Sorting helps make your data easier to analyze, especially when you’re working with large datasets. While Excel allows basic sorting through the ribbon, automating multi-column sorts with VBA offers greater efficiency and repeatability, useful in reports or dashboards.
In this article, you’ll learn a simple and effective VBA method to sort multiple columns in Excel. We’ll walk through a practical example where we sort a student dataset first by class, then by score, just as you’d need in real-world reporting or school administration tasks.
Steps to sort your Excel dataset first by one column (such as Class) and then by another (such as Score):
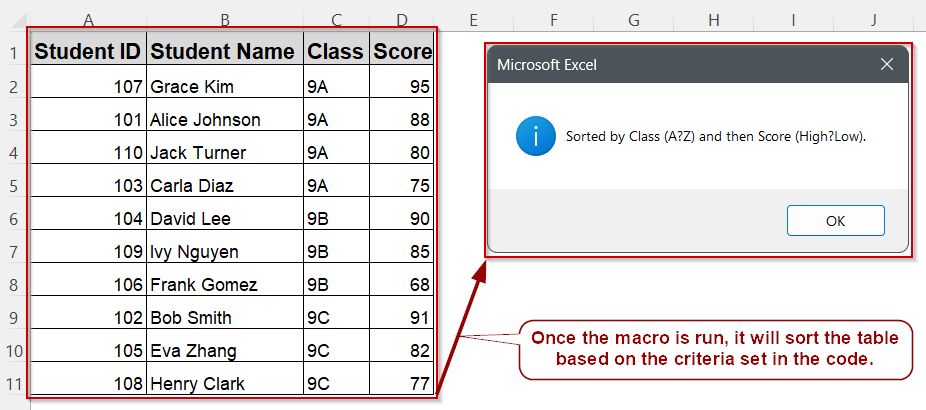
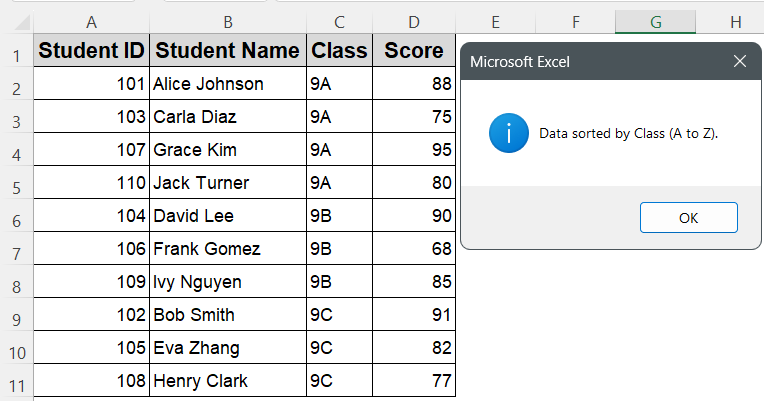
➤ Go to your worksheet and make sure your dataset includes headers: Student ID, Student Name, Class, Score (in columns A to D)
➤ Press Alt + F11 , choose Insert >> Module, and paste the code below:
Sub SortByMultipleColumns()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim dataRange As Range
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1") ' Adjust sheet name if needed
Set dataRange = ws.Range("A1:D11") ' Adjust to fit your dataset range
With ws.Sort
.SortFields.Clear
.SortFields.Add Key:=ws.Range("C2:C11"), _
SortOn:=xlSortOnValues, Order:=xlAscending, DataOption:=xlSortNormal
.SortFields.Add Key:=ws.Range("D2:D11"), _
SortOn:=xlSortOnValues, Order:=xlDescending, DataOption:=xlSortNormal
.SetRange dataRange
.Header = xlYes
.MatchCase = False
.Orientation = xlTopToBottom
.Apply
End With
MsgBox "Sorted by Class (A to Z) and then Score (High to Low).", vbInformation
End Sub➤ The macro first clears any existing sort rules and then adds two sort by Class (Column C) in ascending order, and sort by Score (Column D) in descending order
➤ .SetRange ensures the sort applies to the entire dataset, including headers
➤ A message box confirms the sort is complete
➤ To run the macro, go back to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select SortByMultipleColumns, and click Run
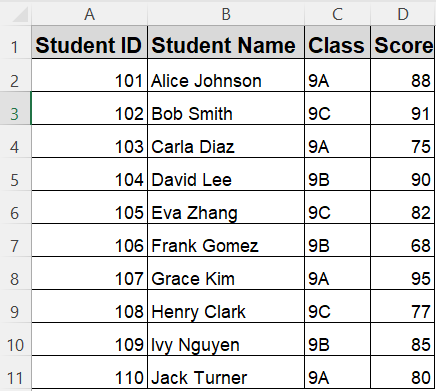
➤ Your dataset will be sorted first by Class and then by Score within each class
Sort by a Single Column Using VBA
When you only need to organise data by one field, a single‑column sort is the quickest solution. This also allows you to have more control over the sorting process by sorting each column one by one.
In this method, we will sort the dataset on Sheet1 by the Class column (column C) in ascending order.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 , choose Insert >> Module.
