In some cases, when working with an Excel dataset, we need to rename one or more sheets in our workbook to keep them organized or to make the sheet names more meaningful for reports or analysis. Doing so manually can be time-consuming and prone to errors. However, you can automate the process and rename sheets quickly, accurately with the help of Excel VBA.
That is why, in today’s article, we will walk you through 10 practical VBA methods to rename worksheets in Excel. These include renaming the active sheet, renaming by index, using a cell value, renaming multiple sheets from a range, renaming by CodeName, matching the file name, and so on.
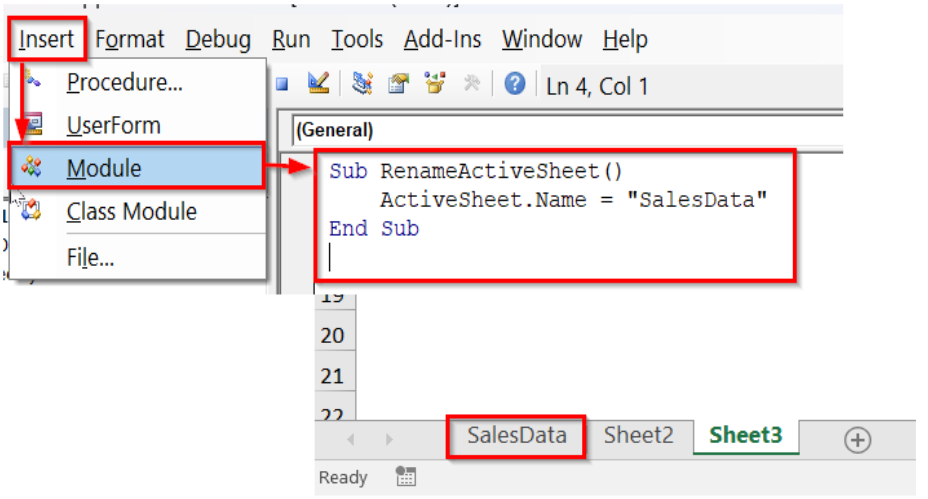
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
➤ In the VBA editor, click Insert >> Module.
➤ In the module, insert the following VBA code.
Sub RenameActiveSheet()
ActiveSheet.Name = "SalesData"
End Sub➤ Run the code.
➤ The VBA code will rename the active sheet to SalesData. Change the ActiveSheet.Name = “SalesData” according to your need or preference.
Rename the Active Sheet
In Excel, you may need to rename the currently active sheet without doing it manually. You can easily perform this task using a simple VBA code. The code assigns a new name to the sheet that is active at the moment.
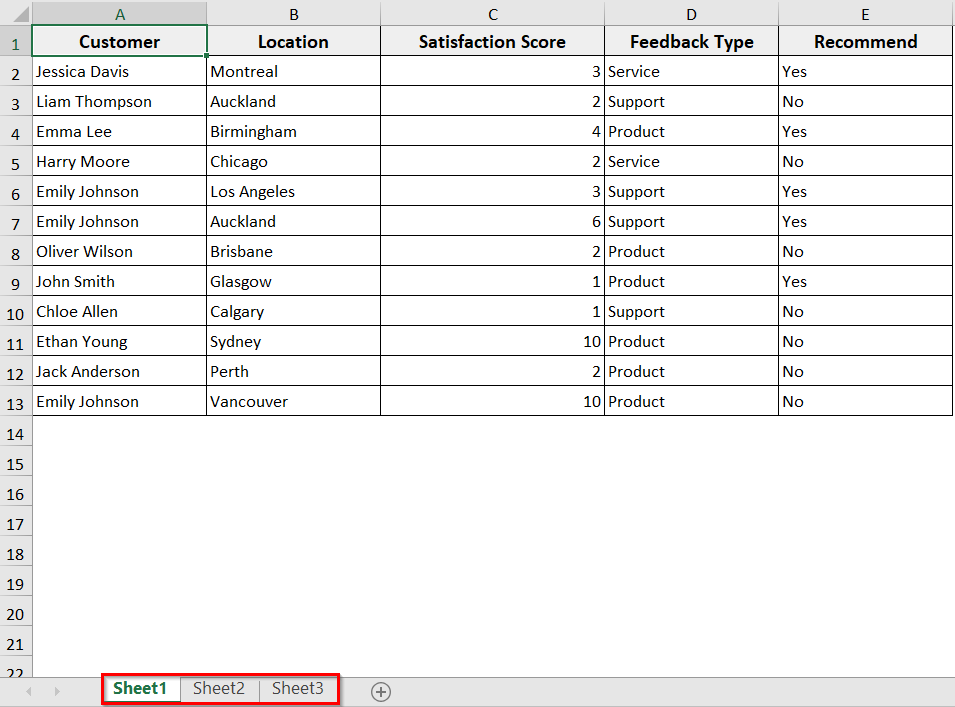
In our workbook, we have three sheets named Sheet1, Sheet2, and Sheet3, having the same dataset. Now our active sheet is Sheet1, and we will rename it to SalesData with Excel VBA.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
➤ Go to Insert >> Module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code. Change the sheet name to the name you want to rename the active sheet.
