When working with Excel, sometimes we need to ensure whether a file exists before running a macro or processing data. Of course, checking the files manually can be time-consuming, that’s especially if you have many folders or files.
In such cases, Excel VBA helps to automate the process. That’s why in today’s article, we will walk you through four practical methods to check if a file exists with Excel VBA. It includes checking with the Dir command, using the FileSystemObject, verifying files and folders with GetAttr, and finding multiple files using Dir with wildcards.
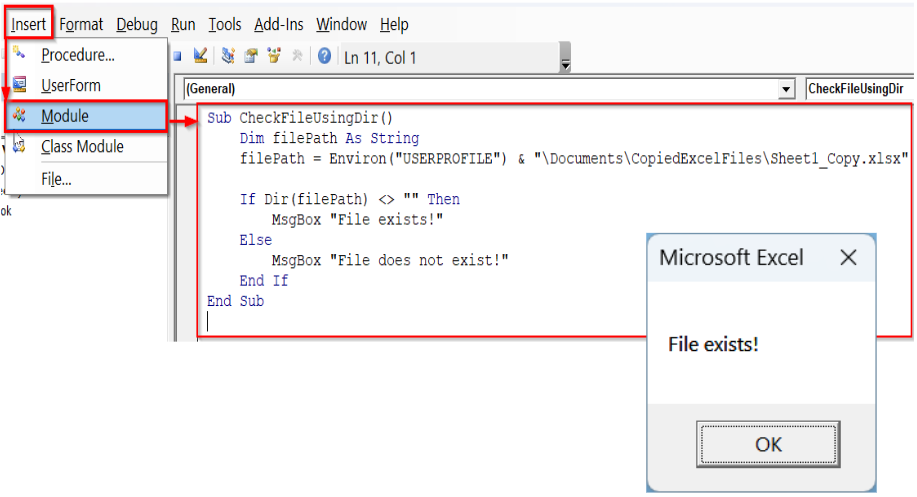
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
➤ In the VBA editor window, click Insert >> Module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code.
Sub CheckFileUsingDir()
Dim filePath As String
filePath = Environ("USERPROFILE") & "\Documents\CopiedExcelFiles\Sheet1_Copy.xlsx"
If Dir(filePath) <> "" Then
MsgBox "File exists!"
Else
MsgBox "File does not exist!"
End If
End Sub➤ Run the code.
➤ The VBA macro will display a message box showing whether the specified file exists or not in the folder.
Using the DIR Command to Check If a File Exists
The Dir function is the simplest and fastest way in Excel VBA to check if a file exists. This command doesn’t require extra objects or references. When you run the VBA with the DIR command, a message box will show whether the file exists or not.
Now, we have a folder located in the following location:
C:\Users\HP USER\Documents\CopiedExcelFiles
This folder, CopiedExcelFiles, contains three files: Sheet1_Copy, Sheet2_Copy, and Sheet3_Copy.
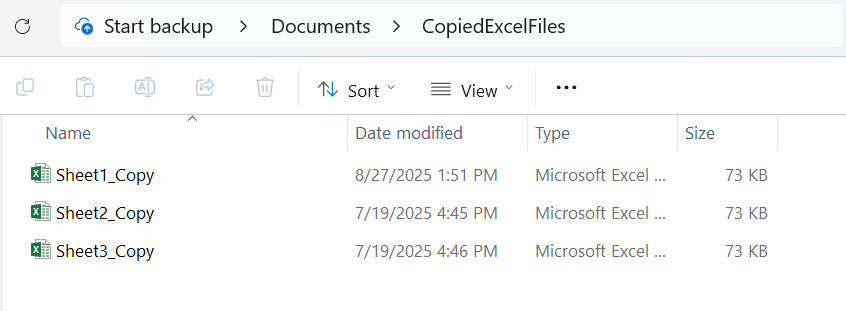
Now we will use VBA using the DIR command to check if the file called Sheet1_Copy exists in this folder.
Syntax:
Dir(pathname, [attributes])
➥ pathname: full path of the file you want to check.
➥ attributes: optional, not required for basic file checks.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
➤ Go to Insert >> Module.
➤ In the new module, insert the following VBA code.
