Finding exact matches in Excel VBA is essential when you’re automating tasks like data validation, record lookups, or targeted replacements. Whether you’re scanning a single column for a precise value or matching multiple fields with case sensitivity, VBA gives you powerful tools to do it efficiently.
In this article, you’ll learn six practical VBA methods to find exact matches. We’ll show you how to search ranges using Find, match values case-sensitively, perform replacements, extract data based on a match, and even use functions like InStr and Match for more advanced scenarios.
Steps to Find an Exact Match in a Range Using VBA and Display the Result in a Message Box
➤ Press Alt + F11 , choose Insert >> Module, and paste the following code:
Sub FindExactMatchInRange()
Dim rng As Range
Dim resultMsg As String
' Search for exact match of "Joseph Grant" in the Name column
Set rng = Sheets("ExactMatch").Range("A2:A11").Find("Joseph Grant", LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
resultMsg = rng.Value & " found at " & rng.Address
MsgBox resultMsg, vbInformation
Else
MsgBox "Name not found.", vbExclamation
End If
End Sub
➤ Range(“A2:A11”) targets the column with the names (adjusted to match your dataset)
➤ .Find(“Joseph Grant”) searches for the full name using exact match mode
➤ If found, it shows the name and cell address in a message box
➤ If not found, it displays “Name not found.”
➤ Press Alt + F8 , run FindExactMatchInRange, and check the message box for the result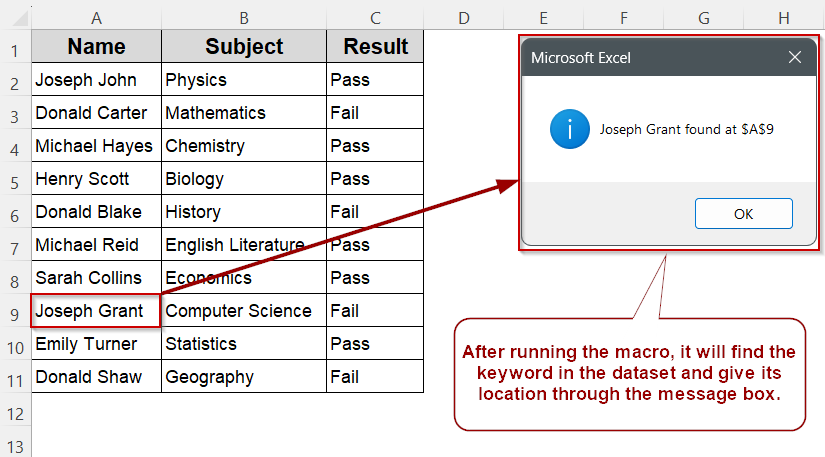
Find an Exact Match in a Range Using VBA (with Message Box Output)
If you have a list of names or values in a worksheet, you may want to locate the exact position of a specific entry. This method uses the Find function in VBA to search through a defined range and return the address of the exact match.
In this method, we’ll search for the name “Joseph Grant” inside a column of names and display the result using a message box.
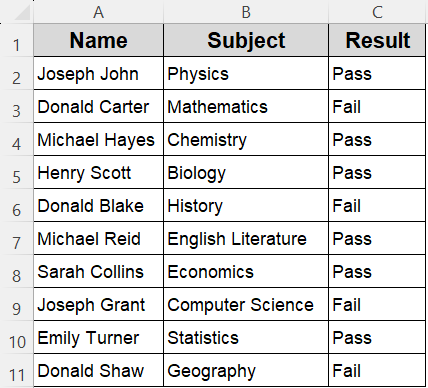
Steps:
➤ Open Excel and press Alt + F11 to launch the VBA editor
➤ Go to Insert >> Module
➤ Paste this code:
Sub FindExactMatchInRange()
Dim rng As Range
Dim resultMsg As String
' Search for exact match of "Joseph Grant" in the Name column
Set rng = Sheets("ExactMatch").Range("B2:B11").Find("Joseph Grant", LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
resultMsg = rng.Value & " found at " & rng.Address
MsgBox resultMsg, vbInformation
Else
MsgBox "Name not found.", vbExclamation
End If
End Sub 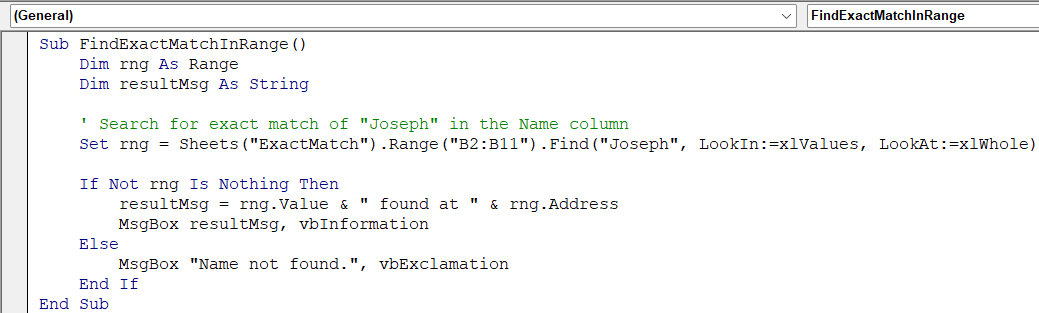
➧ .Find("Joseph Grant") looks for this exact string inside the range
➧ LookAt:=xlWhole ensures the search is for exact matches only (not partial)
➧ If found, the address of the match is returned and shown in a message box
➧ If not found, a message box shows “Name not found.”
