When working with Excel, we commonly need the last row of data in a column or range. It helps you accurately define ranges for formulas, charts, or VBA macros, avoiding including empty cells. It ensures that automated tasks like data import, analysis, or reporting run effectively.
That’s why, in this article, we’ll walk you through six different practical VBA methods to find the last row with data. It includes using Range.End, Range.Find, SpecialCells, CurrentRegion, Excel Tables, and SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants) or SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas) method.
➤ Open your Excel workbook.
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
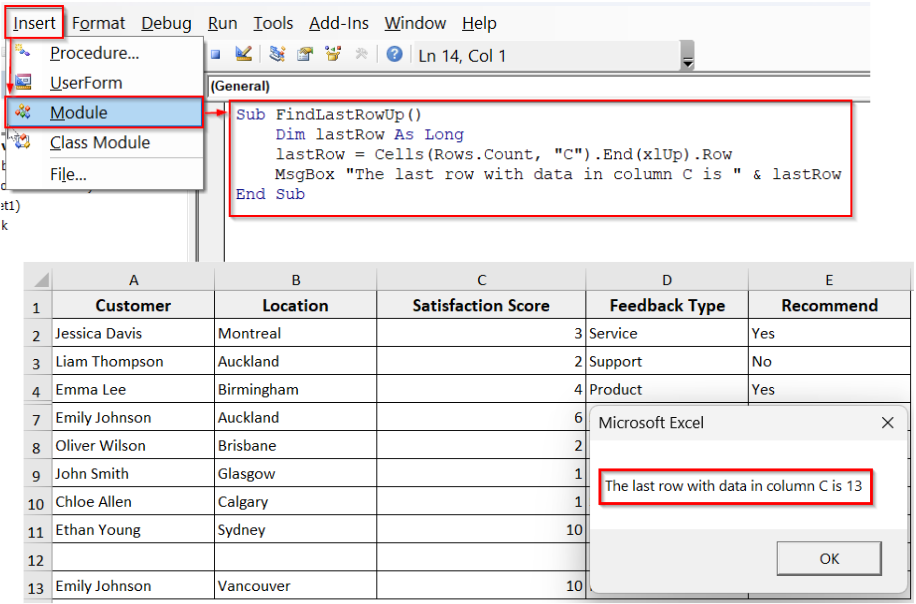
➤ To insert a new module, go to Insert >> Module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code to find the last row with data in a range.
Sub FindLastRowUp()
Dim lastRow As Long
lastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, "C").End(xlUp).Row
MsgBox "The last row with data in column C is " & lastRow
End Sub➤ Run the code.
➤ The code will show the message dialog box showing the last row, row 13.
Using Range.End(xlDown) and Range.End(xlUp) Method
If you want to find the last non-blank cell in a single row or column, you can use the Range.End(xlDown) and Range.End(xlUp) method.
Here, using End(xlDown) is simpler for a range. Here, the code starts at the first row in the range and ends at the first row of the last visible row in the range that contains data, and the last row before an empty cell. As for using End(xlUp), it starts from the very bottom of the worksheet (the last row) and moves upward until it reaches the last non-blank cell.