Sub RenameActiveSheet()
ActiveSheet.Name = "SalesData"
End Sub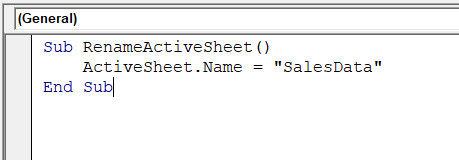
➤ Run the code.
➤ The active sheet, Sheet1 in our case, will be renamed to SalesData, while the other sheets, Sheet2 and Sheet3, remain unchanged.
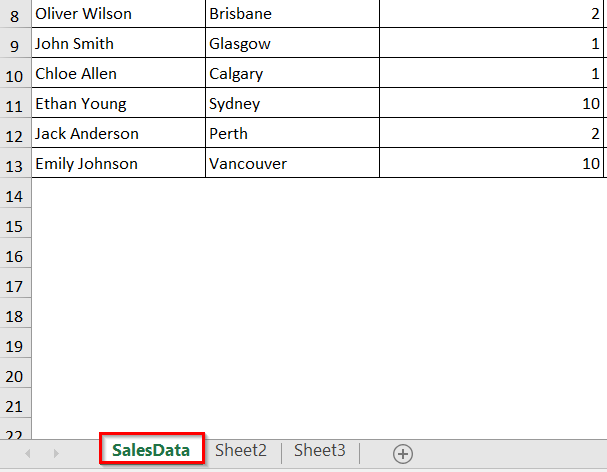
Rename a Worksheet by Its Index Number
In Excel, every worksheet in a workbook has an index number based on its position from left to right. The first sheet is index 1, the second sheet is index 2, and so on. Using VBA, you can rename a sheet by directly referring to its index number.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor and insert a new module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code. Change the index number and sheet name according to your dataset and preference.
Sub RenameSheetByIndex()
Worksheets(2).Name = "EmployeeData"
End Sub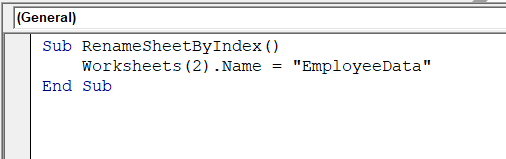
➤ Run the code.
➤ The code renames the sheet at index 2 (Sheet2) to EmployeeData.
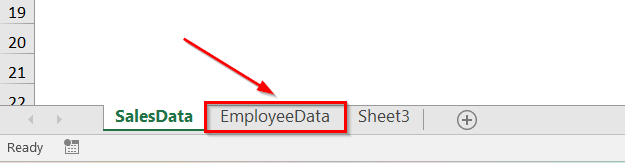
Rename a Worksheet Using a Cell Value
In Excel, you can automatically rename a worksheet based on a cell value. This is useful when the sheet name should match a dataset title, project name, or report period.
In our dataset, in Sheet1, cell A1 contains the value Customer. We will rename the active sheet to match this value.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor.
➤ Insert a new module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code.
Sub RenameSheetByCellValue()
ActiveSheet.Name = Range("A1").Value
End Sub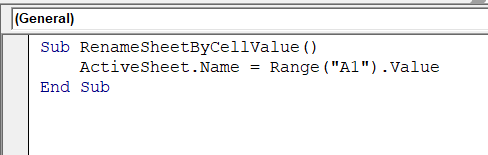
➤ Run the code.