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select FindExactMatchInRange, and click Run
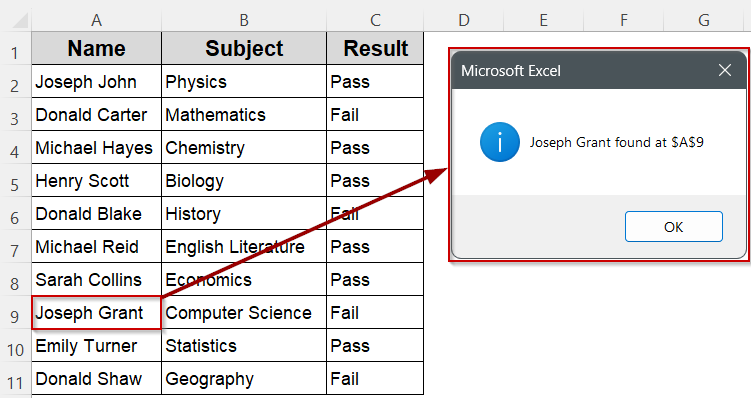
➤ A message box will appear showing the result of the exact match
Perform a Case-Sensitive Exact Match and Replace in VBA
If you want your search to distinguish between uppercase and lowercase letters, VBA provides a way to do that using the MatchCase:=True parameter. This is useful when names like “Donald” and “donald” should be treated differently.
In this method, we’ll locate only the case-sensitive exact matches of “Donald” and replace them with “Henry”.
Steps:
➤ Open Excel and press Alt + F11 to launch the VBA editor
➤ Go to Insert >> Module and paste this code:
Sub CaseSensitiveReplace()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim rng As Range
Dim firstAddr As String
Dim count As Integer
Set ws = Sheets("ExactMatch")
Set rng = ws.Range("B2:B11").Find(What:="Donald", LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, MatchCase:=True)
count = 0
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
firstAddr = rng.Address
Do
rng.Value = "Henry"
count = count + 1
Set rng = ws.Range("B2:B11").FindNext(rng)
Loop While Not rng Is Nothing And rng.Address <> firstAddr
End If
If count > 0 Then
MsgBox count & " case-sensitive match(es) replaced with 'Henry'.", vbInformation
Else
MsgBox "No case-sensitive exact matches found.", vbExclamation
End If
End Sub 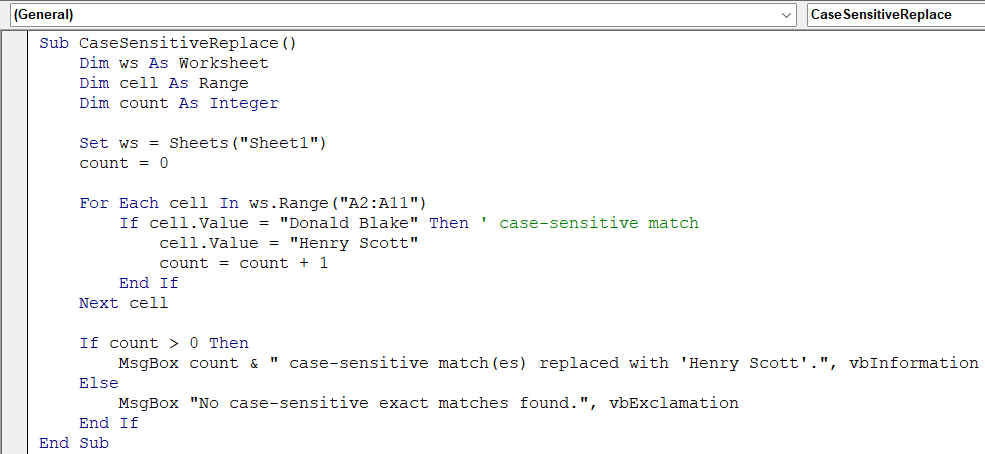
➧ .Find combined with .FindNext allows it to scan through all matching cells
➧ The count variable keeps track of how many names were updated
➧ A final message box displays the result
➤ Go back to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select CaseSensitiveReplace, and click Run
