Searching for data in Excel is common when verifying entries, locating errors, or gathering related information. Doing this manually or with worksheet formulas can be slow, especially on large sheets. VBA lets you automate and tailor each search so you get the exact result you need.
In this article, you will learn four practical VBA methods to find values in a column. We will cover using Range.Find for the first match, looping through every cell, applying WorksheetFunction.Match to return a row index, and using the Like operator for wildcard searches.
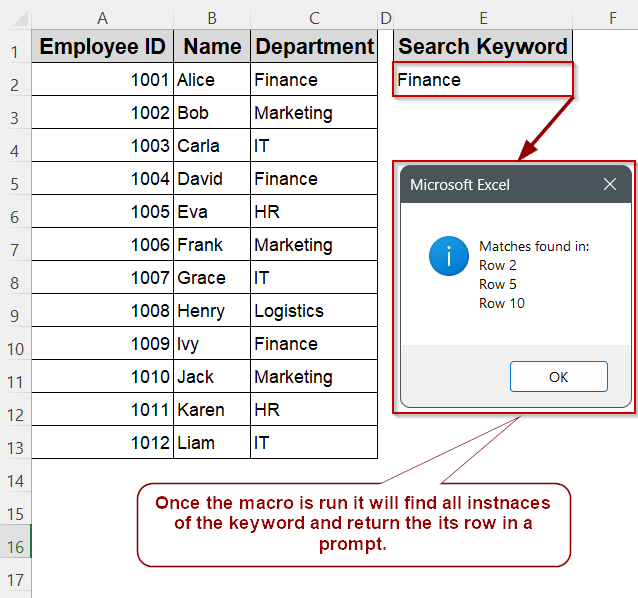
Steps to return every row containing a user‑specified value in column C:
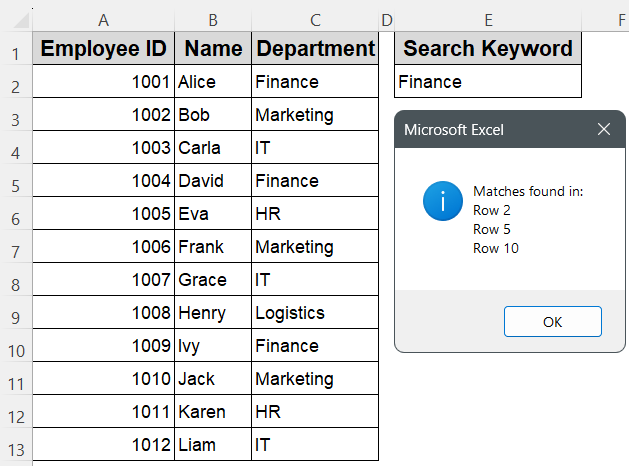
➤ Enter the department to search for (for example, Finance) in cell E2 on Sheet1.
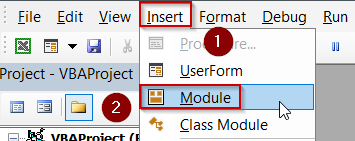
➤ Press Alt + F11 , choose Insert >> Module, and paste the code below:
Sub FindAllMatchesInColumn()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim i As Long
Dim keyword As String
Dim matchList As String
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1") ' Source sheet
keyword = Trim(ws.Range("E2").Value) ' User input
If keyword = "" Then
MsgBox "Please enter a search value in cell E2.", vbExclamation
Exit Sub
End If
lastRow = ws.Cells(ws.Rows.Count, "C").End(xlUp).Row ' Last row in column C
For i = 2 To lastRow ' Skip header in row 1
If LCase(ws.Cells(i, "C").Value) = LCase(keyword) Then
matchList = matchList & "Row " & i & vbCrLf
End If
Next i
If matchList = "" Then
MsgBox "No matches found for '" & keyword & "' in column C.", vbInformation
Else
MsgBox "Matches found in:" & vbCrLf & matchList, vbInformation
End If
End Sub
➤ The macro reads the search term from E2 and trims extra spaces.
➤ lastRow locates the bottom of the data in column C, ensuring the loop covers every row.