➤ The active sheet, Sheet1, will be renamed to Customer, based on the value in cell A1.
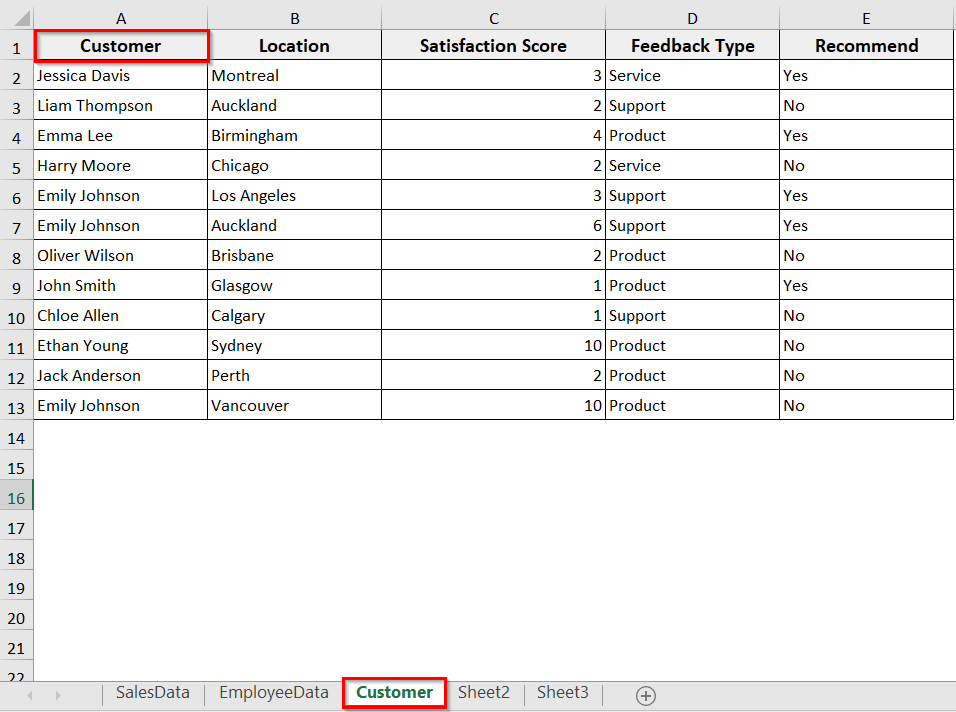
Rename a Worksheet Using a Cell Value for Multiple Sheets
If you want to rename multiple sheets at once, you can use a range of cells. This method works well for automating sheet renaming in large workbooks. However, you need to make sure the names in the cells follow Excel rules. For instance, cells have ≤31 characters or no \/?*:[] and the cell values are unique.
Now, in our dataset, cells A1:A3 contain the names:
A1: Customer
A2: Jessica Davis
A3: Liam Thompson
We will rename all three sheets accordingly with Excel VBA.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor and insert a new module.
➤ In the new module, copy and paste the following VBA code.
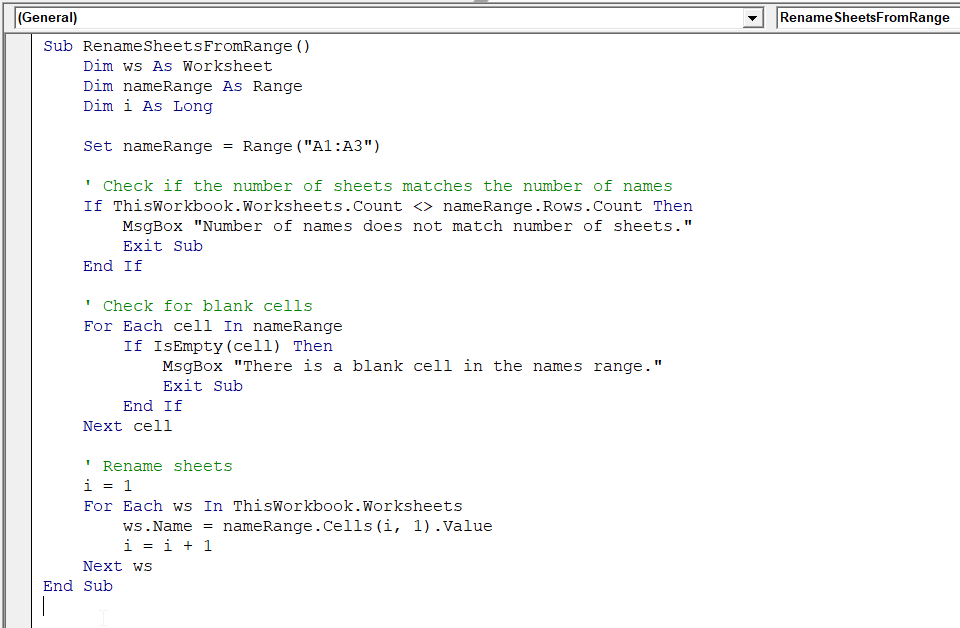
Sub RenameSheetsFromRange()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim nameRange As Range
Dim i As Long
Set nameRange = Range("A1:A3")
' Check if the number of sheets matches the number of names
If ThisWorkbook.Worksheets.Count <> nameRange.Rows.Count Then
MsgBox "Number of names does not match number of sheets."
