When working with Excel VBA, you’ll often need to manipulate rows based on the currently active cell. Whether you’re formatting, copying, or deleting data, selecting the entire row of the active cell gives you a quick and reliable way to target your operations. VBA provides several approaches to achieve this, each with its own flexibility depending on whether you want to select just the row, combine it with other ranges, or use it for advanced operations.
In this article, you’ll learn three practical VBA methods to select the entire row of the active cell. We’ll show you how to use ActiveCell.EntireRow.Select, work with Rows(ActiveCell.Row).Select, and even combine row and column selections using the Union method.
Steps to Select the Entire Row of Active Cell Using ActiveCell.EntireRow.Select
➤ Press Alt + F11 , choose Insert >> Module, and paste this code:
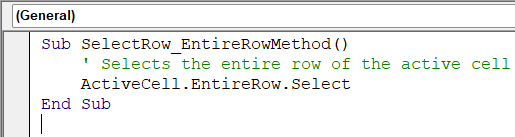
Sub SelectRow_EntireRowMethod()
' Selects the entire row of the active cell
ActiveCell.EntireRow.Select
End Sub➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select SelectRow_EntireRowMethod, and click Run
➤ The entire row of the active cell will now be highlighted
Select Entire Row of Active Cell Using ActiveCell.EntireRow.Select Statement
The most straightforward way to select the entire row of the active cell in VBA is by using the ActiveCell.EntireRow.Select property. This method directly references the row containing your active cell and highlights it completely.
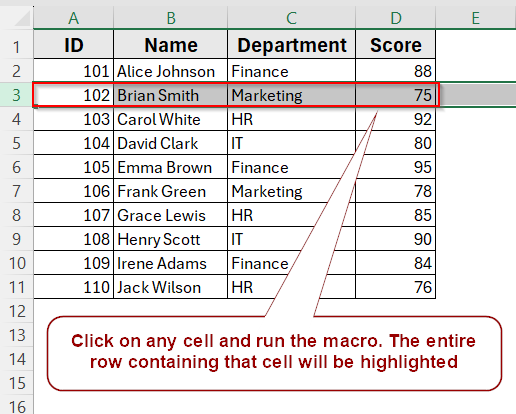
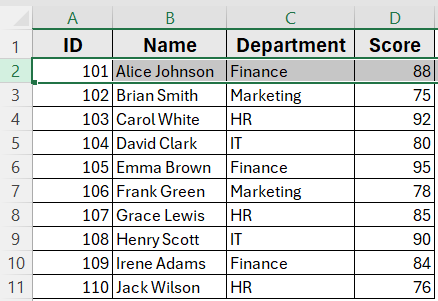
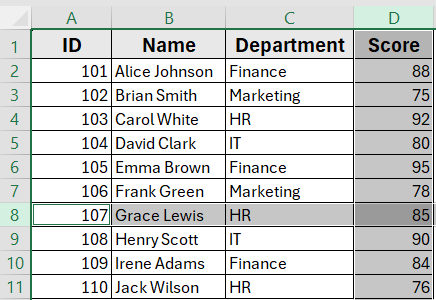
This is the dataset we will be using to demonstrate the methods.
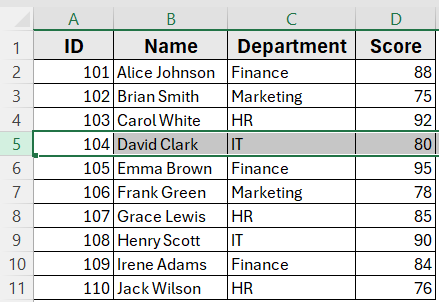
Suppose you click on cell C5 (Finance) in the dataset. Running this macro will select row 5, highlighting the full record for Emma Brown (ID 105, Finance, Score 95).