➤ Inside the loop, each cell’s value is compared to the keyword in a case‑insensitive manner.
➤ All matching row numbers are gathered into matchList and displayed in a message box.
➤ Run the macro with Alt + F8 >> FindAllMatchesInColumn >> Run to list every matching row.
Find the First Match in a Column Using Range.Find
When you only need the first occurrence of a value, such as the first Employee ID that matches a user entry, Range.Find is the fastest approach. It returns the exact cell that holds the match, which you can then select, read, or format.
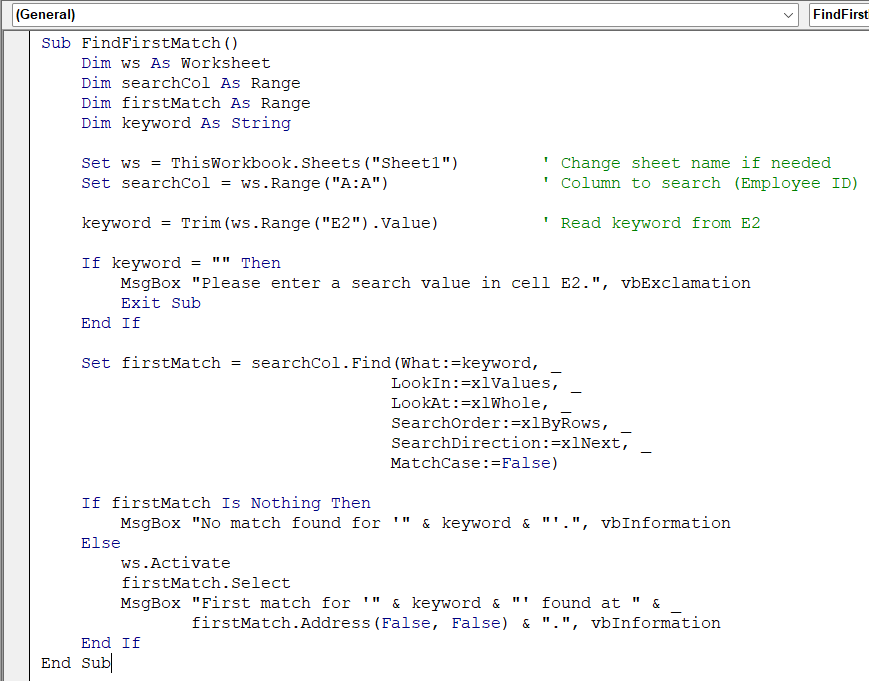
In this method, the user types a keyword in cell E2 on Sheet1. The macro looks for that keyword in column A (Employee ID) and reports the address of the first match.
Steps:
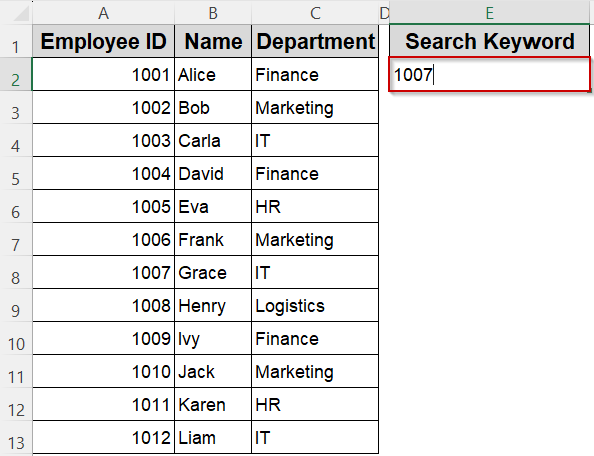
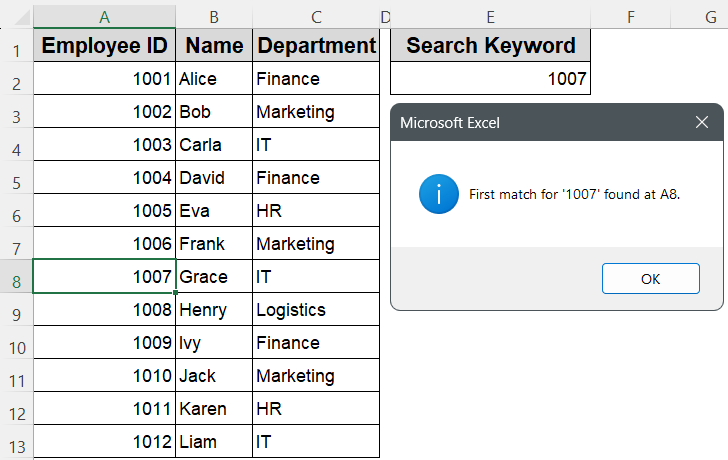
➤ Enter your search keyword (for example, 1007) in cell E2 on Sheet1
➤ Press Alt + F11 , choose Insert >> Module.