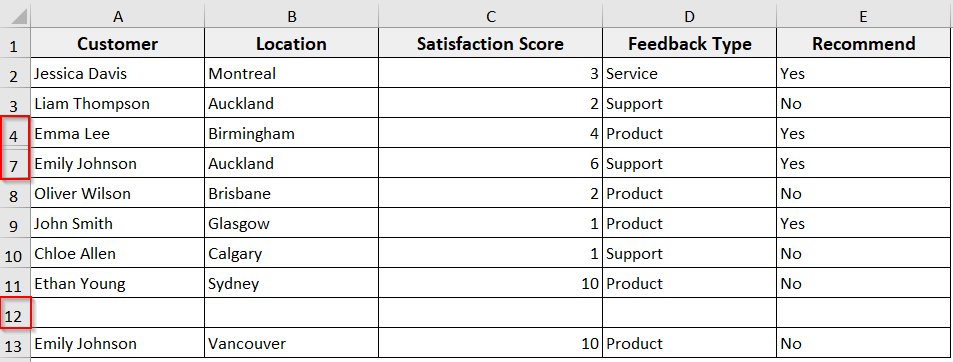
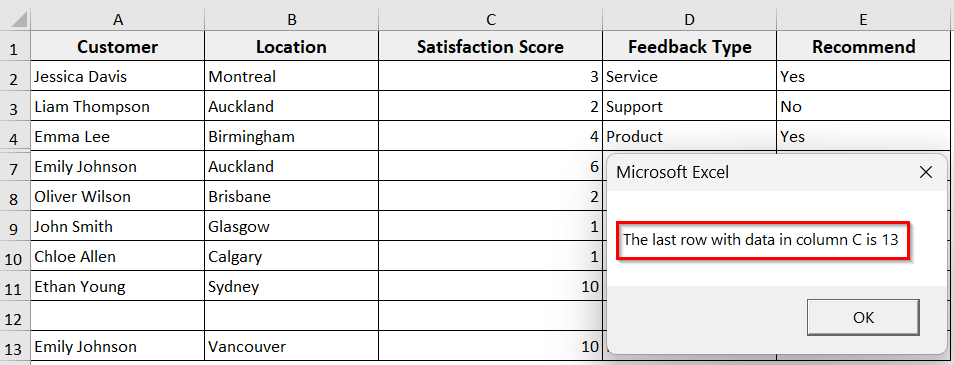
In the following dataset, we have customer feedback with columns like Customer, Location, Satisfaction Score, Feedback Type, and Recommend, with some hidden and blank rows. Now we will use the Range.End(xlDown) and Range.End(xlUp) to find the last row in the Satisfaction Score column.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
➤ Go to Insert >> Module to insert a new module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code to find the last row using xlDown
Sub FindLastRowDown()
Dim lastRow As Long
lastRow = Range("C2", Range("C2").End(xlDown)).Rows.Count + Range("C2").Row - 1
MsgBox "The last row with data in column C is " & lastRow
End Sub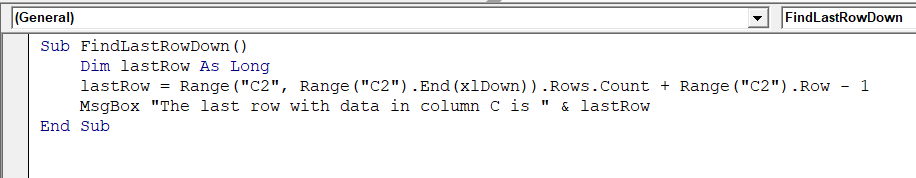
➤ Run the code.
➤ The macro will display a message box showing the last row with data in column C before the blank and empty cell, and returns to 11, counting the hidden rows.
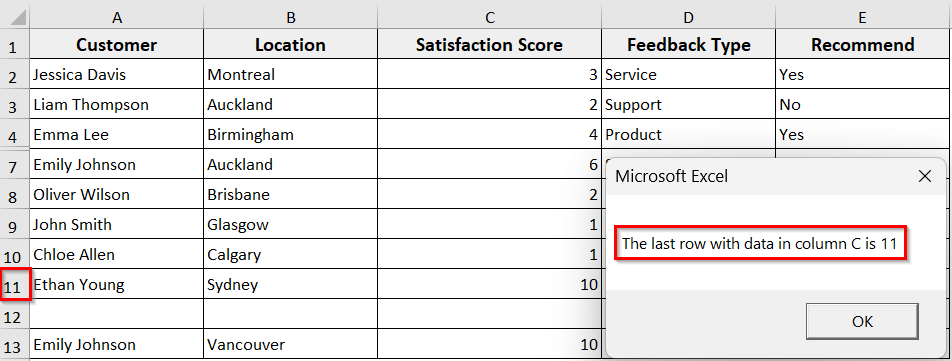
➤ To find the last row using xlUp, insert the following VBA code.
