Microsoft Excel has genuinely two types of cell reference systems: absolute and relative cell reference. These work differently while copying or moving Excel formulas. That’s why understanding the difference between these two cell references is important. This article focuses on the key difference between absolute and relative references with clear examples.
| Feature | Relative Reference | Absolute Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Notation | A1 | $A$1 |
| Behavior When Copied | Changes by default in Excel | Remains fixed |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible for repetitive tasks | Rigid for consistent cell referencing |
| Use cases | Formulas that adjust when applied across rows and columns | When referencing a fixed value (e.g., tax rate, discount rate) |
This article uses real-world sales data as an example to highlight the core difference between absolute and relative references. Excel uses relative references by default, but you can easily use absolute references if needed.
Relative Reference: The Default Behavior
A relative reference changes automatically while a formula is copied or moved to another location. In the new location, it updates the cell reference. When you copy a formula like =A1*B1 from cell C1 to C2, it automatically adjusts to =A2*B2.
Absolute Reference: The Fixed Behavior
An absolute reference in Excel remains fixed whenever the formula is copied. It refers to a specific row and column. Commonly, we use a dollar sign ($) to make any cell reference absolute. There are three forms of absolute cell reference. These are:
- $A1: The column is absolute, but the row is relative.
- A$1: The row is absolute, but the column is relative.
- A$1: Both row and column are absolute.
Absolute Vs Relative Reference to Copy/Move Excel Formula
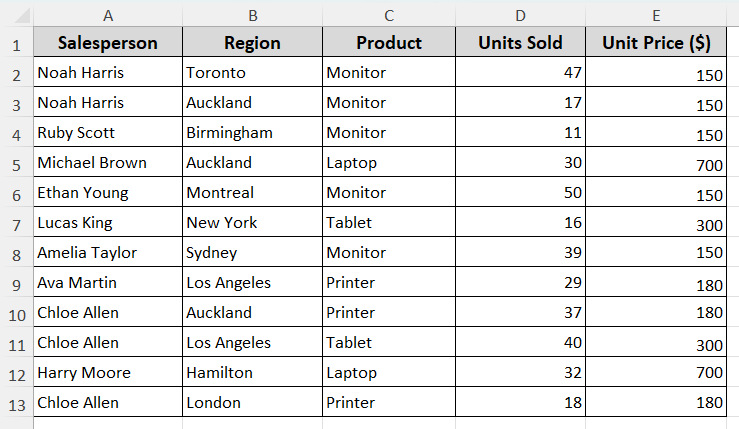
Before discussing the main difference, let’s get familiar with the dataset. We have sales data for some products, including units sold and unit price.
We’ll demonstrate the difference between absolute and relative references practically while copying the formula to the cells below. Follow the steps below.
Steps:
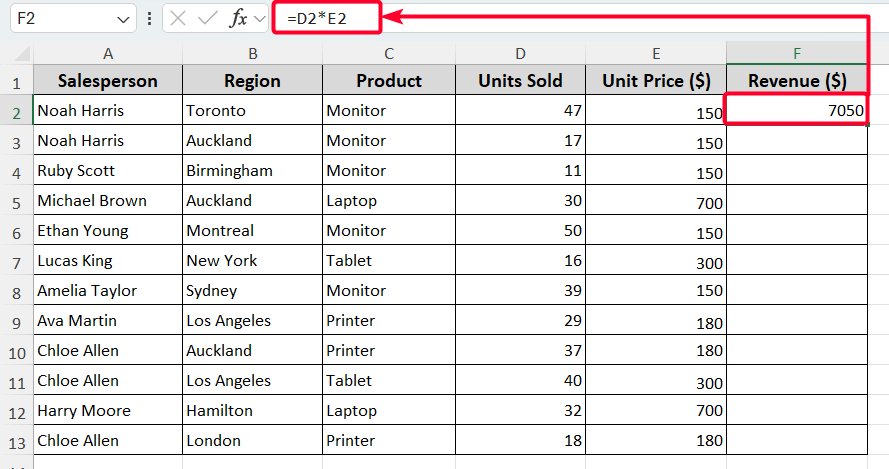
➤ First, we want to find the product-wise revenue. For that, we have to multiply the unit price of each product by the units sold.Therefore, the formula in cell F2 will be as follows.