➤ Paste this code:
Sub FindFirstMatch()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim searchCol As Range
Dim firstMatch As Range
Dim keyword As String
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1") ' Change sheet name if needed
Set searchCol = ws.Range("A:A") ' Column to search (Employee ID)
keyword = Trim(ws.Range("E2").Value) ' Read keyword from E2
If keyword = "" Then
MsgBox "Please enter a search value in cell E2.", vbExclamation
Exit Sub
End If
Set firstMatch = searchCol.Find(What:=keyword, _
LookIn:=xlValues, _
LookAt:=xlWhole, _
SearchOrder:=xlByRows, _
SearchDirection:=xlNext, _
MatchCase:=False)
If firstMatch Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "No match found for '" & keyword & "'.", vbInformation
Else
ws.Activate
firstMatch.Select
MsgBox "First match for '" & keyword & "' found at " & _
firstMatch.Address(False, False) & ".", vbInformation
End If
End Sub
➧ Set searchCol = ws.Range("A:A") limits the search to the Employee ID column
➧ searchCol.Find searches the column for an exact match (LookAt:=xlWhole) and returns the first occurrence.
➧ If firstMatch is Nothing, no match was found. Otherwise, the macro selects the cell and shows its address in a message box.
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select FindFirstMatch, and click Run.
➤ The macro highlights the first cell in column A that matches the keyword in E2 and displays its address.
Search for All Matches in a Column Using a Loop
Sometimes you need to find not just the first match, but all occurrences of a value in a column. For example, you might want to identify every employee from a certain department listed multiple times. This method loops through each cell in the target column and collects all matches.
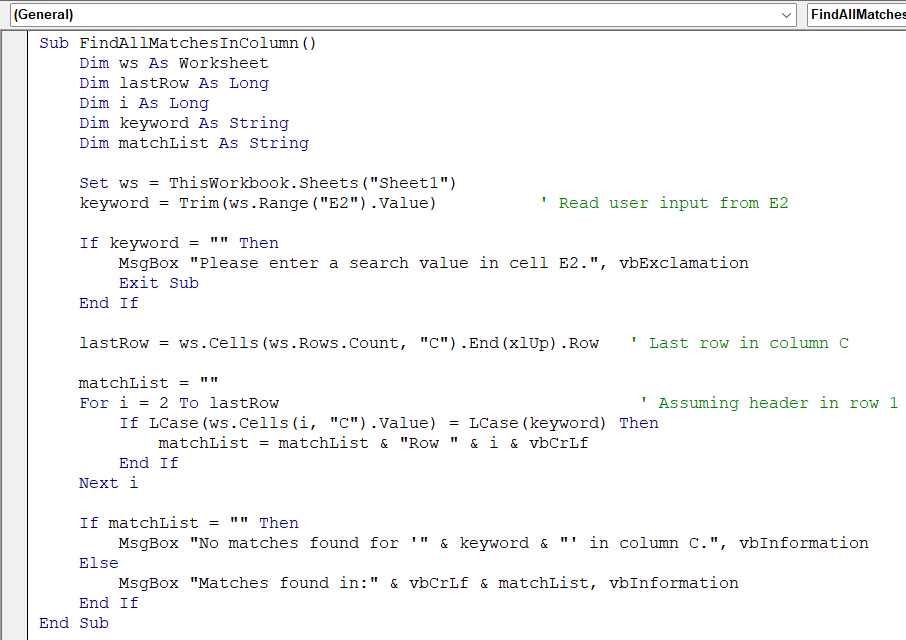
In this case, the user enters a search keyword in cell E2, and the macro scans column C (Department). It lists the row numbers of all matching entries in a message box.