Sub FindLastRowUp()
Dim lastRow As Long
lastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, "C").End(xlUp).Row
MsgBox "The last row with data in column C is " & lastRow
End Sub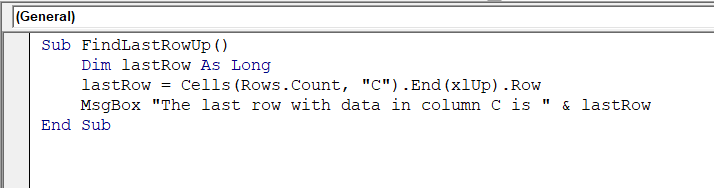
➤ Run the code, and the code will return the true last row, row 13, counting the hidden and blank rows also.
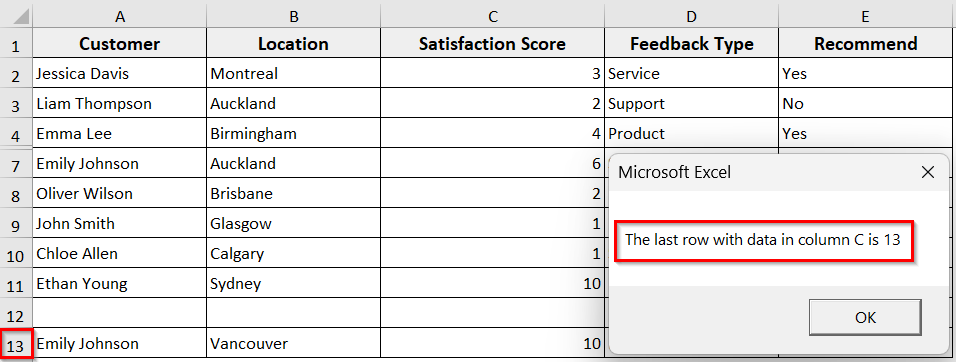
➥ Range("C2", Range("C2").End(xlDown)): It defines a range from cell C2 down to the last filled cell.
➥ Cells(Rows.Count, "C").End(xlUp).Row: It starts from the last row of the sheet and moves up to find the last filled cell.
➥ MsgBox: It displays the result in a message box.
➥ xlDown and xlUp: It lets you choose the direction of the search.
Using Range.Find Method
The Find method is another way to get the last row with data in Excel VBA. Instead of moving cell by cell, it searches the whole column and finds the very last non-blank cell.
Here, the “*” works as a wildcard. It means Excel will match any kind of data, text, or numbers in the cell.
When we set SearchDirection:=xlPrevious, the search begins from the last cell of the worksheet and moves upward. SearchOrder:=xlByRows checks row by row until it finds a filled cell.
When it finds one, it stops and returns the row number. When your dataset has hidden rows or formatted empty rows, Range.Find often gives more accurate results than Range.End.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor and insert a new module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code.
Sub FindLastRowUsingFind()
Dim lastCell As Range
Set lastCell = Columns("C").Find(What:="*", _
SearchOrder:=xlByRows, _
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)
If Not lastCell Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "The last row with data in column C is " & lastCell.Row
Else
MsgBox "No data found in column C."
End If
End Sub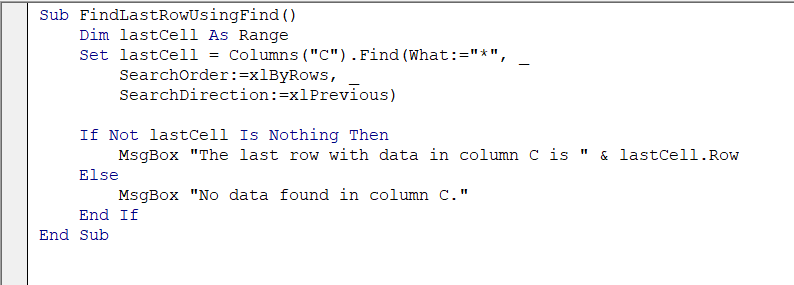
➤ Run the code.