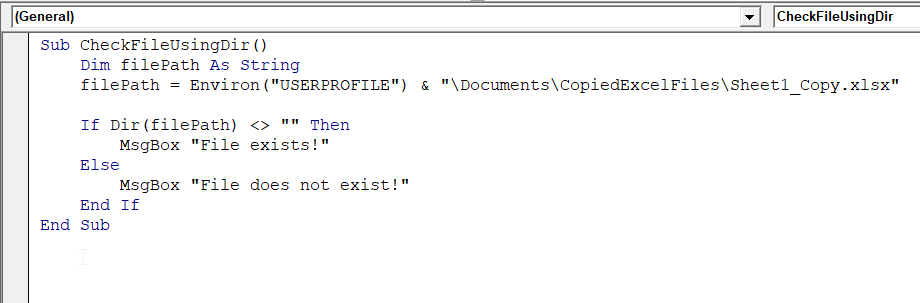
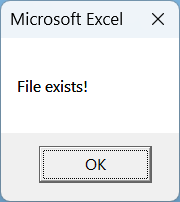
Sub CheckFileUsingDir()
Dim filePath As String
filePath = Environ("USERPROFILE") & "\Documents\CopiedExcelFiles\Sheet1_Copy.xlsx"
If Dir(filePath) <> "" Then
MsgBox "File exists!"
Else
MsgBox "File does not exist!"
End If
End Sub
Note:
In this VBA code,
➥ Replace the file name, Sheet1_Copy.xlsx, with your own file name.
➥ Replace the folder path, Environ(“USERPROFILE”) & “\Documents\CopiedExcelFiles\” with your folder path if it’s different.
For example,
If your file is Report.xlsx in C:\Users\HP USER\Documents\Reports\, update filePath accordingly:
filePath = “C:\Users\HP USER\Documents\Reports\Report.xlsx”
➤ Run the macro either by pressing F5 or going to Run >> Run Sub/UserForm
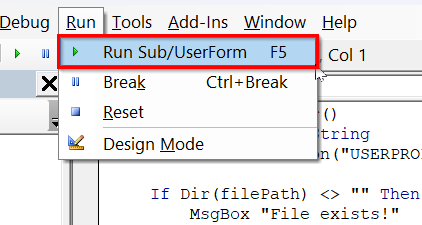
➤ After running the code, a message box will show whether the file exists or not.
➥ filePath: It stores the full path of the file we want to check.
➥ Dir(filePath): It returns the file name if it exists, otherwise it returns to empty string.
➥ If statement: It triggers a message box.
Check If a File Exists Using the FileSystemObject Command
The FileSystemObject (FSO) method allows you to check if a file exists in a folder. It is more versatile than the DIR command. That’s because with it you can also work with folders, check, copy, or delete files. Here also, a message box will show whether the file exists or not after running the VBA with the FileSystemObject command.
Syntax:
Object.FileExists(path)
➥ Object: the FileSystemObject you create in VBA.
➥ path: full path of the file you want to check.
➥ Returns True if the file exists, False if it doesn’t.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor.
➤ Insert a new module.
➤ In the new module, copy and paste the following VBA code.
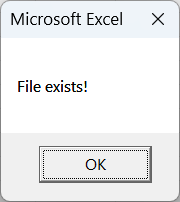
Sub CheckFileUsingFSO()
Dim fso As Object
Dim filePath As String
' Set your file path
filePath = Environ("USERPROFILE") & "\Documents\CopiedExcelFiles\Sheet1_Copy.xlsx"
' Create FileSystemObject
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
' Check if the file exists
If fso.FileExists(filePath) Then
MsgBox "File exists!"
Else
MsgBox "File does not exist!"
End If
End Sub
Note:
In the VBA macro,
➥ Sheet1_Copy.xlsx: Replace the file name with your own.
➥ Environ(“USERPROFILE”) & “\Documents\CopiedExcelFiles\”: Replace the folder path with your folder path.
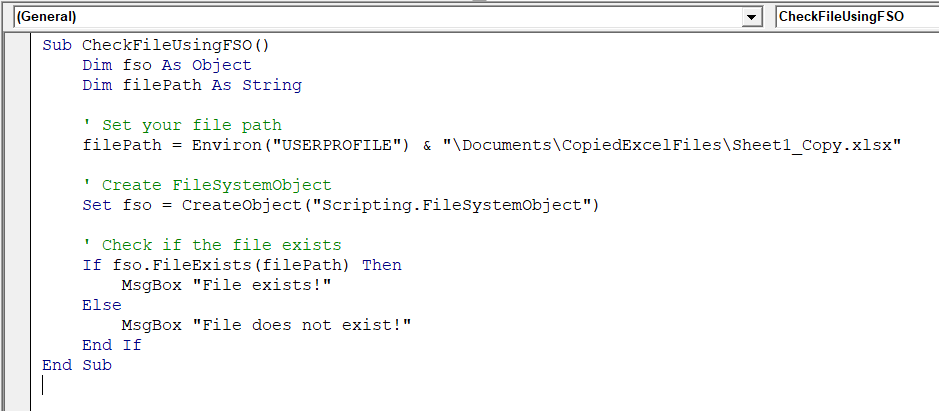
➤ Run the macro either by pressing F5 or going to Run >> Run Sub/UserForm
➤ The code will return True if the file exists and False if it doesn’t.
