During working with large datasets in Excel we frequently need to find and replace specific patterns, particularly if the data has inconsistent formatting. Here, Regular Expressions (RegEx) provide powerful pattern-matching capabilities, and they help us to clean, standardize, and reformat data efficiently. Common use cases include standardizing phone numbers, reformatting product codes, or correcting inconsistent text patterns.
To find and replace data with RegEx in Excel, follow these steps:
➤ Open the VBA Editor (ALT + F11).
➤ Enable Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5 under Tools → References.
➤ Insert a VBA script to perform RegEx-based find-and-replace on your target range.
In this article, we will explain two main methods to achieve RegEx-like replacements in Excel using a VBA RegEx macro for full pattern matching, and using Excel’s built-in Find & Replace for simpler cases.
How Does RegEx Work in Excel?
Regular Expressions, or RegEx, are sequences of characters that define a search pattern. They are widely used for advanced text matching and replacement in programming and data cleaning. While Excel does not natively support RegEx in its standard Find & Replace, you can implement it using VBA macros or approximate simpler matches with Excel’s wildcard characters (*, ?, ~).
Using REGEXREPLACE Function to Find & Replace with Regular Expression
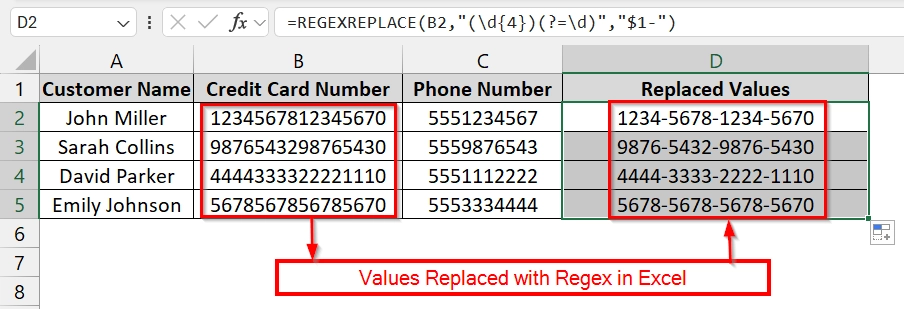
REGEXREPLACE is a built-in Excel function that replaces text based on a pattern defined by a regular expression. It is useful when you need to clean or reformat datasets without manual cell editing, for example, formatted credit card numbers, phone numbers, or product codes. This method is perfect when we deal with large datasets that require uniformity across thousands of rows.
We have a dataset that manages customer payment details. The raw data has unformatted credit card numbers, which makes them hard to read or verify. We will use REGEXREPLACE to quickly reformat all numbers into the standard 4-digit block style for better clarity.
Steps:
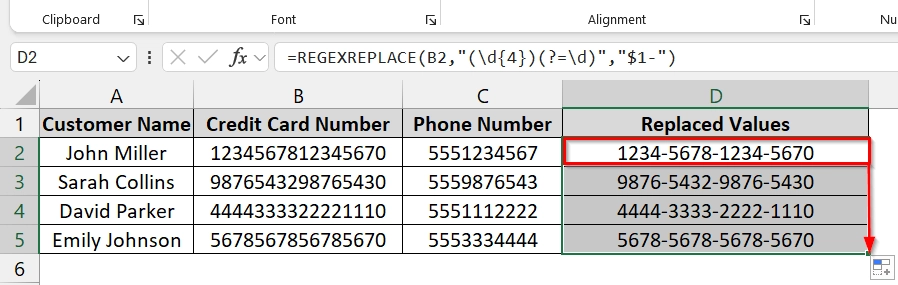
➤ Open your dataset. We have the Customer Name in Column A, and Credit Card Number in Column B, and the Phone Number in Column C. We want to restore the replaced values in Column D with the help of the regexreplace tool.
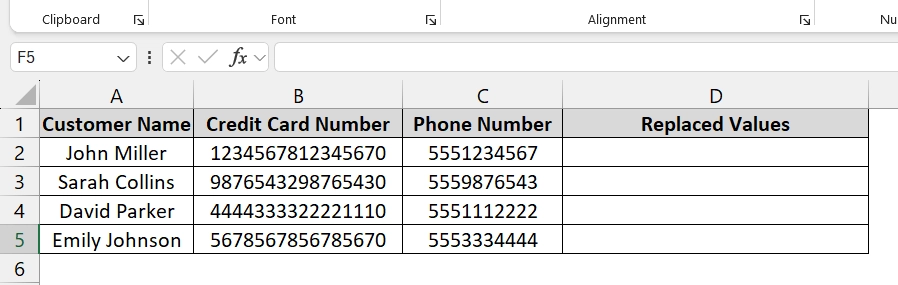
➤ Click in cell E2 and enter the formula and press Enter.