Exit Sub
End If
' Check for blank cells
For each cell in nameRange
If IsEmpty(cell) Then
MsgBox "There is a blank cell in the names range."
Exit Sub
End If
Next cell
' Rename sheets
i = 1
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
ws.Name = nameRange.Cells(i, 1).Value
i = i + 1
Next ws
End Sub
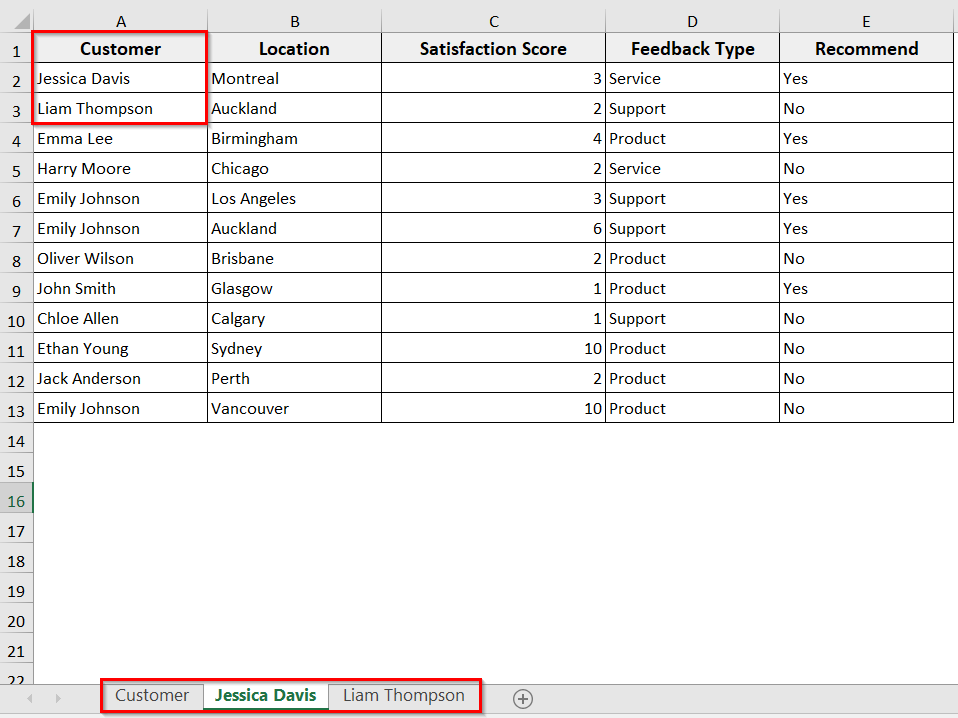
➤ Run the code.
➤ The VBA will rename each sheet based on the values in A1:A3. If the number of names or blank cells doesn’t match, the code will stop and show a message.