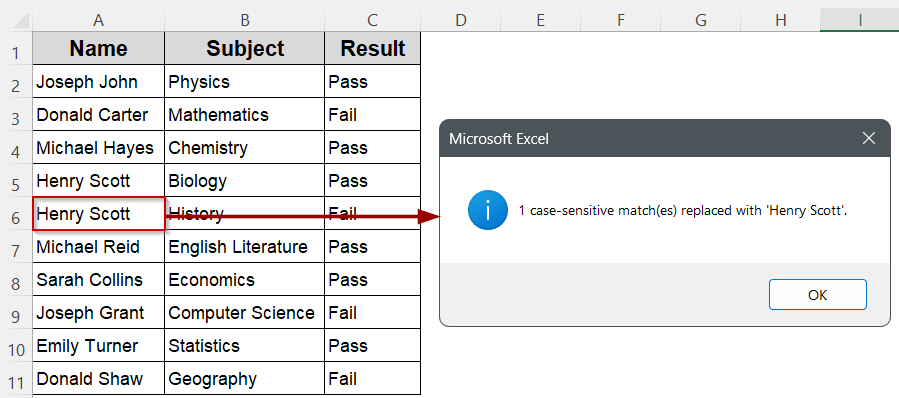
➤ You will receive a message box summarizing how many case-sensitive matches were replaced
Find an Exact Match and Replace It Using VBA
Sometimes you need to correct specific entries in a dataset, for instance, fixing a wrongly typed name. VBA can help find a specific exact match and replace it automatically throughout a given range.
In this method, we’ll search for “Donald Blake” in the name column and replace each exact match with “Henry Scott”.
Steps:
➤ Open Excel and press Alt + F11 to launch the VBA editor
➤ Go to Insert >> Module
➤ Paste this code:
Sub FindAndReplaceExactMatch()
Dim rng As Range
Dim cell As Range
Dim count As Integer
count = 0
' Define the search range
Set rng = Sheets("ExactMatch").Range("B2:B11")
' Loop through each cell to find and replace the full name exactly
For Each cell In rng
If cell.Value = "Donald Blake" Then
cell.Value = "Henry Scott"
count = count + 1
End If
Next cell
' Confirmation message
If count > 0 Then
MsgBox count & " match(es) replaced with 'Henry Scott'.", vbInformation
Else
MsgBox "No exact matches found to replace.", vbExclamation
End If
End Sub 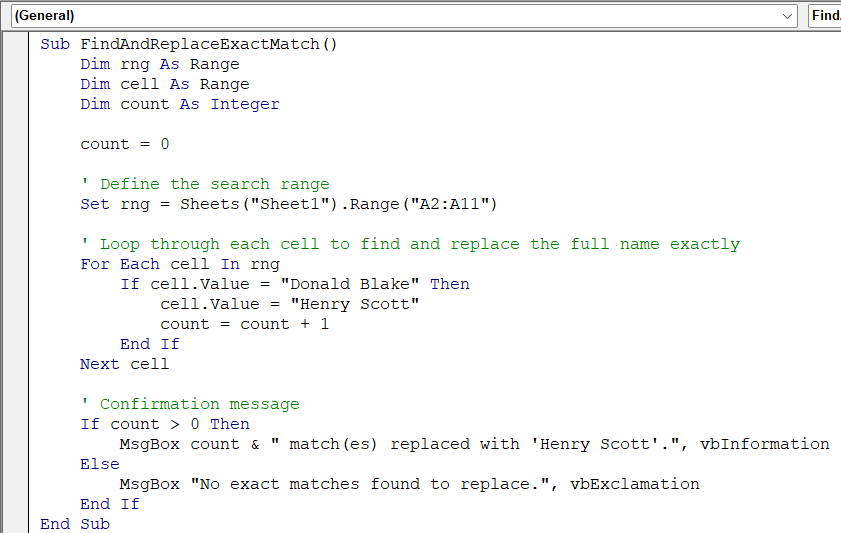
➧ If cell.Value = "Donald" ensures an exact and case-sensitive match
➧ If found, the value is replaced with "Henry"
➧ The count variable tracks how many replacements were made
➧ A message box summarizes the outcome at the end
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select FindAndReplaceExactMatch, and click Run
Use the InStr Function to Identify Exact Matches in VBA
Sometimes you need to check if a specific word or phrase exists within a cell, rather than matching the entire cell content. The VBA function InStr can help you find partial or exact matches inside strings.