=REGEXREPLACE(B2,"(\d{4})(?=\d)","$1-")
The formatted version of the first credit card number should now appear in E2 with dashes inserted.
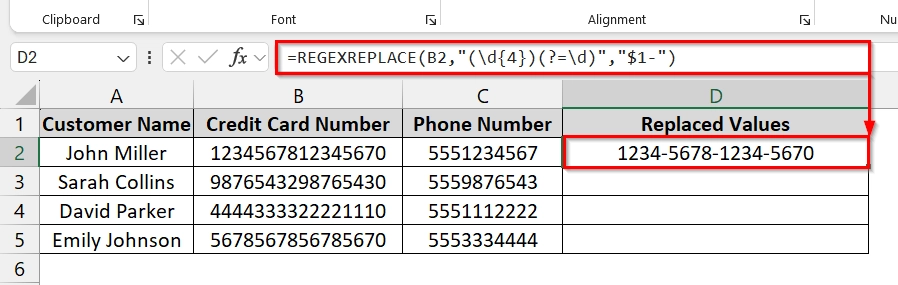
➤ Drag the fill handle down from D2 to fill the formula for all rows containing data.
Applying Custom VBA to Find and Replace Data with RegEx in Excel
This method uses Excel’s VBA editor with Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5 to find and replace text based on complex patterns. It is good for large datasets where formats vary, like inconsistent emails, order IDs, or phone numbers. You should use this when Excel’s default Find & Replace can not handle the required complexity.
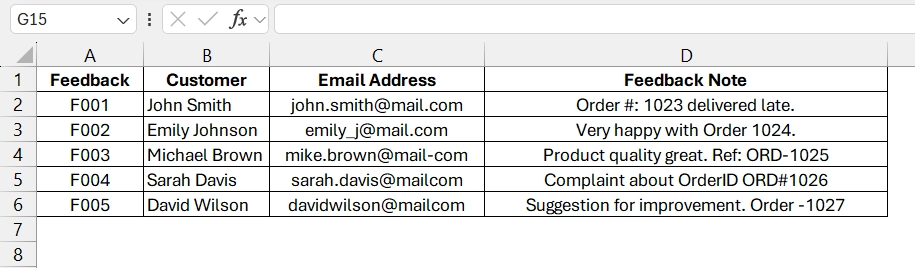
We have a dataset that contains inconsistent email formats in Column C and various ways of writing order IDs in Column D. We will use a VBA RegEx macro to quickly standardize both fields to make sure of a clean, uniform format for reporting.
Steps:
➤ Open your dataset. We have Feedback ID in Column A, Customer in Column B, Email address in Column C, and Feedback Note in Column D.
➤ Open the Excel workbook, press Alt + F11 to open the VBA Editor window. Go to Insert > Module.