➤ The macro will display the last row containing data, row 13. In this dataset, even if rows are hidden or if there are blanks in between.
➥ Cells.Find(What:="*"): It searches for any value (text or number).
➥ SearchOrder:=xlByRows: It makes the search row by row.
➥ SearchDirection:=xlPrevious: It starts from the end and moves upward.
➥ Row: It returns the row number of the last found cell.
Using Range.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell) Method
The SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell) method helps you find the last cell that Excel thinks is “used.” When you use this method, Excel looks at the whole sheet and jumps straight to the very last used cell.
Then it gives back that cell’s row number. That’s why sometimes the result may look higher than expected if you have formatting applied beyond your data.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor and insert a new module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code.
Sub FindLastRowSpecialCells()
Dim lastRow As Long
lastRow = Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Row
MsgBox "The last used row is " & lastRow
End Sub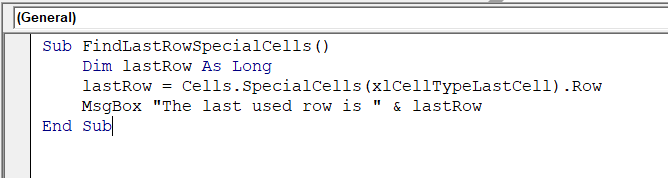
➤ Run the code.
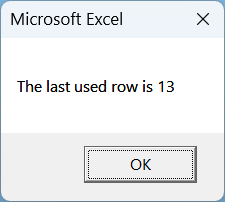
➤ The VBA will show the last used row number. It may give you unintended results if the VBA finds the last cell with any sort of data or formatting associated with it.
➥ Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell): It finds the bottom-rightmost used cell in the sheet.
➥ .Row: It extracts the row number from that cell.
Using the CurrentRegion Method
The CurrentRegion method is useful when your data is arranged in a contiguous block without completely empty rows or columns inside it. CurrentRegion automatically starts from a starting cell and includes all the connected data around it. After the VBA gets the region, you can find its last row easily.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor and insert the following VBA code in the new module.
Sub FindLastRowCurrentRegion()
Dim rng As Range
Dim lastRow As Long
Set rng = Range("C2").CurrentRegion
lastRow = rng.Rows(rng.Rows.Count).Row
MsgBox "The last row with data in the Satisfaction Score column is " & lastRow
End Sub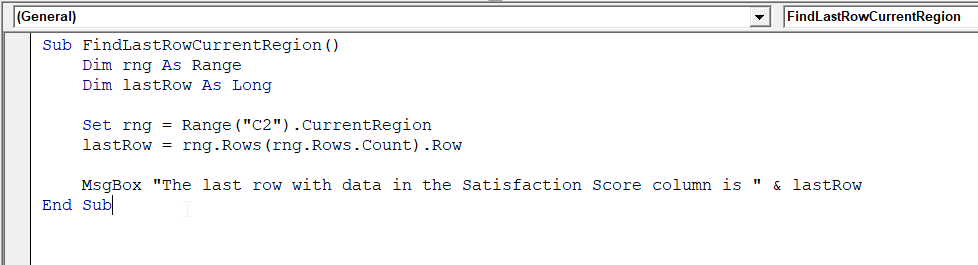
➤ Run the code.
➤ The code will show the last row number within the current contiguous block of data.
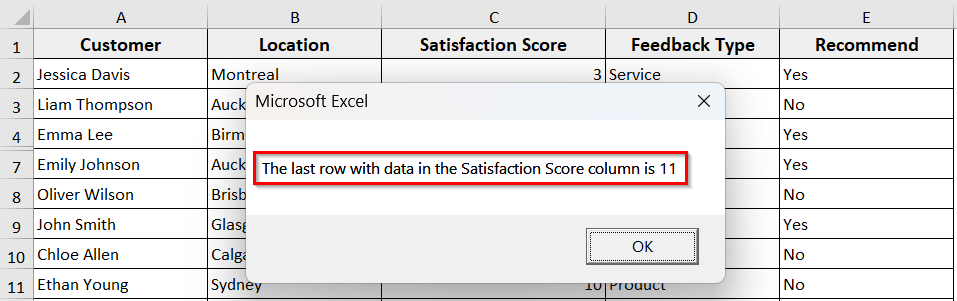
➥ Range("C2").CurrentRegion: It starts from cell C2 and expands to include all connected cells with data.
