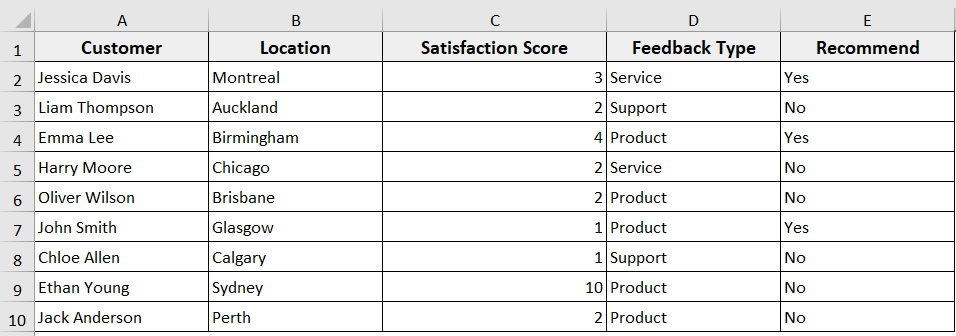
Deleting Blank Rows
Now, if your dataset contains one or multiple blank rows that are empty or have blank cells in a specific column, you can apply the following VBA code. The code loops through rows from the bottom up, checks if a row or cell is blank. When it finds it true, the code deletes the entire row.
In the same Customer Feedback dataset, we have added some blank rows to help you understand how this code actually works. Now we’ll delete the blank rows from the dataset with Excel VBA.
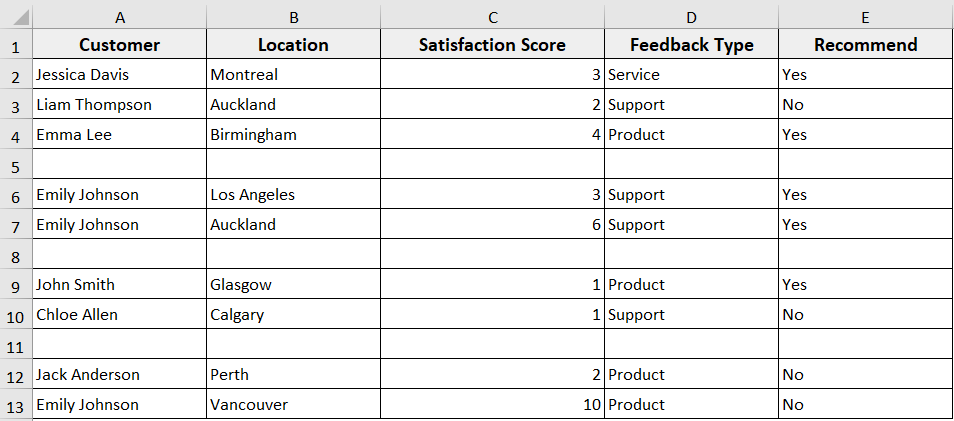
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor.
➤ Insert a new module.
➤ Insert the following VBA code in the module.
Sub DeleteBlankRows_Loop()
Dim i As Long, lastRow As Long
lastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
For i = lastRow To 1 Step -1
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(Rows(i)) = 0 Then
Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next i
End Sub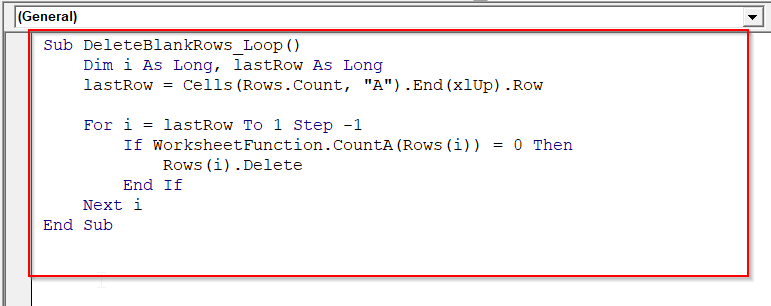
➤ Run the code.
➤ Deletes rows that are completely empty in the worksheet based on column A’s last used row.