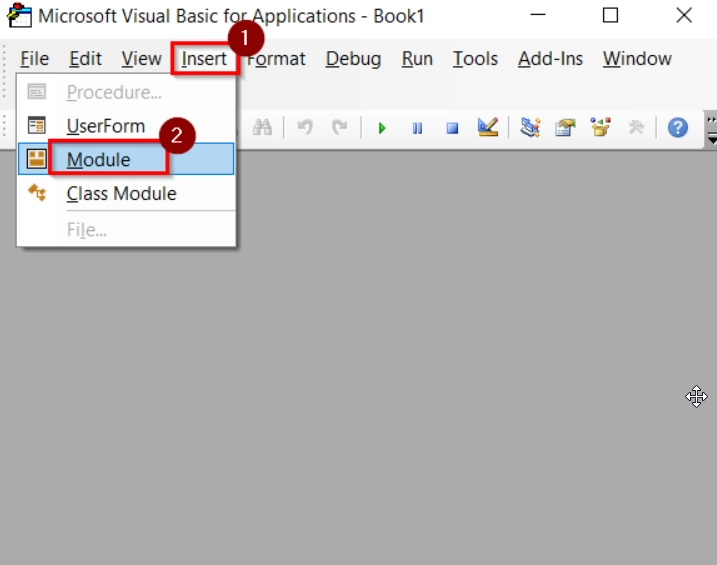
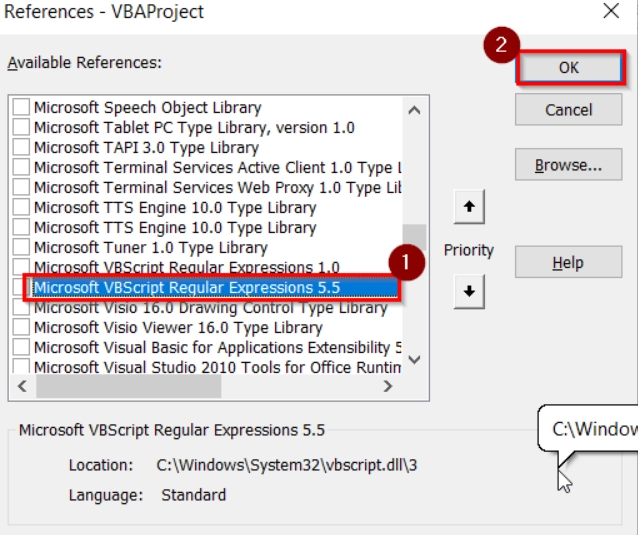
➤ Go to Tools → References.
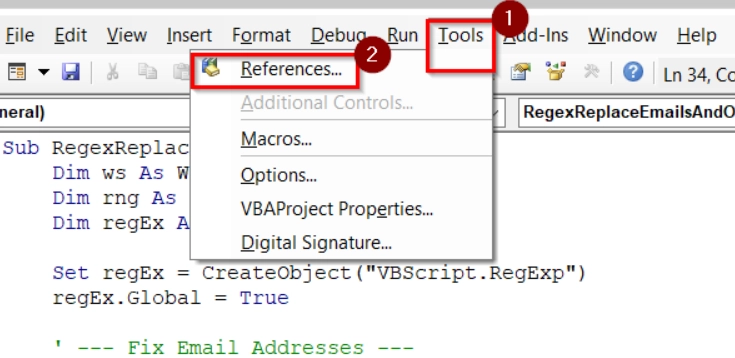
➤ You have to choose Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5 and Click OK.
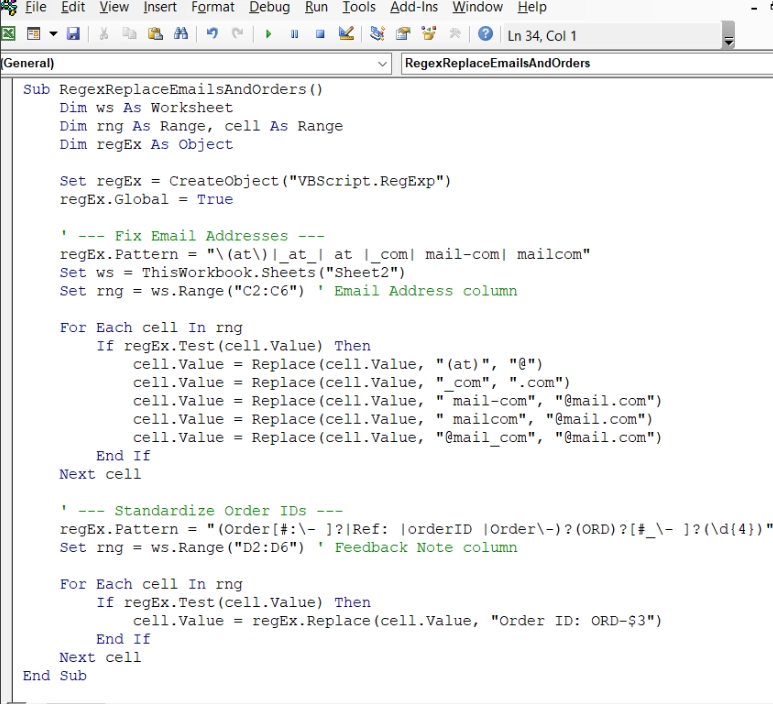
➤ Paste the following VBA code in the module window. Then press Ctrl + S and close the VBA window.