=D2*E2
➤ Next, use the Fill Handle tool to copy the formula to the cells below.
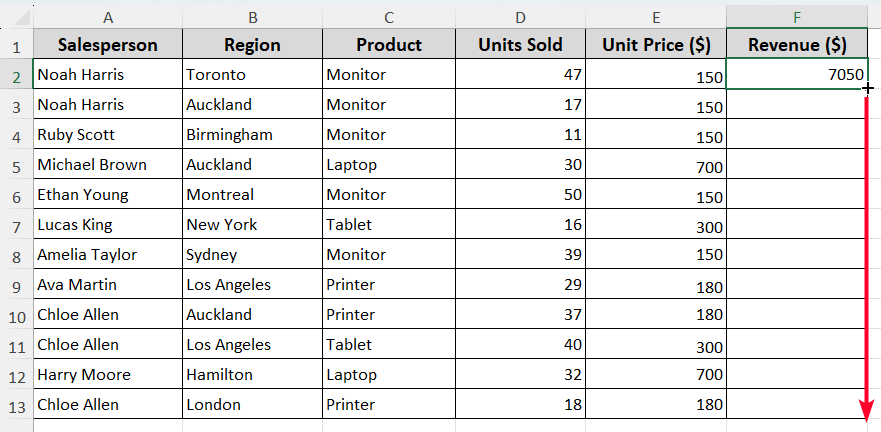
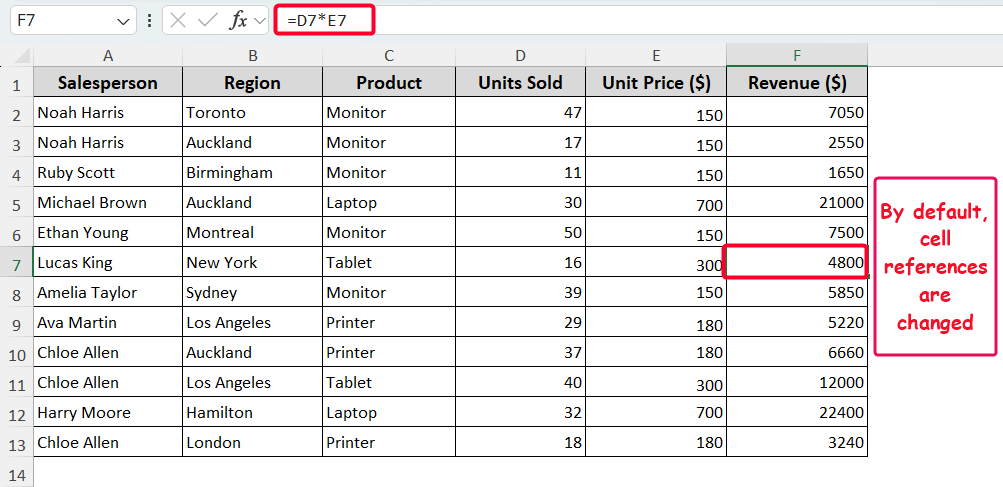
By default, cell references are changed. And you’ll get the revenue for each product. For better visualization, you can view the formula in cell F7. This is how the relative reference system works in Excel.
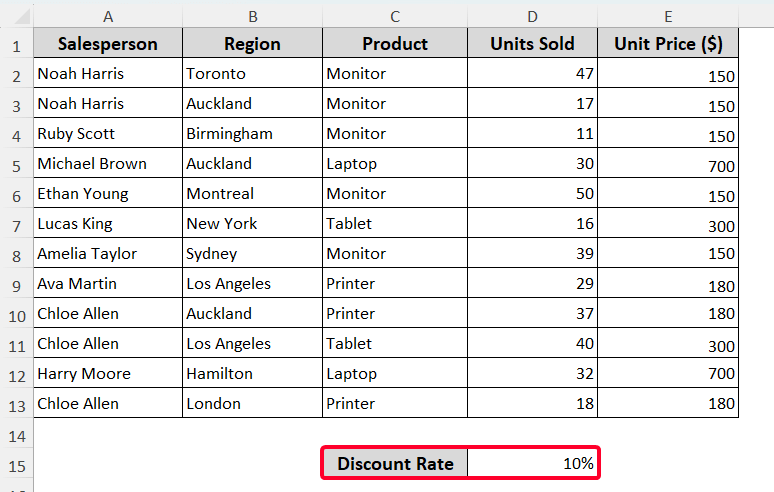
Let’s now demonstrate the effect of using an absolute reference in Excel. As shown below in the image, we have a common discount rate for all products. And we need to calculate the discounted price based on the given discount rate.