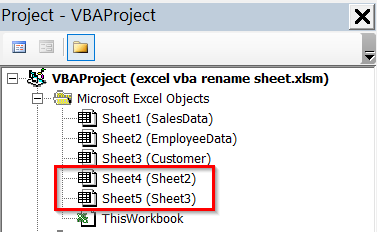
Rename a Worksheet by Its CodeName
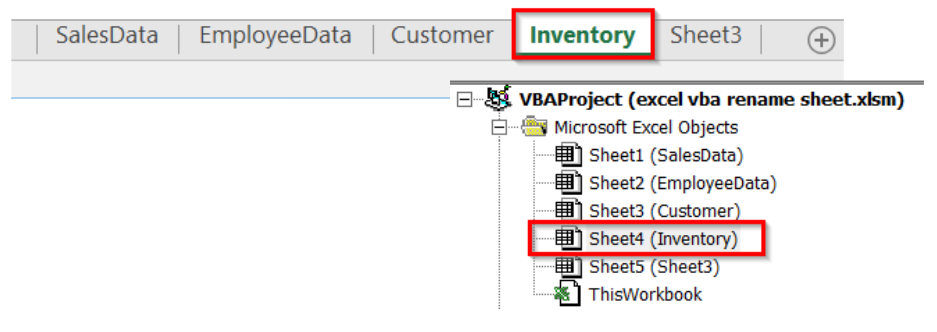
In Excel, every worksheet has a CodeName in addition to the visible tab name. The CodeName is the name before parentheses, and the visible name is in parentheses.
For example, in our Project Explorer right now, for Sheet4 and Sheet5, the CodeName is Sheet4 and Sheet5, but the visible name is Sheet2 and Sheet3.
You can use the Codename to rename sheets in Excel. Using the CodeName is Useful for workbooks that are updated frequently or shared with others. Your code will still work even if the visible sheet name changes. Moreover, you won’t need to rely on index numbers or cell values.
In our dataset, we will rename the Excel sheet with Codename Sheet4 to Inventory.
Steps:
➤ Insert a new module in the VBA editor.
➤ Copy and paste the following code into the new module.
Sub RenameSheetByCodeNameExample()
Sheet4.Name = "Inventory"
End Sub
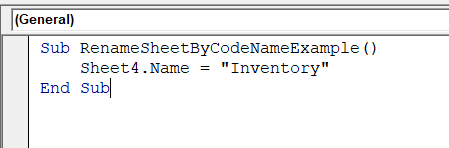
➤ Run the code.
➤ The sheet with CodeName Sheet4 will now have the visible tab name Inventory.
Rename Worksheets to Match the File Name
While working with an Excel dataset, if you need to rename the worksheet’s name to match the Excel file name, you can use this method. This is helpful for reports or dashboards where the sheet should show the title of the workbook automatically.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor.
➤ Insert a new module and in the module, copy and paste the following VBA code.
Sub RenameSheetToFileName()
Dim fileName As String
' Get workbook name without extension
fileName = Left(ThisWorkbook.Name, InStrRev(ThisWorkbook.Name, ".") - 1)
' Rename the active sheet
ActiveSheet.Name = fileName
End Sub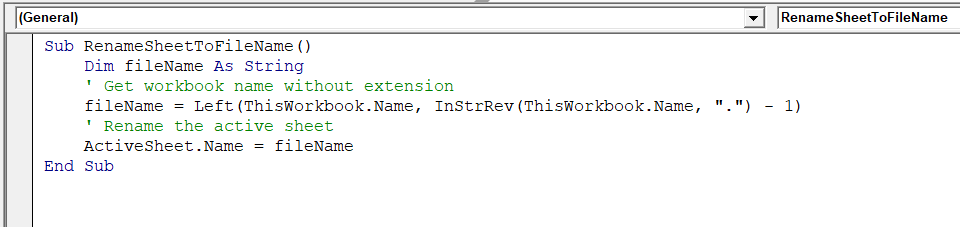
➤ Run the code.
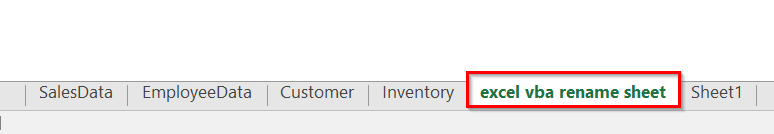
➤ The code will rename the active sheet to match the file name of the workbook. If the workbook name is Excel VBA rename sheet.xlsm, the sheet will also be named Excel VBA rename sheet.
