Cleaning up data in Excel often involves dealing with numbers stored as text. A common scenario is when numbers contain spaces (e.g., “1 2 3 4” instead of “1234”). Such values won’t behave like real numbers which is why they can’t be summed, sorted numerically, or used in calculations until cleaned.
In this article, we’ll explore four practical methods to convert text with spaces into usable numbers. Each method includes a sample dataset and easy-to-follow steps so you can practice along. Let’s get started.
Steps to convert text with spaces to number in Excel:
➤ Place your dataset in A2:D11.
➤ In B2, enter the following formula:
=SUBSTITUTE(A2,” “,””)+0
➤ Press Enter to remove spaces and convert to a number.
➤ Drag the fill handle down to apply it to all rows.
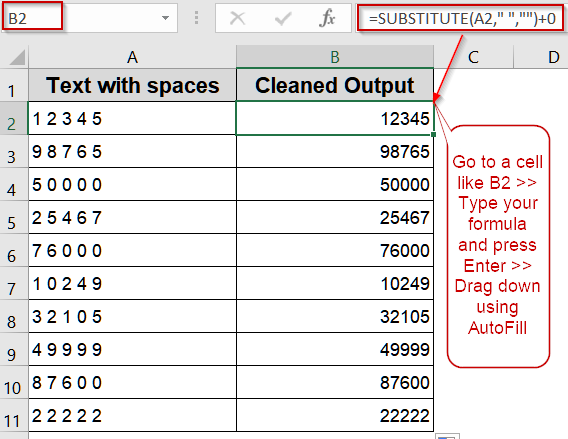
Convert Text with Spaces Using SUBSTITUTE Function & Arithmetic Operations
Numbers imported from PDFs, web pages, or other sources often contain spaces, making Excel treat them as text. The SUBSTITUTE function removes these spaces, and combining it with +0 or *1 which forces Excel to recognize the result as a number, allowing calculations, sorting, and other numeric operations. We’ll use the following dataset:

Steps:
➤ Place your dataset in A2:D11.
➤ In B2, enter the following formula:
=SUBSTITUTE(A2," ","")+0
➤ Press Enter to remove spaces and convert to a number.
➤ Drag the fill handle down to apply it to all rows.

➤ Alternatively, you can also use this formula:
=SUBSTITUTE(A2," ","")*1
Here, multiplication by 1 forces Excel to treat the cleaned text as a number.
➤ Press Enter and drag down.

Insert VALUE and SUBSTITUTE Functions to Convert Text
If you need a quick, formula-only approach, combining SUBSTITUTE with VALUE function is ideal. SUBSTITUTE function removes all spaces from your numbers stored as text, and VALUE function converts the cleaned result into a proper numeric format. This method is compact, efficient, and works for large datasets.
Steps:
➤ Place your dataset in A2:A11.
➤ In B2, type:
=VALUE(SUBSTITUTE(A2," ",""))
➤ Press Enter and drag down.
➤ Check by performing a sum or average to confirm conversion.

Combine VALUE, SUBSTITUTE, and CHAR for Non-breaking Spaces
Some datasets contain non-breaking or invisible spaces that prevent Excel from recognizing numbers correctly. This method uses SUBSTITUTE with CHAR and VALUE functions to remove even these tricky spaces, ensuring all text-based numbers are converted into proper numeric format for calculations and analysis.
Steps:
➤ In B2, enter:
=VALUE(SUBSTITUTE(A2,CHAR(32),""))
➤ Press Enter and drag the formula down.

This guarantees conversion even when invisible or non-standard spaces are present.
Use Text to Columns with CONCAT & VALUE Functions
When spaces separate digits in your numbers, Excel treats each segment as text. Using Text to Columns splits the values, and then combining CONCAT with VALUE function rejoins them into a proper number, ready for calculations.
Steps:
➤ Highlight A2:A11.
➤ Go to the Data tab >> Click on Text to Columns under Data Tools.

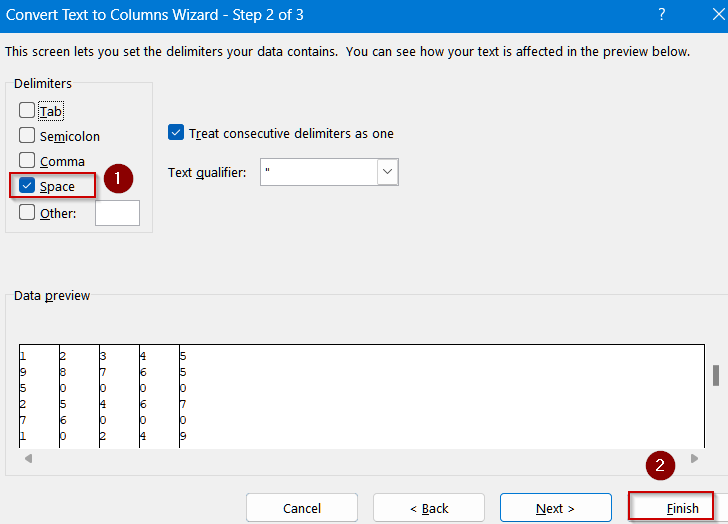
➤ Choose Delimited and click on Next.

➤ Choose Space >> Click Finish to split values into adjacent columns B,C,D and E.
➤ In a new column such as F, join the split numbers:
=VALUE(CONCAT(A2:E2))
➤ Press Enter and drag down.
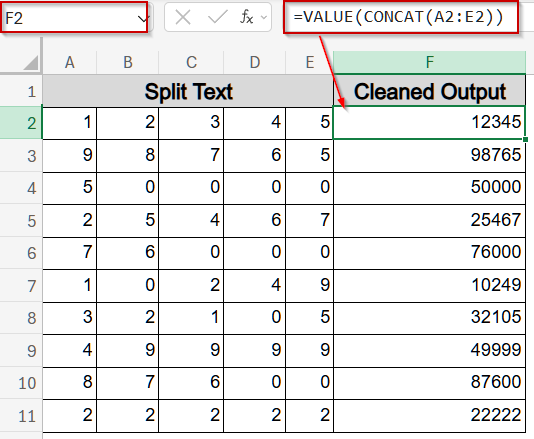
The concatenation removes spaces, and VALUE function converts the result into a number.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does Excel store numbers with spaces as text?
Excel treats any numeric entry with spaces as text because spaces interrupt the numeric sequence. This prevents calculations, sorting, or summing until spaces are removed or the text is converted into a proper number format.
Can I use Find and Replace instead of formulas?
Yes, Find and Replace works well. Press Ctrl+H, enter a space in “Find” and leave “Replace” blank. After replacing, use the VALUE function or simple arithmetic operations to convert the cleaned text into numbers.
What if spaces are non-breaking or invisible?
Non-breaking or invisible spaces often appear when copying data from websites or PDFs. Use SUBSTITUTE with CHAR codes or TRIM function to remove these hidden spaces, ensuring proper numeric conversion.
Will these methods work for decimals or negative numbers?
Yes, they work for both decimals and negative numbers as long as only spaces are removed. Ensure the underlying number format remains valid after conversion, so Excel can recognize the value correctly.
Does Text to Columns overwrite my original data?
Text to Columns can overwrite your original dataset if not careful. Always copy the column to a safe location first. This prevents accidental data loss while splitting, concatenating, or converting numbers.
Wrapping Up
In this tutorial, we explored four effective methods to convert text with spaces into numbers in Excel. From simple SUBSTITUTE formulas to handling non-breaking spaces, these techniques ensure your data is clean, usable, and ready for calculations. Feel free to download the practice file and share your feedback.