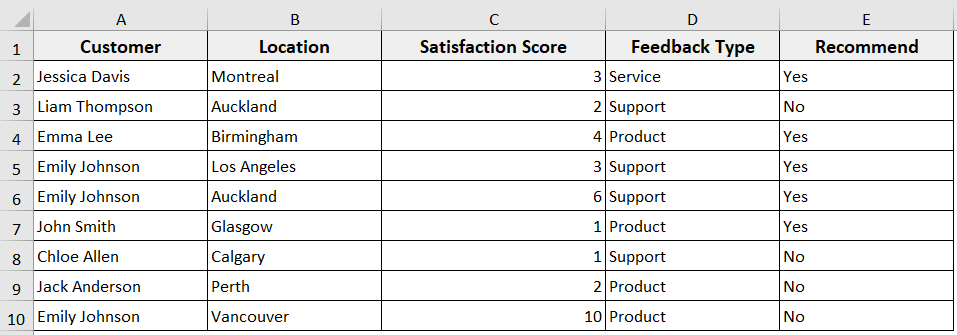
Deleting Alternate Rows
You can use this method to remove every 2nd, 3rd, or nth row from your dataset. This helps clean where you need to remove rows in a pattern. The VBA code will loop through the rows from bottom to top and delete rows at the intervals, skipping the headers based on the step value you set.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor and insert a new module.
➤ Insert the following VBA code in the module.
➤ Here For i = lastRow To 1 Step -2, change -2 to the interval you want to delete rows.
Sub DeleteEverySecondRow()
Dim i As Long, lastRow As Long
lastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
For i = lastRow To 2 Step -2 ' Start from last row down to row 2 to keep header
Rows(i).Delete
Next i
End Sub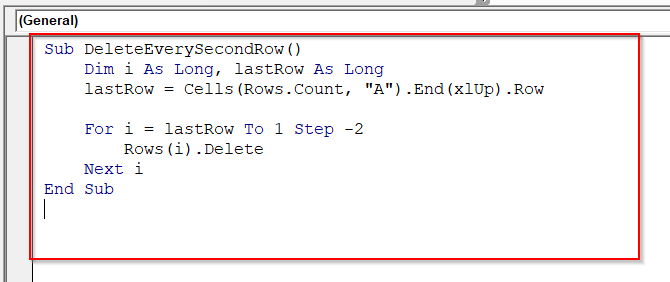
➤ Run the code.
➤ The code will delete every second row starting from the bottom, skipping the header row.
➤ If you delete rows in every Nth row, you can use the following VBA code. Deletes every nth row, for example, every 2nd row (n = 2) from the bottom.
Sub DeleteEveryNthRow()
Dim i As Long, lastRow As Long, n As Long
n = 3 'Change this number to delete every nth row
lastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
For i = lastRow To 1 Step -n
Rows(i).Delete
Next i
End Sub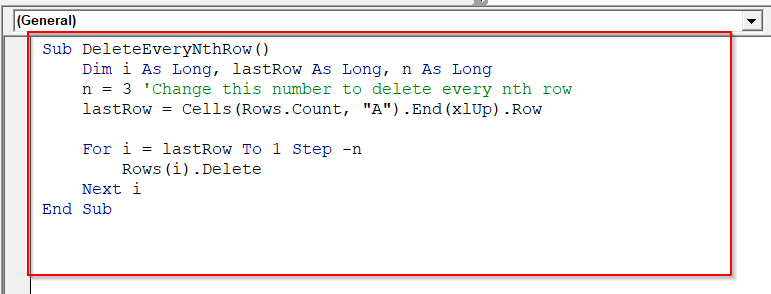
Delete Duplicate Rows
If your worksheet contains multiple rows with duplicate information, you can follow this method. The VBA removes duplicate rows based on one or more columns. It keeps the first data and deletes subsequent duplicates entirely.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor and insert a new module.
➤ In the module, copy and paste the following VBA code. This VBA code checks for duplicates based on Column A.