Steps:
➤ Open Excel and press Alt + F11 to launch the VBA editor
➤ Go to Insert >> Module
➤ Paste this code:
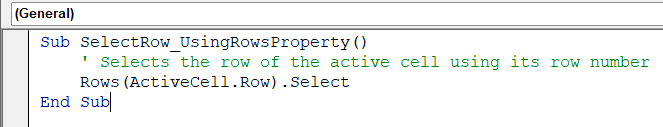
Sub SelectRow_EntireRowMethod()
' Selects the entire row of the active cell
ActiveCell.EntireRow.Select
End Sub
➧ .EntireRow refers to the whole row of that active cell
➧ .Select highlights the row so you can format, copy, or manipulate it
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , choose SelectRow_EntireRowMethod, and click Run
➤ The entire row of your active cell will be selected
Highlight Active Cell’s Entire Row Using Rows(ActiveCell.Row).Select Statement
Another reliable way to select the entire row of the active cell in VBA is by using the Rows(ActiveCell.Row).Select property. Instead of directly referencing the row object, this method uses the row number of the active cell and selects it.
In this method when you click on cell B7 (Grace Lewis) in the dataset. Running this macro will select row 7, highlighting the full record for Grace Lewis (ID 107, HR, Score 85).
Steps:
➤ Open Excel and press Alt + F11 to launch the VBA editor and go to Insert >> Module
➤ Paste this code:
Sub SelectRow_UsingRowsProperty()
' Selects the row of the active cell using its row number
Rows(ActiveCell.Row).Select
End Sub
➧ Rows(ActiveCell.Row) uses that row number to point to the entire row
➧ .Select highlights the row so you can apply actions to the full record
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , choose SelectRow_UsingRowsProperty, and click Run
➤ The row containing the active cell (e.g., Grace Lewis in row 7) will be fully selected
Select Both Row and Column of Active Cell Using the Union Method
When working with Excel, you may need to highlight both the entire row and the entire column of the active cell at the same time. Using VBA’s Union method, you can combine these two ranges into a single selection, making it easier to perform actions on both simultaneously.
For example, clicking on cell D8 (Score 90) and running this macro will select row 8 for Henry Scott as well as the Score column (column D). The row and column are highlighted together in one operation.
Steps:
➤ Open Excel and press Alt + F11 to launch the VBA editor
➤ Go to Insert >> Module
➤ Paste this code:
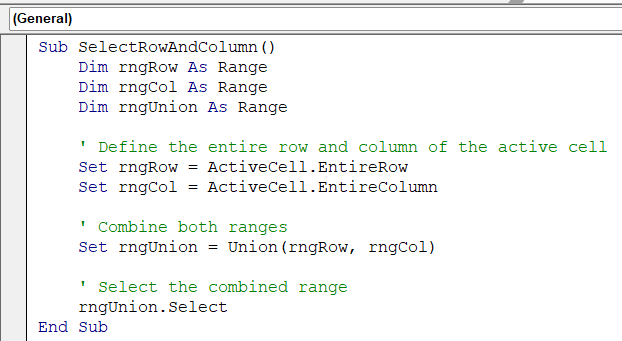
Sub SelectRowAndColumn()
Dim rngRow As Range
Dim rngCol As Range
Dim rngUnion As Range
' Define the entire row and column of the active cell
Set rngRow = ActiveCell.EntireRow
Set rngCol = ActiveCell.EntireColumn
' Combine both ranges
Set rngUnion = Union(rngRow, rngCol)
' Select the combined range
rngUnion.Select
End Sub
➧ ActiveCell.EntireColumn selects the full column containing the active cell
➧ Union(rngRow, rngCol) merges the row and column ranges into a single selection
➧ .Select highlights both the row and column together
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , choose SelectRowAndColumn, and click Run
➤ The macro highlights the entire row and column of the active cell (for example, row 8 and column D) simultaneously
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I select multiple rows based on multiple active cells?
You can extend the logic using the Selection object and loop through all selected cells, applying Union to combine their rows.
What’s the difference between ActiveCell.EntireRow and Rows(ActiveCell.Row)?
Both achieve the same effect. ActiveCell.EntireRow is more direct, while Rows(ActiveCell.Row) explicitly converts the row number into a range.
Can I format the entire row instead of just selecting it?
Yes, instead of .Select, you can directly apply formatting. For example:
ActiveCell.EntireRow.Font.Bold = TrueWhat happens if no cell is active?
There will always be an active cell in a worksheet, so one of these methods will always work.
Wrapping Up
Selecting the entire row of the active cell in VBA is a common task that streamlines formatting, data manipulation, and automation. You can use the direct ActiveCell.EntireRow.Select method for simplicity, Rows(ActiveCell.Row).Select when you want more explicit row control, or the Union method if you need to combine rows and columns for broader selection.