➥ rng.Rows(rng.Rows.Count).Row: It gets the row number of the bottom-most row in that region.
➥ MsgBox: It shows the result in a message box.
Using the ListObject (Excel Table) Method
If your data is formatted as an Excel Table, the ListObject method is the most reliable way to find the last row with data. Tables automatically expand when you add rows. So VBA can directly reference the DataBodyRange of the table without considering extra blanks or formatting outside the data.
For example, we have converted our customer feedback dataset into a table named Table1.
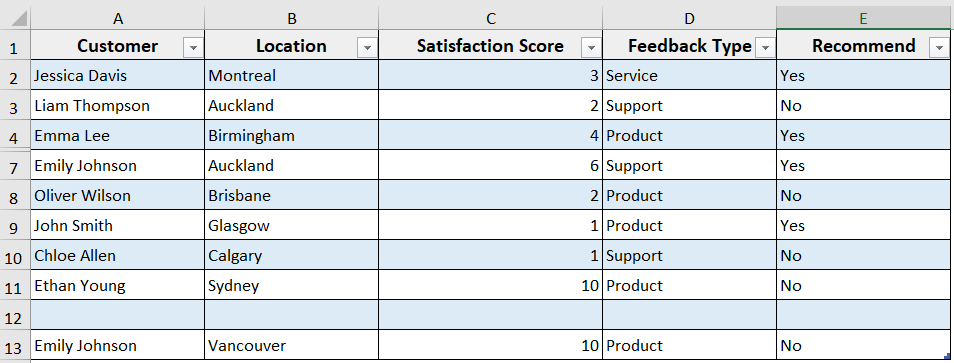
Steps:
➤ Insert a new module and write the following VBA code.
Sub FindLastRowListObject()
Dim lo As ListObject
Dim lastRow As Long
Set lo = Worksheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("Table1")
lastRow = lo.DataBodyRange.Row + lo.DataBodyRange.Rows.Count - 1
MsgBox "The last row with data in Table1 is " & lastRow
End Sub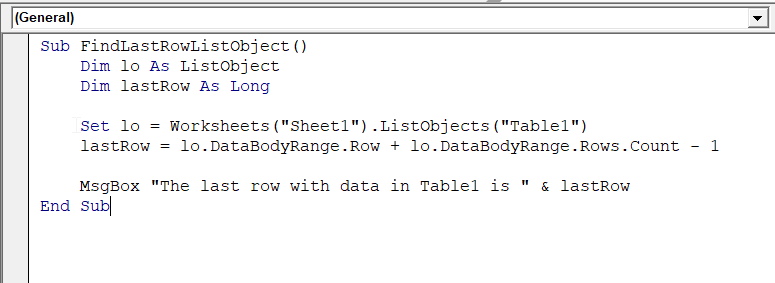
➤ Run the code.
➤ The code will show the last row of the table, regardless of hidden rows or blanks.
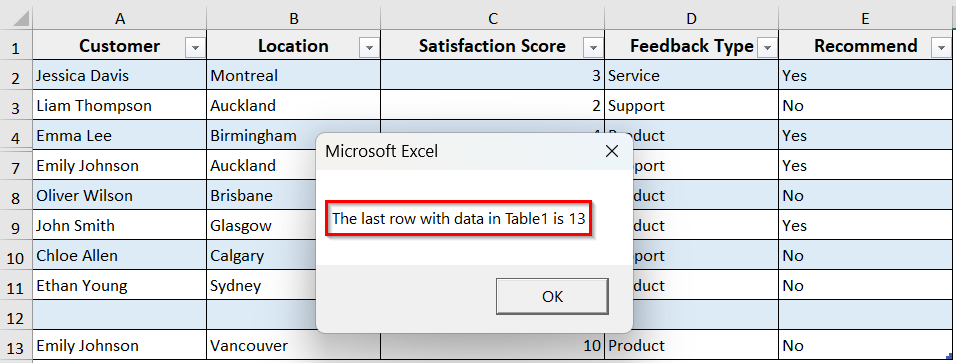
➥ Worksheets("Sheet1").ListObjects("Table1"): It refers to the table named Table1 on Sheet1.