➥ filePath: It stores the full path of the file to check.
➥ CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject"): It creates the FSO object
➥ fso.FileExists(filePath): It returns True if the file exists, False if it doesn’t.
➥ If statement: It triggers the message box showing the result.
Using the GetAttr Command to Check Both File/Folder Existence
You can check whether a file or folder exists using the GetAttr function in Excel VBA. The method can be useful when you want to use a single method for checking the existence of both a file and a folder. The VBA with the GetAttr command also shows a message box telling whether a file or folder exists or not.
Syntax:
GetAttr(pathname)
➥pathname: full path of the file or folder.
➥Returns attributes if the file/folder exists.
➥ Generates an error if it doesn’t exist, so we handle it using On Error Resume Next
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
➤ In the VBA editor, insert a new module.
➤ In the new module, copy and paste the following VBA code.
Sub CheckFileOrFolderUsingGetAttr()
Dim filePath As String
Dim folderPath As String
' File path example
filePath = Environ("USERPROFILE") & "\Documents\CopiedExcelFiles\Sheet1_Copy.xlsx"
' Folder path example
folderPath = Environ("USERPROFILE") & "\Documents\CopiedExcelFiles"
On Error Resume Next ' Prevent errors if file/folder doesn't exist.
' Check file existence
If Err.Number = 0 And Dir(filePath) <> "" Then
MsgBox "File exists!"
Else
MsgBox "File does not exist!"
Err.Clear
End If
' Check folder existence
If (GetAttr(folderPath) And vbDirectory) = vbDirectory Then
MsgBox "Folder exists!"
Else
MsgBox "Folder does not exist!"
End If
On Error GoTo 0 ' Reset error handling
End Sub
Note:
In the VBA code,
➥ Replace the file name, Sheet1_Copy.xlsx, with your own file.
➥ Replace the folder path, Environ(“USERPROFILE”) & “\Documents\CopiedExcelFiles” with your folder path.
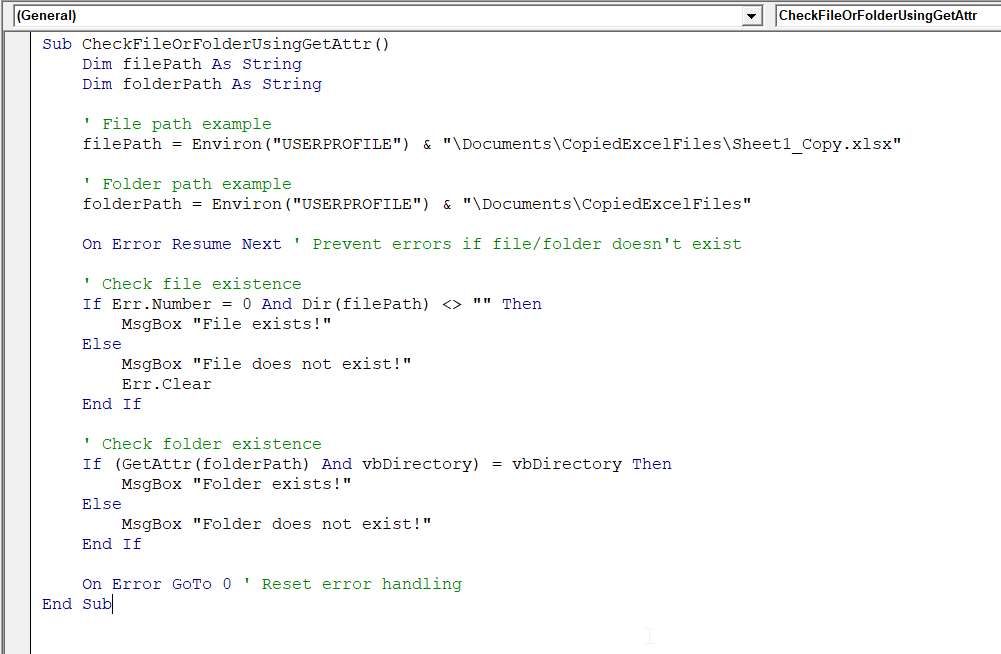
➤ Run the code either by pressing F5 or by Run >> Run Sub/UserForm.