In this example, we’ll scan a range of results to find cells containing the word “Pass” and mark their status in an adjacent column.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor
➤ Go to Insert >> Module and paste the following code:
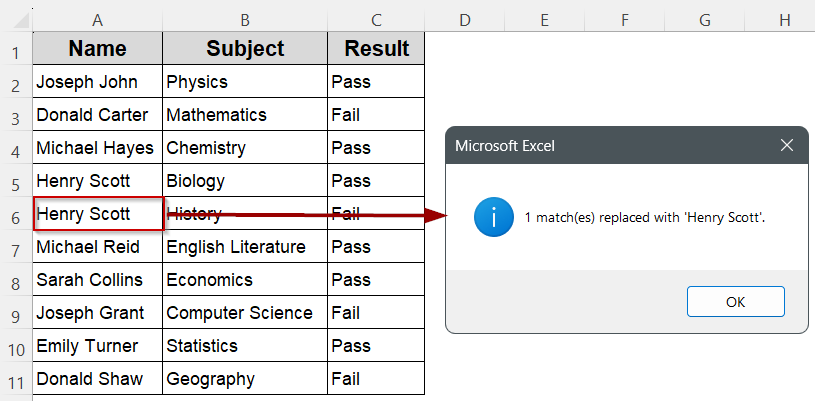
Sub MarkPassedStudents()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Sheets("ExactMatch").Range("C2:C11")
If InStr(cell.Value, "Pass") > 0 Then
cell.Offset(0, 1).Value = "Passed"
Else
cell.Offset(0, 1).Value = ""
End If
Next cell
End Sub 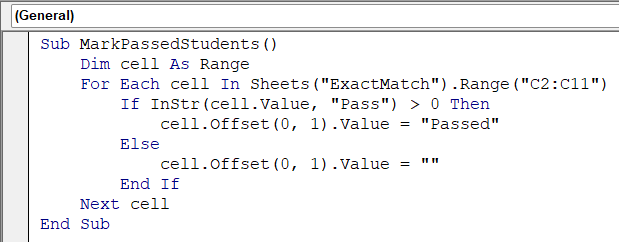
➧ cell.Offset(0, 1) writes the word "Passed" in the next column to the right (column D)
➧ The loop processes every cell from C2 to C11, which corresponds to your Result column
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select MarkPassedStudents, and click Run
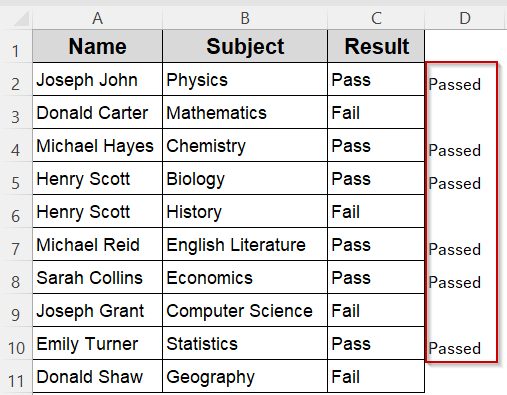
➤ The cells in column D will now show “Passed” next to students who passed their subject
Extract Data Based on an Exact Match Using VBA
When you need to pull out rows matching specific criteria from a dataset, VBA can help automate this by searching for an exact match and copying the matching data to another location.