Rename a Worksheet Only If It Exists
Sometimes, you may want to rename a worksheet, but avoid errors if the sheet does not exist. This method first checks if your specified sheets exist. If it does, it renames the sheet to your desired name. If not, a message box will alert you that the sheet does not exist.
Steps:
➤ In the VBA editor, insert a new module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code. You can just copy and paste it. However, you can modify Sheet1 and Summary to match your workbook and desired sheet name.
Sub RenameSheetIfExists()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim sheetName As String
sheetName = "Summary" ' Desired new name
On Error Resume Next
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1") ' Sheet to rename
On Error GoTo 0
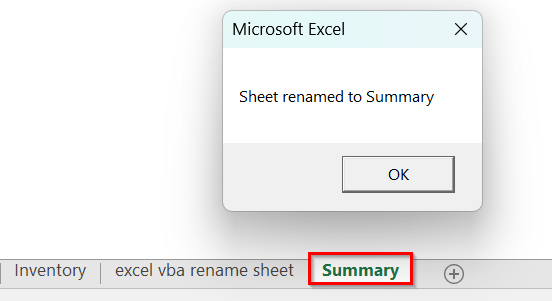
If Not ws Is Nothing Then
ws.Name = sheetName
MsgBox "Sheet renamed to " & sheetName
Else
MsgBox "Sheet does not exist."
End If
End Sub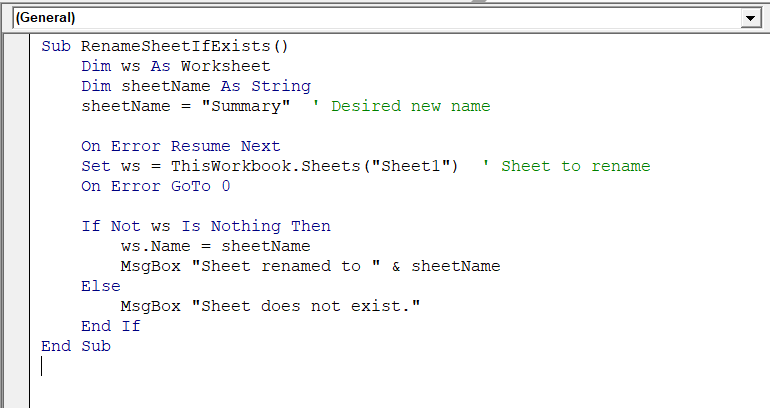
➤ Run the code.
➤ The code checks if Sheet1 exists. If it does, it renames the sheet to Summary with a message box confirming it. If not, a message box will alert you that the sheet does not exist.
Add and Rename a New Worksheet Immediately
You can create a new worksheet and rename it immediately using VBA. It saves time when you need to add multiple sheets with specific names.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor (Alt + F11) and insert a new module.
➤ Copy and paste the following VBA code:
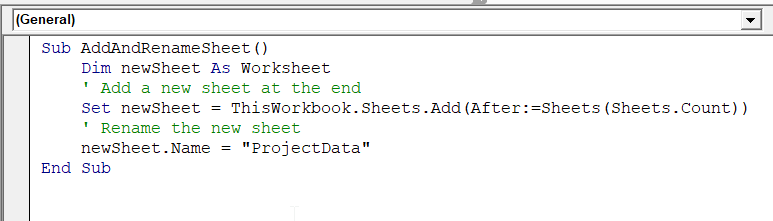
Sub AddAndRenameSheet()
Dim newSheet As Worksheet
' Add a new sheet at the end
Set newSheet = ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Add(After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count))
' Rename the new sheet
newSheet.Name = "ProjectData"
End SubNote:
➥ If you want to add the sheet at the beginning, change After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count) to Before:=Sheets(1).
➤ Run the code.
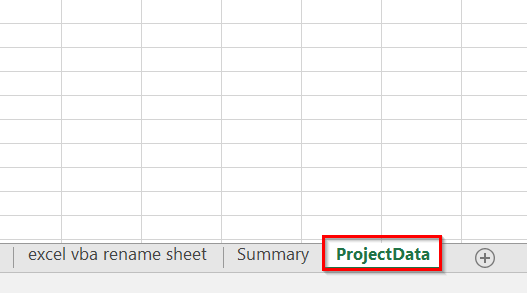
➤ The code will add a new blank worksheet at the end of the workbook and immediately rename it to ProjectData. You can change the name to whatever you need.