➤ Once you run the code, message boxes will show whether your file and folder exist or not.
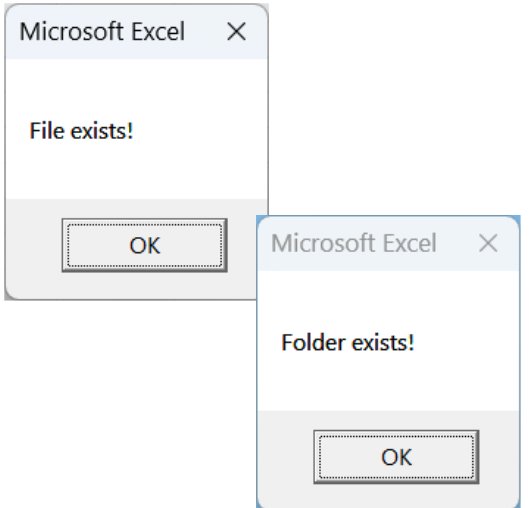
➥ filePath: It stores the file to check.
➥ folderPath: It stores the folder to check.
➥ On Error Resume Next: It prevents the macro from stopping if the file/folder doesn’t exist.
➥ Dir(filePath) <> "": It checks if the file exists.
➥ (GetAttr(folderPath) And vbDirectory) = vbDirectory: It checks if the folder exists.
➥ Message boxes show the results separately for the file and the folder.
Check If Multiple Files Exist Using the DIR Command with Wildcards
If you want to check if multiple files exist, you can use the DIR command with wildcards like * or ?. It is a useful method when you want to find whether all the files in a folder exist or not. Here, a message box or loop output will show which files exist.
Syntax:
Dir(pathname, [attributes])
➥ pathname: folder path with file pattern, e.g., “C:\Folder\*.xlsx”.
➥ Wildcards:
● * – matches any number of characters
● ? – matches a single character
➥ Returns the first matching file, then uses a loop to get all matches.
Steps:
➤ Open the VBA editor.
➤ Insert a new module.
➤ In the new module, copy and paste the following VBA code. The macro automatically loops through all matching files in the folder.
Sub CheckMultipleFilesUsingDir()
Dim folderPath As String
Dim fileName As String
' Folder containing files
folderPath = Environ("USERPROFILE") & "\Documents\CopiedExcelFiles\"
' Use wildcard to find all Excel files starting with "Sheet"
fileName = Dir(folderPath & "Sheet*.xlsx")
If fileName = "" Then
MsgBox "No matching files found!"
Else
Do While fileName <> ""
MsgBox "File exists: " & fileName
fileName = Dir ' Get next matching file
Loop
End If
End Sub
Note:
In the VBA macro,
➥ folderPath = “C:\Users\HP USER\Documents\CopiedExcelFiles\”: Change the file path with your actual file path.
➥ Change the file pattern according to your needs.
➥ “Sheet*.xlsx”: It looks for all Excel files starting with the word Sheet. Change according to your file pattern.
➥ “*.xls*”: It looks for all Excel files regardless of the name.
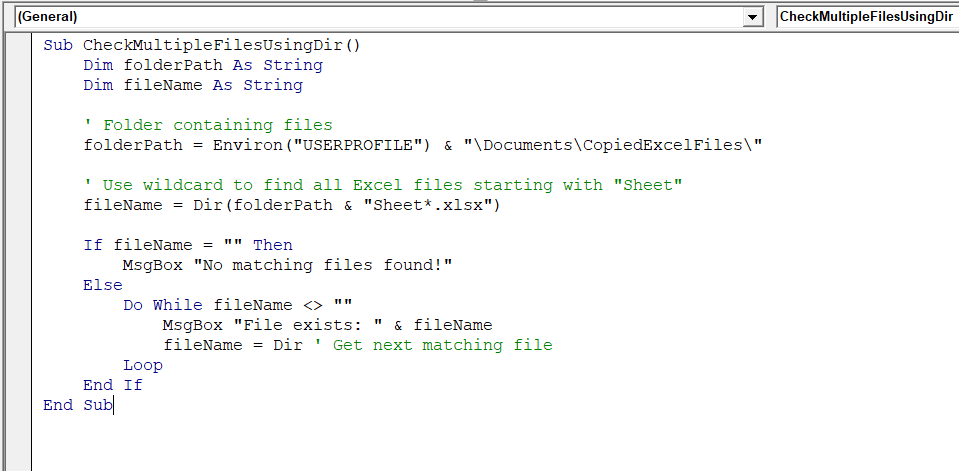
➤ Run the VBA code.