In this example, we will look for the name “Michael Reid” in the dataset and extract all matching rows to a new area on the worksheet.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor
➤ Go to Insert >> Module
➤ Paste this code:
Sub ExtractMatchingRows()
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim i As Long, outputRow As Long
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Sheets("ExactMatch") ' Update to your actual sheet name
lastRow = ws.Cells(ws.Rows.Count, "B").End(xlUp).Row
outputRow = 2 ' Start output in column E, row 2
For i = 2 To lastRow
If Trim(ws.Cells(i, "B").Value) = "Michael Reid" Then
ws.Range("B" & i & ":D" & i).Copy Destination:=ws.Range("E" & outputRow)
outputRow = outputRow + 1
End If
Next i
If outputRow = 2 Then
MsgBox "No exact matches found for 'Michael Reid'.", vbExclamation
Else
MsgBox "Matching rows for 'Michael Reid' copied to columns E:G.", vbInformation
End If
End Sub 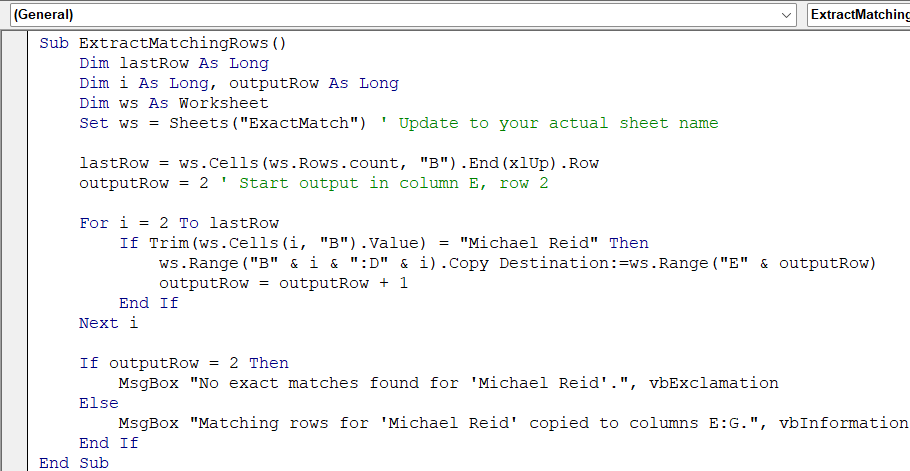
➧ The loop scans column B for the name "Michael Reid"
➧ If found, it copies columns B to D of that row to columns E to G, starting from row 2
➧ outputRow ensures new matches are written to the next available row in the output range
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select ExtractMatchingRows, and click Run
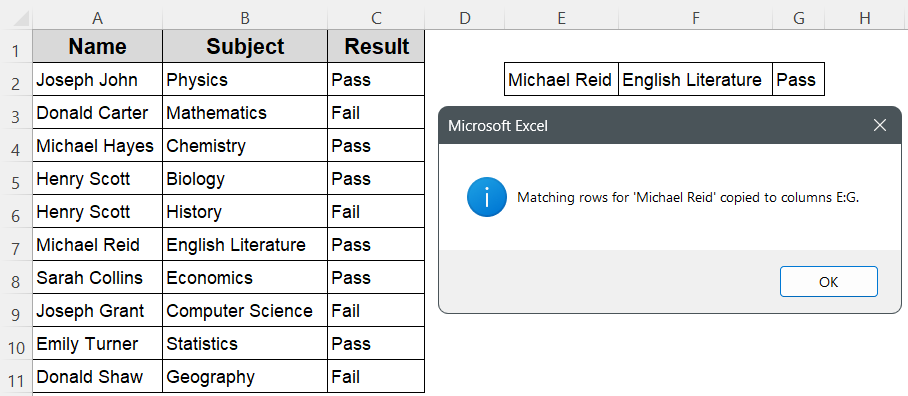
➤ The extracted data for Michael Reid will now appear in columns E to G starting from row 2
Use WorksheetFunction.Match to Find an Exact Match in VBA
Sometimes you want to quickly find the position of an exact match in a range without looping through each cell. VBA’s WorksheetFunction.Match is a powerful way to do this efficiently.