➥ lo.DataBodyRange: It refers to the range of all rows inside the table (excluding headers).
➥ lo.DataBodyRange.Row + lo.DataBodyRange.Rows.Count - 1: It calculates the last row by adding the first row of the table’s data to the total number of rows.
➥ MsgBox: It displays the row number in a message box.
Using SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants) or SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas) Method
The SpecialCells method allows you to specifically target either cells with constants or cells with formulas. This is useful when you want more control.
Steps:
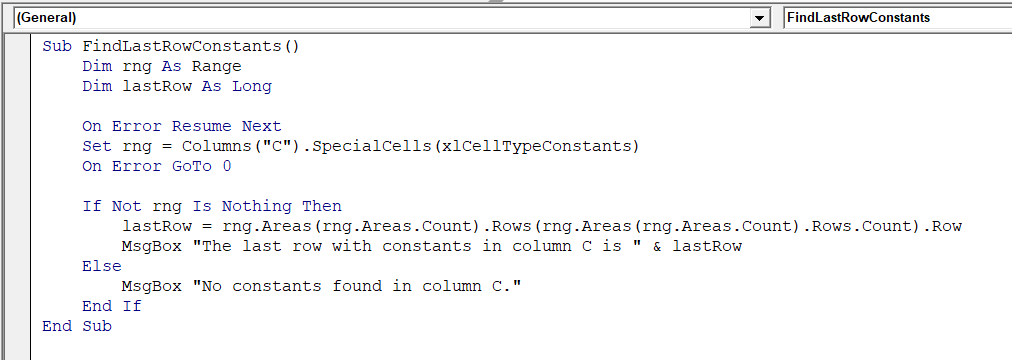
➤ Insert the following VBA code in the new module to find the last row with constants.
Sub FindLastRowConstants()
Dim rng As Range
Dim lastRow As Long
On Error Resume Next
Set rng = Columns("C").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants)
On Error GoTo 0
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
lastRow = rng.Areas(rng.Areas.Count).Rows(rng.Areas(rng.Areas.Count).Rows.Count).Row
MsgBox "The last row with constants in column C is " & lastRow
Else
MsgBox "No constants found in column C."
End If
End Sub
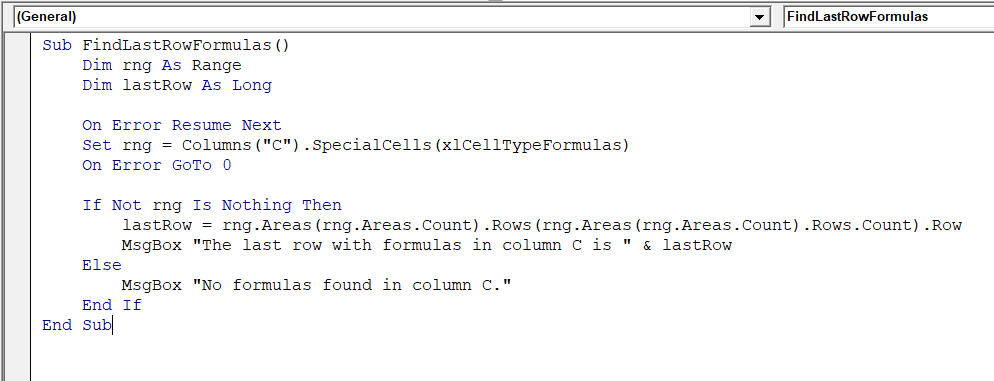
➤ To find the last row with formulas, insert the following VBA code.