Sub RegexReplaceEmailsAndOrders()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim rng As Range, cell As Range
Dim regEx As Object
Set regEx = CreateObject("VBScript.RegExp")
regEx.Global = True
' --- Fix Email Addresses ---
regEx.Pattern = "\(at\)|_at_| at |_com| mail-com| mailcom"
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet2")
Set rng = ws.Range("C2:C6") ' Email Address column
For Each cell In rng
If regEx.Test(cell.Value) Then
cell.Value = Replace(cell.Value, "(at)", "@")
cell.Value = Replace(cell.Value, "_com", ".com")
cell.Value = Replace(cell.Value, " mail-com", "@mail.com")
cell.Value = Replace(cell.Value, " mailcom", "@mail.com")
cell.Value = Replace(cell.Value, "@mail_com", "@mail.com")
End If
Next cell
' --- Standardize Order IDs ---
regEx.Pattern = "(Order[#:\- ]?|Ref: |orderID |Order\-)?(ORD)?[#_\- ]?(\d{4})"
Set rng = ws.Range("D2:D6") ' Feedback Note column
For Each cell In rng
If regEx.Test(cell.Value) Then
cell.Value = regEx.Replace(cell.Value, "Order ID: ORD-$3")
End If
Next cell
End Sub➥ Order ID Section: Captures multiple variations (Order#, Ref:, ORD_) and standardizes them to Order ID: ORD-XXXX.
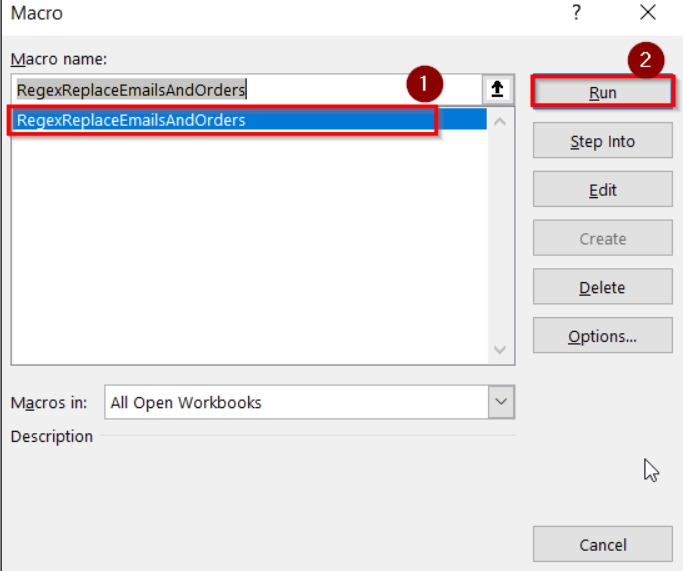
➤ Press Alt + F8 . Then select RegexReplaceEmailsAndOrders, and click Run.
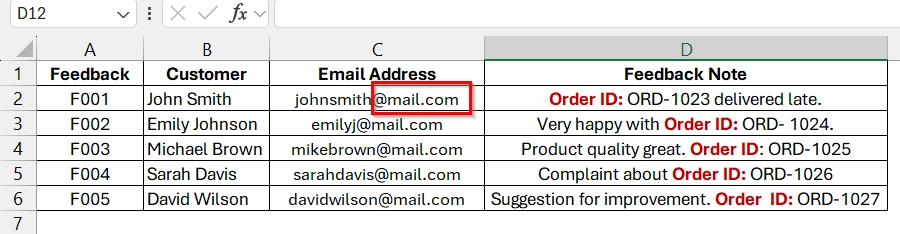
➤ Check your sheet to confirm all Email addresses and Order IDs have been standardized by replacing the non standard format with standard format.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use regex in Excel to find and replace?
Yes, but not directly through Excel’s native tools. You can use a VBA macro with VBScript.RegExp to enable full RegEx functionality.
How to use regex to find and replace?
Enable VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5 in VBA, write a macro defining the pattern, and run it on your target range.
Can I use regex in an Excel formula?
Not natively, but you can use certain Excel functions combined with helper columns or Office Scripts in Excel 365.
What is the regex replace formula?
In VBA, it’s typically RegEx.Replace(text, replacement), where regEx.A pattern defines the search expression.
Concluding Words
Finding and replacing data with RegEx in Excel is best done through Custom VBA Regex Replace for full flexibility, or Find & Replace with Wildcards for simpler patterns. By understanding both methods, you can choose the most efficient approach for your data cleaning tasks, saving time and improving accuracy.