Steps:
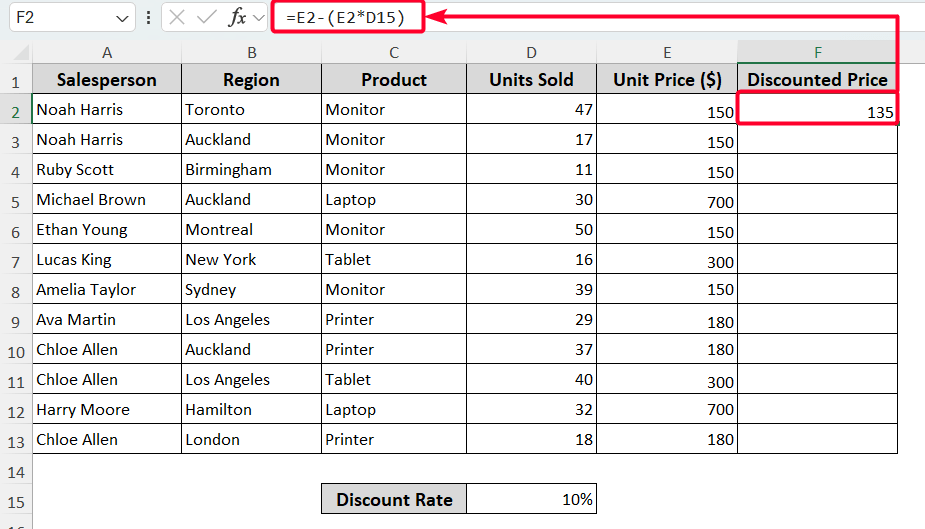
➤ To find the discounted price, enter the formula below in the F2 cell.
=E2-(E2*D15)
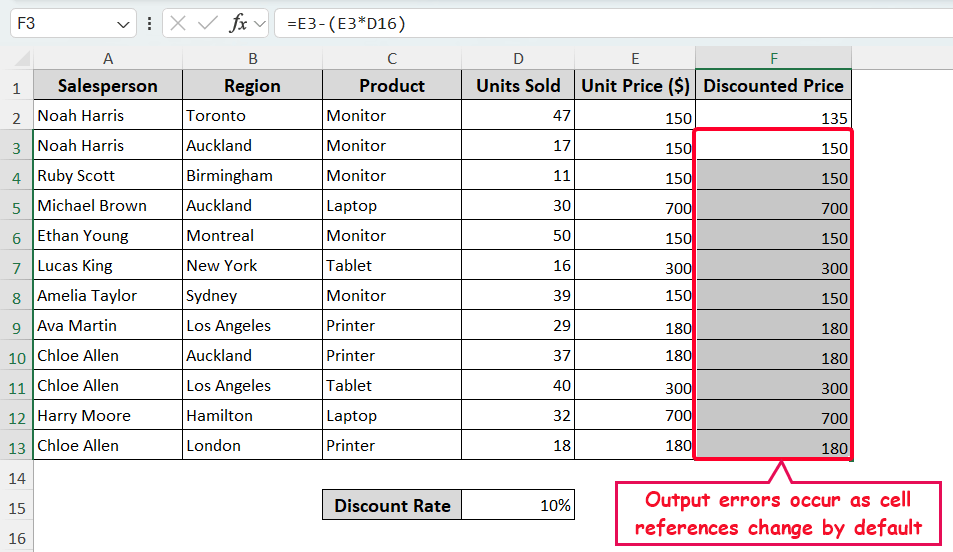
➤ Like relative reference as shown earlier, copy the formula in the F2 cell to the cells below. After that, you’ll get the following output, which contains errors.
As F3:F17 cells are the same as the unit price in the E3:E17 cells, though they should be different. This error happens because the cell reference in the formula changes when you copy it.
That’s why we need to fix the cell reference (D15) of the discount rate. To do this, do the following things.
➤ Select the D15 cell in the formula bar >> press the F4 key.