Steps:
➤ Type the department you want to search for (e.g., Finance) into cell E2 on Sheet1.
➤ Press Alt + F11 , choose Insert >> Module, and paste this code:
Sub FindAllMatchesInColumn()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim i As Long
Dim keyword As String
Dim matchList As String
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1")
keyword = Trim(ws.Range("E2").Value) ' Read user input from E2
If keyword = "" Then
MsgBox "Please enter a search value in cell E2.", vbExclamation
Exit Sub
End If
lastRow = ws.Cells(ws.Rows.Count, "C").End(xlUp).Row ' Last row in column C
matchList = ""
For i = 2 To lastRow ' Assuming header in row 1
If LCase(ws.Cells(i, "C").Value) = LCase(keyword) Then
matchList = matchList & "Row " & i & vbCrLf
End If
Next i
If matchList = "" Then
MsgBox "No matches found for '" & keyword & "' in column C.", vbInformation
Else
MsgBox "Matches found in:" & vbCrLf & matchList, vbInformation
End If
End Sub
➧ lastRow dynamically finds the last used row in column C.
➧ The loop compares every cell in column C to the keyword (case-insensitive).
➧ Matching row numbers are stored in matchList and shown in a message box.
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , choose FindAllMatchesInColumn, and click Run.
➤ You’ll get a message showing which rows match the department name entered in E2.
Retrieve the Row Number with WorksheetFunction.Match
Sometimes you do not need the cell itself; you only need to know which row contains a value. Using WorksheetFunction.Match, VBA can return the row index of an exact match in a column, making it ideal for quick lookups or driving other automation.
In this method, the user types a keyword in cell E2 on Sheet1. The macro searches column B (Name) for an exact match and reports the worksheet row number.
Steps:
➤ Enter the employee name you want to find (for example, Grace) into cell E2 on Sheet1.
➤ Press Alt + F11 , choose Insert >> Module, and paste this code:
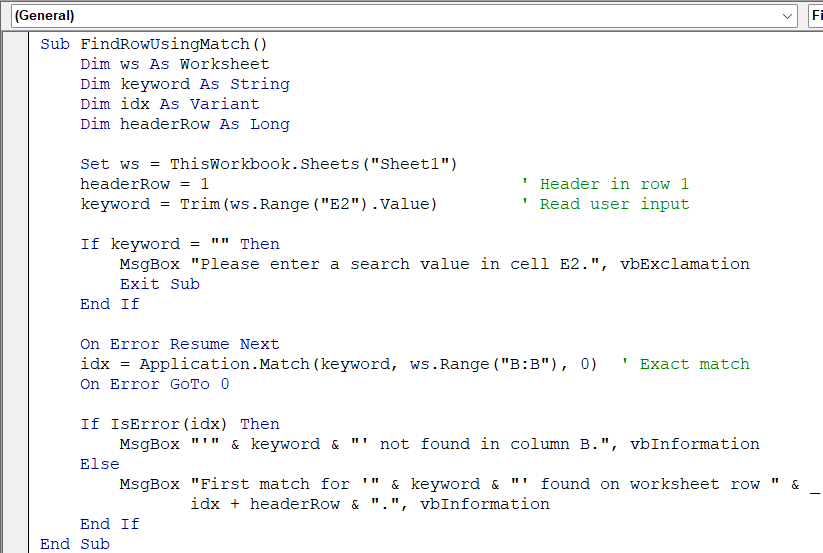
Sub FindRowUsingMatch()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim keyword As String
Dim idx As Variant
Dim headerRow As Long
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1")
headerRow = 1 ' Header in row 1
keyword = Trim(ws.Range("E2").Value) ' Read user input
If keyword = "" Then
MsgBox "Please enter a search value in cell E2.", vbExclamation
Exit Sub
End If
On Error Resume Next
idx = Application.Match(keyword, ws.Range("B:B"), 0) ' Exact match
On Error GoTo 0
If IsError(idx) Then
MsgBox "'" & keyword & "' not found in column B.", vbInformation
Else
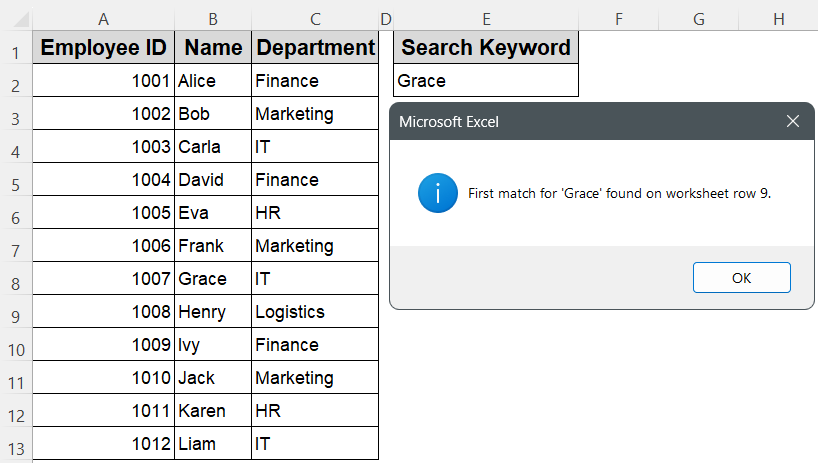
MsgBox "First match for '" & keyword & "' found on worksheet row " & _
idx + headerRow & ".", vbInformation
End If
End Sub
➧ Application.Match(keyword, ws.Range("B:B"), 0) searches column B for an exact match; 0 means exact lookup.
➧ If Match fails, it returns an error value, which triggers the “not found” message.
➧ If successful, idx is the relative row number within the range; adding headerRow converts it to the absolute worksheet row.
➧ The macro displays the row number where the first match is located.
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select FindRowUsingMatch, and click Run.
➤ A message box shows the worksheet row containing the employee name typed in E2.
Search a Column and Return the Entire Matching Row
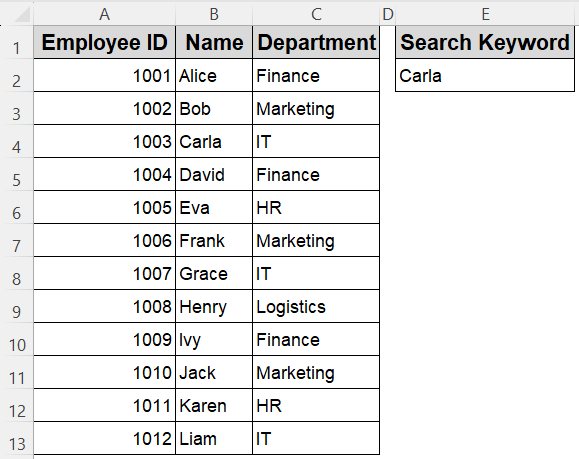
In some automation tasks, finding a match is just the start, you often need to extract the full row where that match occurs. This method searches for a user-specified value in column B (Employee Name), and if found, copies the entire matching row to another sheet for further analysis or reporting.
The user provides the search value in cell E2 on Sheet1. The macro then copies the full row to Sheet2, starting from the next empty row.
Steps:
➤ In Sheet1, type the keyword you want to search (e.g., Carla) into cell E2.