Rename a Worksheet in a Closed Workbook
With the help of Excel VBA, you can rename a worksheet in a workbook that is not currently open. VBA allows you to do this without manually opening the file.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 and open the VBA editor.
➤ Insert a new module and copy and paste the following VBA code.
Sub RenameSheetInClosedWorkbook()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim filePath As String
Dim sheetName As String
' Path to the closed workbook
filePath = "C:\Users\HP USER\Downloads\excel vba rename sheet.xlsm"
' New sheet name
sheetName = "UpdatedSheet"
' Open the workbook
Set wb = Workbooks.Open(filePath)
' Rename the first sheet
wb.Sheets(1).Name = sheetName
' Save and close the workbook
wb.Close SaveChanges:=True
MsgBox "Sheet renamed successfully in the closed workbook."
End SubNote:
➥ Change the file path, sheet index, and new name according to your needs.
➥ Make sure the workbook is not already open, or the code may cause an error.
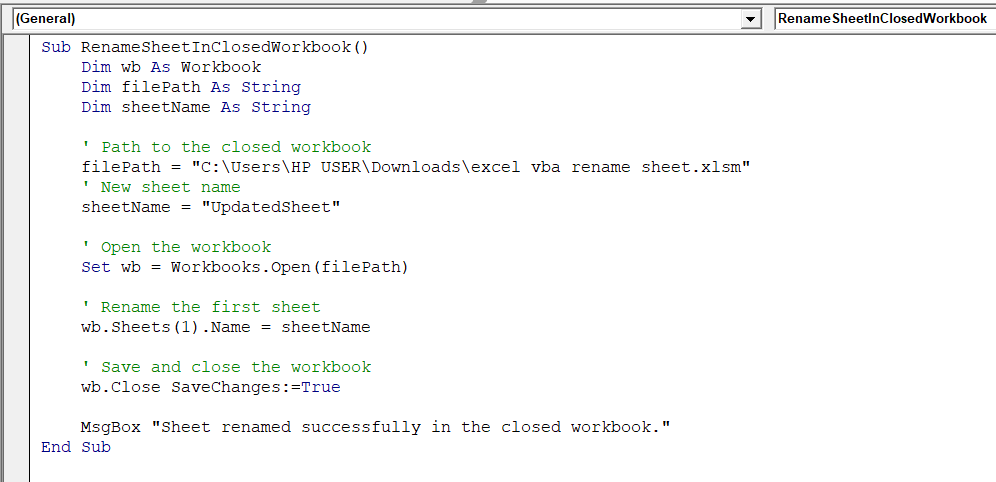
➤ Run the code.
➤ It shows a confirmation message saying, sheet was renamed successfully in the closed workbook.
➤ The macro opens the closed workbook, renames the first sheet to UpdatedSheet, saves, and closes it.
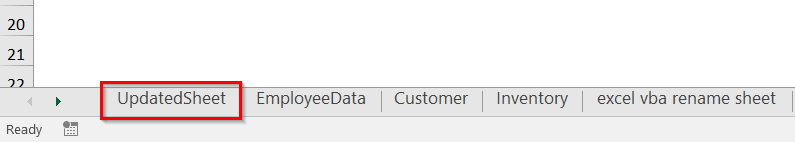
Auto-Rename Sequentially from an Active or Selected Sheet
Sometimes you may want to rename multiple worksheets in a sequence, like Week1, Week2, Week3, and so on. VBA makes this process quick and error-free. You can apply this method in two ways: starting from the active sheet or renaming only the selected sheets.
Use this method when you want to quickly rename multiple sheets in order, either starting from a specific sheet or for selected ones only.
Steps:
➤ Select the sheet from which you want to start the sequence.
➤ Open the VBA editor and insert a new module.
➤ In the VBA editor, insert the following module to rename sheets sequentially from the active sheet
Sub RenameFromActive()
Dim i As Long
For i = ActiveSheet.Index To Worksheets.Count
Worksheets(i).Name = "Week" & i
Next i
End Sub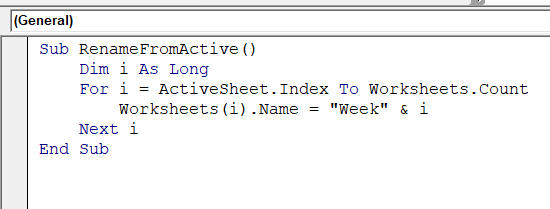
➤ Run the code.