In this example, we’ll search for the exact value “Henry Scott” in a range and display its row number.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor
➤ Go to Insert >> Module
➤ Paste this code:
Sub FindExactMatchUsingMatch()
Dim matchRow As Variant
Dim searchValue As String
Dim searchRange As Range
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Sheets("Sheet1") ' Change to your sheet name
searchValue = "Henry Scott"
Set searchRange = ws.Range("A2:A11") ' Names are in Column A
On Error Resume Next
matchRow = Application.WorksheetFunction.Match(searchValue, searchRange, 0)
On Error GoTo 0
If Not IsError(matchRow) Then
MsgBox searchValue & " found at row " & (matchRow + searchRange.Row - 1)
Else
MsgBox searchValue & " not found in the range."
End If
End Sub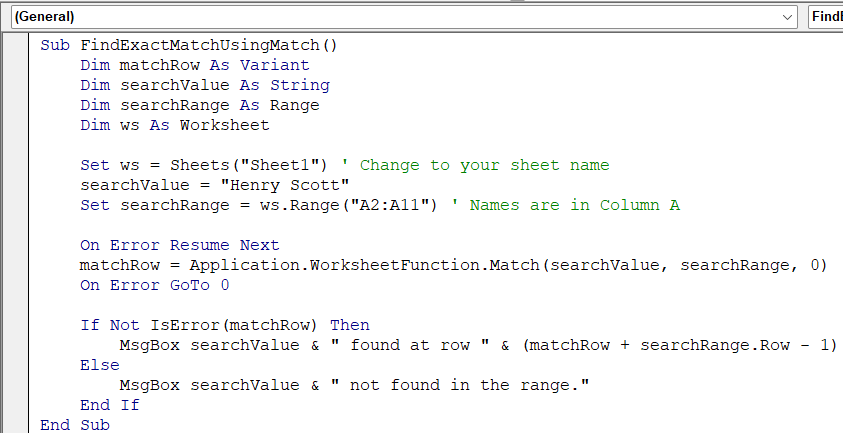
➧ searchRange is set to A2:A11, the range containing names
➧ Match(..., 0) looks for an exact match
➧ If found, it adds the match’s position to the range’s starting row to give the actual row
➧ The result is displayed in a message box
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select FindExactMatchUsingMatch, and click Run
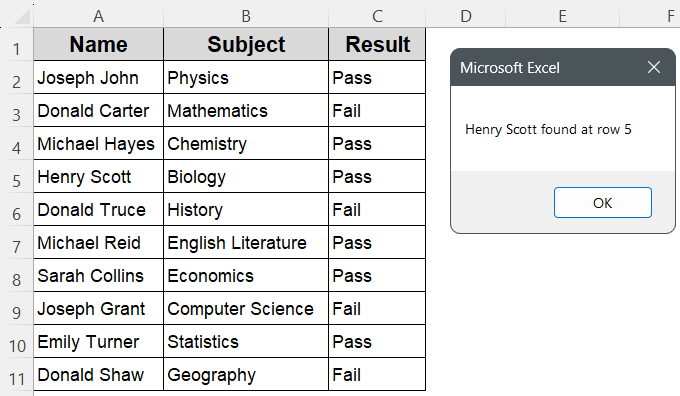
➤ A message box will pop up showing the exact row where “Henry Scott” appears, or it will tell you if it’s not found.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I check for an exact match without looping through each cell?
You can use the .Find method or WorksheetFunction.Match to avoid manual loops. These functions are optimized and much faster when searching through large ranges.
What’s the difference between .Find and InStr in VBA?
.Find is used to search cells in a range for a value, and it can be configured for exact matches with options like LookAt:=xlWhole and MatchCase:=True. InStr is a string function that checks whether a substring exists within another string. It’s ideal when working with individual cell values or text parsing.
How can I make my search case-sensitive in VBA?
Set MatchCase:=True when using the .Find method. For example:
Set rng = Range(“B5:B14”).Find(“Michael James”, LookAt:=xlWhole, MatchCase:=True)
Can I find and replace multiple occurrences of the same value?
Yes, use a loop with .Find and .FindNext to cycle through all matches and replace them. The loop should continue until the search wraps around or returns Nothing.
Wrapping Up
Finding exact matches with VBA in Excel empowers you to search, extract, and manipulate data more dynamically than traditional worksheet functions. Whether you’re checking for a single match, performing case-sensitive searches, replacing entries, or using functions like InStr and WorksheetFunction.Match, VBA gives you the flexibility to automate these tasks with precision.