Sub FindLastRowFormulas()
Dim rng As Range
Dim lastRow As Long
On Error Resume Next
Set rng = Columns("C").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas)
On Error GoTo 0
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
lastRow = rng.Areas(rng.Areas.Count).Rows(rng.Areas(rng.Areas.Count).Rows.Count).Row
MsgBox "The last row with formulas in column C is " & lastRow
Else
MsgBox "No formulas found in column C."
End If
End Sub
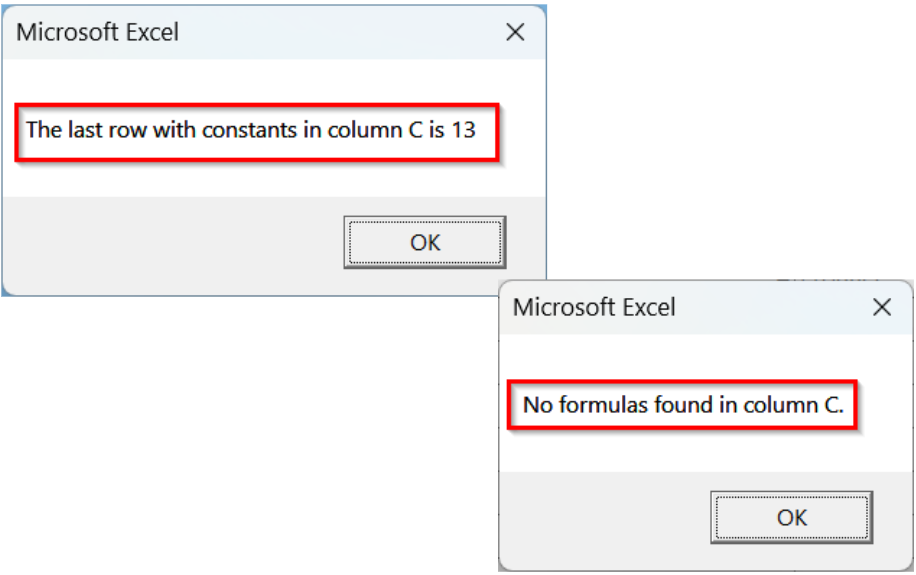
➤ Run the code.
➤ The codes will show the last row number in column C that contains either constants or formulas, depending on which macro you execute.
➥ Columns("C").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants): It finds only cells with manually entered values in column C.
➥ Columns("C").SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas): It finds only cells with formulas in column C.
➥ rng.Areas(rng.Areas.Count).Rows(...): It gets the bottom-most row of the last area found.
➥ On Error Resume Next: It avoids runtime errors when there are no constants/formulas.
➥ MsgBox: It shows the last row result in a message box.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to select a specific data range with VBA?
➤ You can use the Range object to select a specific data range with VBA.
➤ Insert the following VBA code.
Dim lastRow As Long
lastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
Range("A2:C" & lastRow).Select➤ Run the code.
➤ The code will select all rows in columns A to C up to the last row with data.
How to select a range in VBA dynamically?
➤ You can use End(xlUp/xlDown) to select a range in VBA dynamically.
➤ Insert the following VBA code.
Dim lastRow As Long
lastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
Range("A2:C" & lastRow).Select➤ Run the code.
➤ The code will dynamically select from A2 to the last filled row in column A in multiple columns.
How to select and cut the range with VBA?
➤ In VBA, you can select a range and cut it to move data elsewhere in the workbook. The Cut method works like the manual Ctrl + X command.
➤ Insert the following code.
Range("A2:C10").Cut Destination:=Worksheets("Sheet2").Range("A2")➤ The code cuts the range A2:C10 from the active sheet and pastes it starting at A2 on Sheet2.
Wrapping Up
In this quick tutorial, we have learnt multiple ways to find the last row with data in a range using Excel VBA. These methods help you handle different datasets in different scenarios. Feel free to download the sample workbook and try out the VBA macros yourself. Let us know how these codes have simplified your Excel tasks.