➤ The code starts renaming from the active sheet. It continues to rename all subsequent sheets until the last one.
In our dataset, the active sheet is the 8th one. So, they have renamed them as Week8, Week9, Week10, and so on until the last sheet, Sheet12.
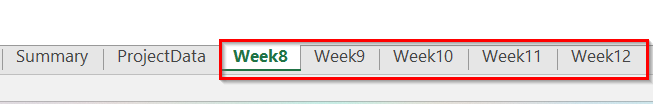
➤ Insert the following VBA code if you want to rename only selected sheets.
Sub RenameSelectedSheets()
Dim i As Integer: i = 1
Dim sh As Worksheet
For Each sh In ThisWorkbook.Windows(1).SelectedSheets
sh.Name = "Week" & i
i = i + 1
Next sh
End Sub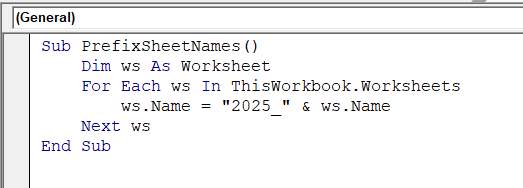
➤ Run the code.
➤ The VBA will rename only the sheets you manually select by holding Ctrl and clicking sheet tabs. It will rename the sheets in sequence.
Append or Prefix Sheet Name Dynamically
In some cases, while working with an Excel dataset, you don’t want to replace the entire sheet name but just add a prefix or suffix (append) to it. For instance, you need to mark sheets by date, project name, or category without removing their original names. You can do so with this Excel VBA.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor and insert a new module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code to add a prefix to all sheets.
Sub PrefixSheetNames()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
ws.Name = "2025_" & ws.Name
Next ws
End Sub➤ Run the code.
➤ The code will add the 2025_ prefix to all the sheets in the workbook. Change the prefix name according to your preference.

➤ If you want to add a suffix to all sheets, use the following VBA code and run the code.
➤ The code will add a suffix to all sheets.
Sub AppendSheetNames()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
ws.Name = ws.Name & "_2025"
Next ws
End Sub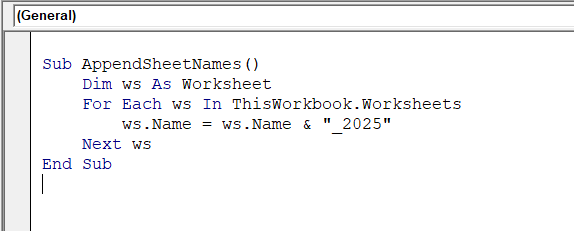
Frequently Asked Questions
How to put the sheet name in an Excel cell using VBA?
You can put the sheet name in cell A1 with the following VBA. Insert the VBA code in the module.
Sub InsertSheetName()
Range("A1").Value = ActiveSheet.Name
End SubThe code will automatically insert the active sheet’s name into the specified cell A1.
How to check the sheet name in VBA?
In VBA, you can check the name of a sheet by referring to its Name property. For example, insert the following VBA code in the VBA editor.
Sub CheckSheetName()
MsgBox "The active sheet name is: " & ActiveSheet.Name
End SubRun the VBA code, and a message box will appear showing the name of the active sheet.
How do you refer to a worksheet name in VBA?
In VBA, you can refer to a worksheet using its name, index number, or CodeName. For example
‘ By sheet name
Worksheets(“Sheet1”).Range(“A1”).Value = “Data”
‘ By index number
Worksheets(1).Range(“A1”).Value = “Data”
‘ By CodeName (as seen in VBA Project Explorer)
Sheet1.Range(“A1”).Value = “Data”
Wrapping Up
In this tutorial, we have learnt how to rename sheets in the workbook with Excel VBA in 10 effective ways. With these VBA codes, you can save time, reduce manual work, and keep your Excel projects organized. Feel free to download the sample workbook and try out the VBA macros yourself. Let us know how these codes have simplified your Excel tasks.