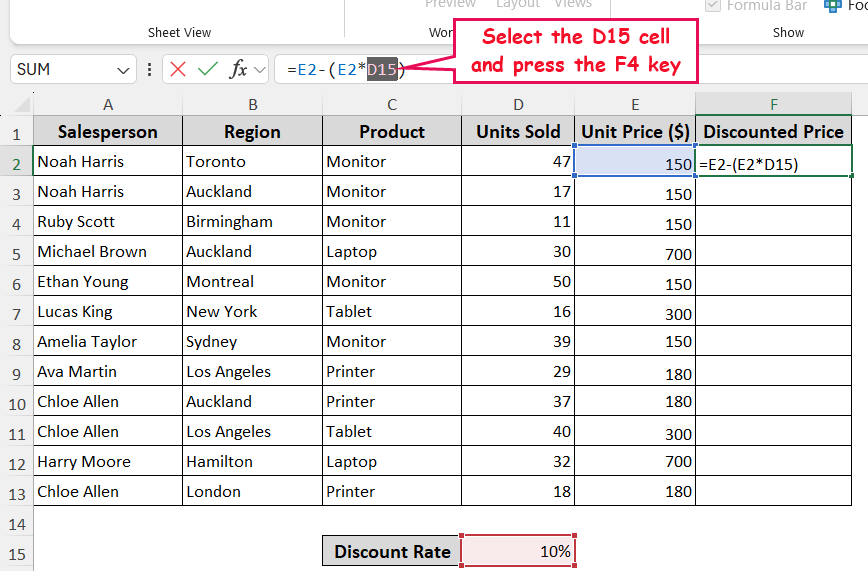
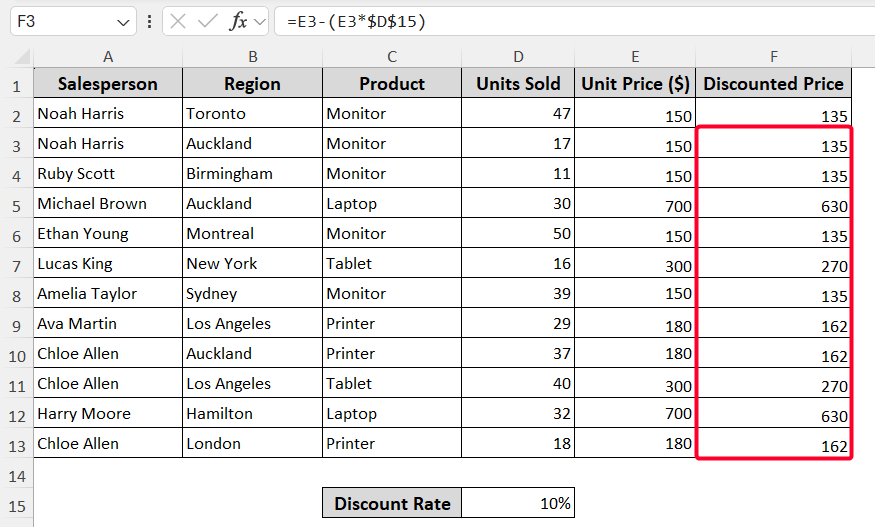
➤ Press the Enter button, and use the Fill Handle tool for the cells below. And you’ll get the expected output. This is how the absolute reference system works in Excel.
Note:
Copying a formula in Excel often leads to changes in cell references, but a similar situation arises when you move a formula. When you cut and paste a formula to a new location, Excel automatically adjusts the cell references within that formula.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Switch Between References in Excel?
You can easily switch between references in Excel. To do this, go to the formula bar in Excel >> select a cell >> press the F4 key repeatedly. On the first click, you’ll get the absolute references. Then, sequentially, you’ll see absolute rows, absolute columns, and relative references.
Can I mix absolute and relative references in the same formula?
Yes, of course. For example, if you need an absolute column, use the dollar sign before the column ($A1) but not before the row.
Do Absolute References Work Across Different Sheets?
Yes. An absolute reference like ‘Sheet1’!$A$1 remains fixed regardless of where the formula is used.
Wrapping Up
In this article, we explored the basic difference between absolute and relative references in Excel with real-world example. Hopefully you have enjoyed the article. Feel free to download the practice file and share your thoughts and suggestions.