Sub DeleteDuplicateRows()
Dim lastRow As Long
lastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
'Remove duplicates based on Column A
Range("A1:A" & lastRow).RemoveDuplicates Columns:=1, Header:=xlYes
End Sub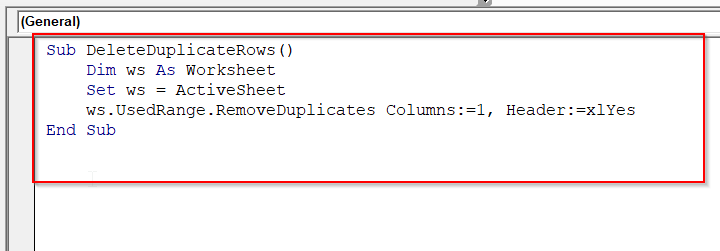
➤ Run the code.
➤ The code will delete duplicate rows based on Column A values while keeping the first row.
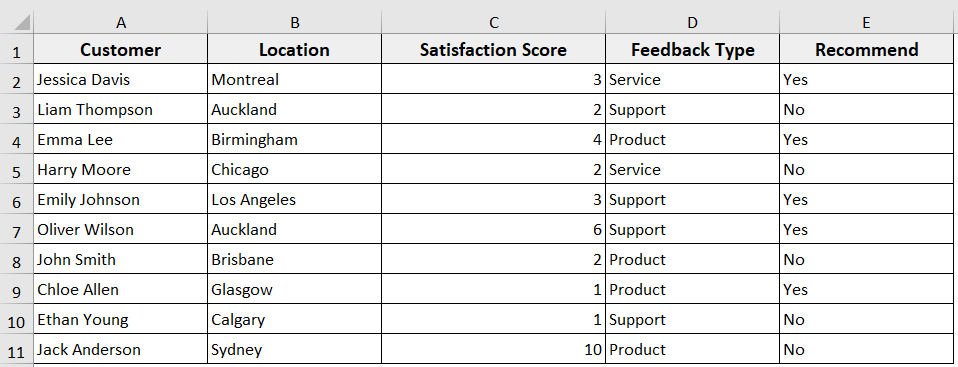
Delete Rows in Excel Tables
In Excel, if you are working with structured data in a table and need to delete a row entirely, this method can help you out. The code accesses the table by name, then deletes specific rows within that table based on your specified condition. This keeps the table formatting and formulas intact.
To demonstrate the method, we have converted our customer feedback dataset into a table. Now we are going to delete a specific row (the second one) with Excel VBA.
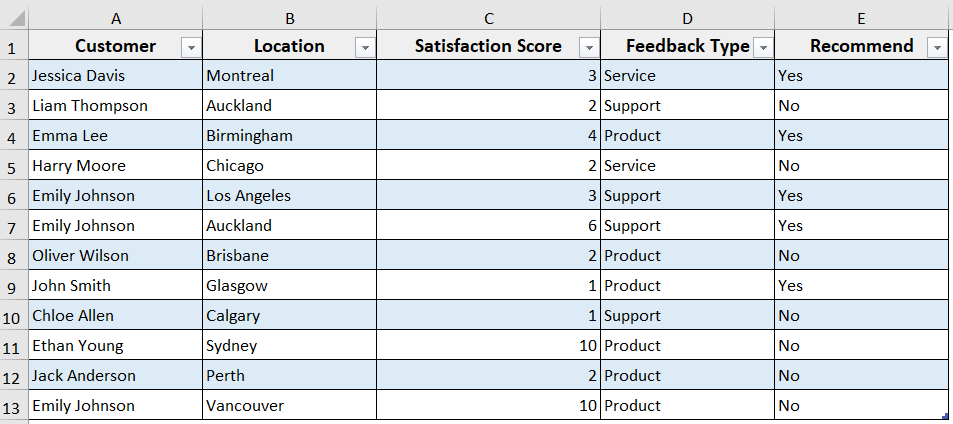
Steps:
➤ Open your Excel worksheet where it has a table.
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
➤ Insert a new module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code.