➤ Press Alt + F11 , choose Insert >> Module, and paste the following code:
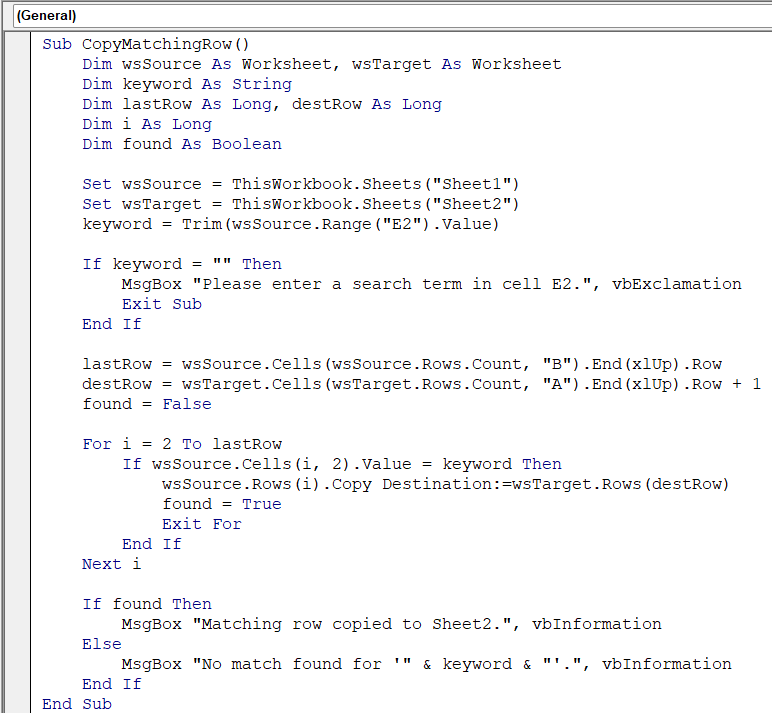
Sub CopyMatchingRow()
Dim wsSource As Worksheet, wsTarget As Worksheet
Dim keyword As String
Dim lastRow As Long, destRow As Long
Dim i As Long
Dim found As Boolean
Set wsSource = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1")
Set wsTarget = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet2")
keyword = Trim(wsSource.Range("E2").Value)
If keyword = "" Then
MsgBox "Please enter a search term in cell E2.", vbExclamation
Exit Sub
End If
lastRow = wsSource.Cells(wsSource.Rows.Count, "B").End(xlUp).Row
destRow = wsTarget.Cells(wsTarget.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row + 1
found = False
For i = 2 To lastRow
If wsSource.Cells(i, 2).Value = keyword Then
wsSource.Rows(i).Copy Destination:=wsTarget.Rows(destRow)
found = True
Exit For
End If
Next i
If found Then
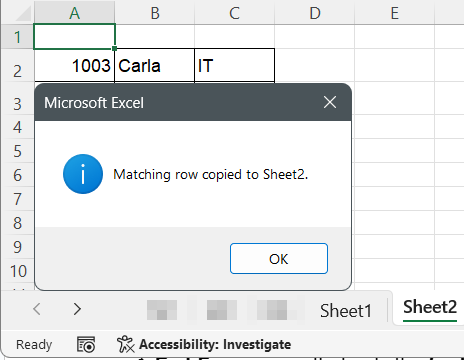
MsgBox "Matching row copied to Sheet2.", vbInformation
Else
MsgBox "No match found for '" & keyword & "'.", vbInformation
End If
End Sub
➧ The macro scans column B from row 2 onward (excluding header) using a loop.
➧ On finding an exact match, it copies the entire row to the next available row in Sheet2.
➧ If no match is found, the user is notified via message box.
➧ Exit For ensures that only the first match is copied.
➤ Go back to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select CopyMatchingRow, and click Run.
➤ If a match is found, the entire row will appear in Sheet2 for your review or further use.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I find a value in a column using VBA?
Use Find method: Range(“B:B”).Find(What:=searchValue) locates the first match in column B. It returns a Range object if found, or Nothing otherwise.
How can I search for a value and return its row number?
Use Match: Application.Match(value, Range(“B:B”), 0) returns the row index of the first match. Combine with .Row if using the Find method.
How to copy a row when a match is found in a specific column?
Loop through the column, compare cell values to the search term, and use .EntireRow.Copy to move the row to another sheet or location.
Can I make the search case-insensitive in VBA?
Yes, by converting both cell value and search term to lowercase with LCase(), you can perform a case-insensitive comparison inside the loop.
Wrapping Up
Finding values in a column using VBA can save you a lot of time, especially when working with large datasets or automating repetitive lookup tasks. In this article, you learned four practical VBA techniques to search for a value based on user input in cell E2. Whether you prefer using the Find method, looping with If, or capturing row locations for further action, each approach has its strengths depending on your scenario.