➤ It will show a loop of results showing whether all the files in the folder exist or not.
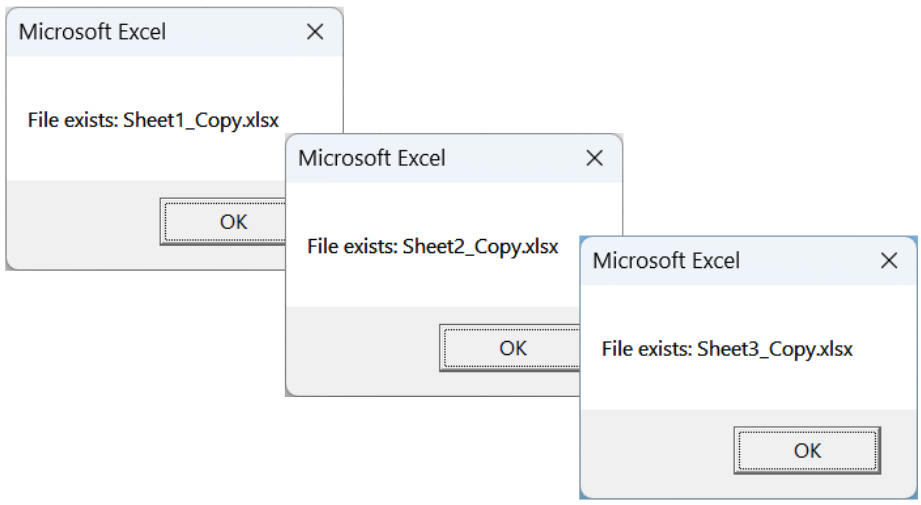
➥ folderPath: It stores the folder to search.
➥ Dir(folderPath & "Sheet*.xlsx"): It finds the first file that starts with "Sheet" and ends with .xlsx.
➥ The Do While loop: The loop continues to get all matching files.
➥ Each file found triggers a message box showing the file name.
➥ If no files match, a message box will show “No matching files found!”
Frequently Asked Questions
How to check if a file exists in a folder and its subfolders with Excel VBA?
You can use the FileSystemObject to check whether a file exists in the subfolder. For example, insert the following VBA code and run it. It will return True if the file is found in the folder or any subfolder.
Function FileExistsInSubFolders(folderPath As String, fileName As String) As Boolean
Dim fso As Object, folder As Object, subFolder As Object, file As Object
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set folder = fso.GetFolder(folderPath)
'Check files in the main folder
For Each file In folder.Files
If LCase(file.Name) = LCase(fileName) Then
FileExistsInSubFolders = True
Exit Function
End If
Next file
'Loop through subfolders
For Each subFolder In folder.SubFolders
If FileExistsInSubFolders(subFolder.Path, fileName) Then
FileExistsInSubFolders = True
Exit Function
End If
Next subFolder
End Function
How to get a list of all files in a folder and subfolders using Excel VBA?
You can use VBA with the FileSystemObject (FSO) to loop through all folders and subfolders and list the files in a worksheet. For example, insert the following VBA code and run it.
Sub ListAllFiles()
Dim fso As Object, folder As Object, subFolder As Object, file As Object
Dim ws As Worksheet, i As Long
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set folder = fso.GetFolder("C:\Users\HP USER\Documents\")
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(1)
i = 1
Call ListFilesInFolder(folder, ws, i)
End Sub
Sub ListFilesInFolder(fld As Object, ws As Worksheet, ByRef i As Long)
Dim subFld As Object, f As Object
For Each f In fld.Files
ws.Cells(i, 1).Value = f.Path
i = i + 1
Next f
For Each subFld In fld.SubFolders
ListFilesInFolder subFld, ws, i
Next subFld
End Sub
How to get the file name in a folder in VBA?
Use the Dir function in VBA to get file names from a folder. The following code will list all file names from the folder in your worksheet.
Sub GetFileNames()
Dim filePath As String
Dim fileName As String
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim i As Long
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(1)
filePath = "C:\Users\HP USER\Documents\"
i = 1
fileName = Dir(filePath & "*.*") 'Get first file
Do While fileName <> ""
ws.Cells(i, 1).Value = fileName
i = i + 1
fileName = Dir 'Get next file
Loop
End Sub
Wrapping Up
In this quick tutorial, we learnt how to check if files exist in Excel using different VBA methods. These methods help you automate file checks quickly and accurately. Feel free to download our sample workbook and try these macros by yourself. Let us know how these VBA solutions have made managing and organizing your Excel data faster and more efficient.