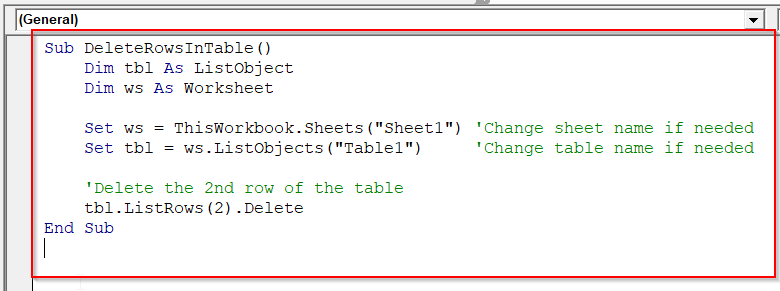
Sub DeleteRowsInTable()
Dim tbl As ListObject
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1") 'Change sheet name if needed
Set tbl = ws.ListObjects("Table1") 'Change table name if needed
'Delete the 2nd row of the table
tbl.ListRows(2).Delete
End SubNote:
➥ ThisWorkbook.Sheets(“Sheet1”): Replace “Sheet1” with your worksheet’s name.
➥ Set tbl = ws.ListObjects(“Table1”): Replace “Table1” with your actual table name.
➥ tbl.ListRows(2).Delete: Change the row number (2) to the specific table row you want to delete.
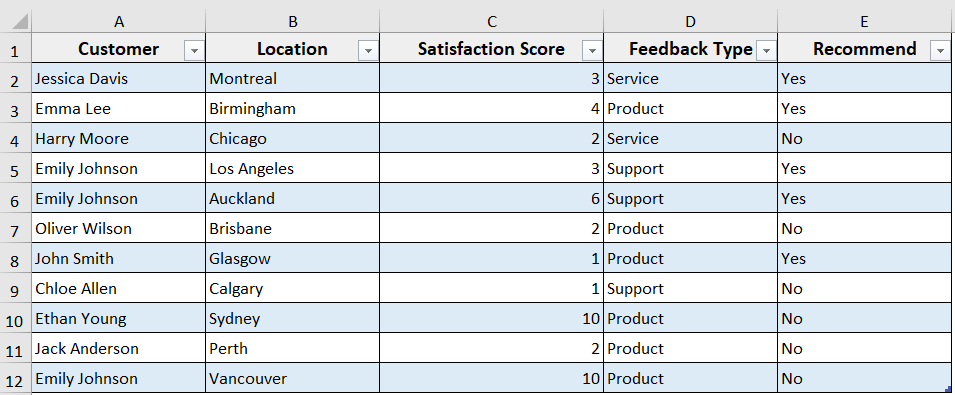
➤ Run the code.
➤ The code will delete the 2nd row from Table1 on Sheet1 and resize the table automatically.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to delete the current row in VBA?
➤ Open the VBA editor.
➤ To delete the current row in VBA, insert the following VBA in the VBA editor.
Sub DeleteCurrentRow()
ActiveCell.EntireRow.Delete
End Sub➤ Run the code.
➤ The code will delete the row of the currently selected cell in your worksheet.
How do I delete the entire row and column?
➤ Open the VBA editor.
➤ Insert the following VBA in the editor to delete the entire row and column.
Sub DeleteRowAndColumn()
Rows(5).EntireRow.Delete ' Delete row 5
Columns("C").EntireColumn.Delete ' Delete column C
End Sub➤ Run the code.
➤ The code will delete the specified entire row (row 5) and the entire column (column C) from the active worksheet.
How do I delete a row in Excel without deleting the whole row?
➤ Use the following VBA code to delete a row in Excel without deleting the whole row.
Sub ClearRowContents()
Rows(5).ClearContents
End Sub➤ Run the code.
➤ The code will remove all data and formulas from that row (row 5) but keep the row itself in place.
Wrapping Up
In this quick tutorial, we have learnt how to delete entire one or multiple rows in a dataset with Excel VBA in different scenarios. This VBA code helps you automate row deletion easily and accurately. It saves you both time and effort. Feel free to download our sample workbook and try these macros yourself. Let us know how these VBA solutions have made your Excel tasks faster and simpler.