➤ Paste this code:
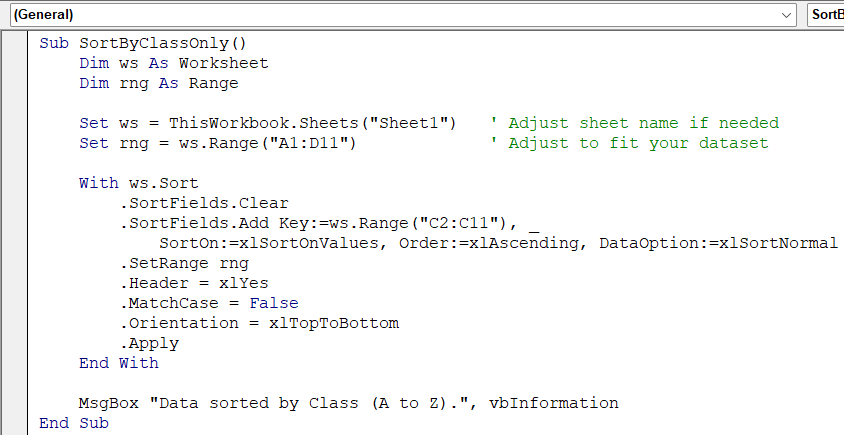
Sub SortByClassOnly()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim rng As Range
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1") ' Adjust sheet name if needed
Set rng = ws.Range("A1:D11") ' Adjust to fit your dataset
With ws.Sort
.SortFields.Clear
.SortFields.Add Key:=ws.Range("C2:C11"), _
SortOn:=xlSortOnValues, Order:=xlAscending, DataOption:=xlSortNormal
.SetRange rng
.Header = xlYes
.MatchCase = False
.Orientation = xlTopToBottom
.Apply
End With
MsgBox "Data sorted by Class (A to Z).", vbInformation
End Sub➧ .SetRange rng applies the sort to the full data block including headers.
➧ .Header = xlYes keeps the header row at the top.
➧ The message box confirms completion.
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select SortByClassOnly, and click Run.
➤ Your data is now sorted by Class in ascending order.
Sorting Multiple Columns Using VBA
In many Excel tasks, sorting by a single column isn’t enough. You might need to sort a dataset first by one column, and then by another, for example, by Class and then by Score. Doing this manually every time can be tedious. With VBA, you can perform a multi-level sort quickly and consistently.
In this example, we will sort a dataset on Sheet1 that contains columns: Student ID, Student Name, Class, and Score. The macro will sort first by the Class column (ascending), and then by the Score column (descending), keeping the dataset neatly ordered.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 , choose Insert >> Module.
➤ Paste this code:
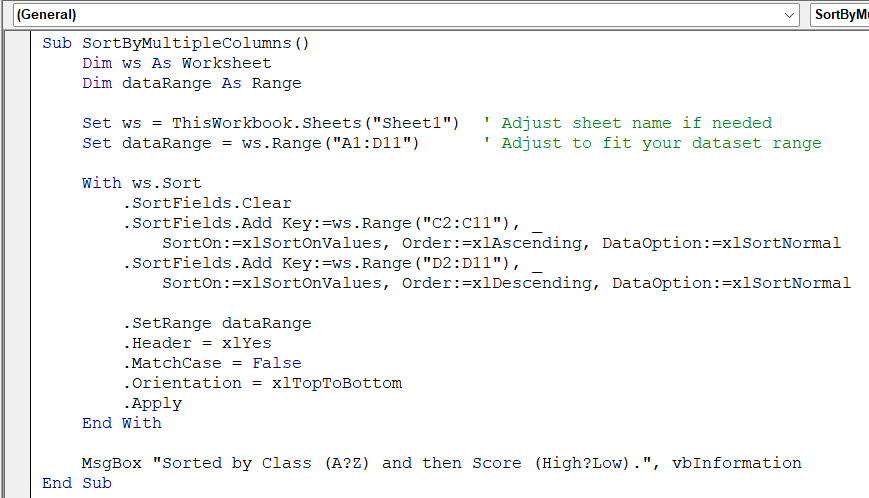
Sub SortByMultipleColumns()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim dataRange As Range
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1") ' Adjust sheet name if needed
Set dataRange = ws.Range("A1:D11") ' Adjust to fit your dataset range
With ws.Sort
.SortFields.Clear
.SortFields.Add Key:=ws.Range("C2:C11"), _
SortOn:=xlSortOnValues, Order:=xlAscending, DataOption:=xlSortNormal
.SortFields.Add Key:=ws.Range("D2:D11"), _
SortOn:=xlSortOnValues, Order:=xlDescending, DataOption:=xlSortNormal
.SetRange dataRange
.Header = xlYes
.MatchCase = False
.Orientation = xlTopToBottom
.Apply
End With
MsgBox "Sorted by Class (A→Z) and then Score (High→Low).", vbInformation
End Sub➧ ws.Range("D2:D11") is the Score column (second sort level).
➧ The range A1:D11 includes both headers and data, modify as needed.
➧ The macro uses ws.Sort.SortFields to add two sorting rules, apply them, and show a message box when done.
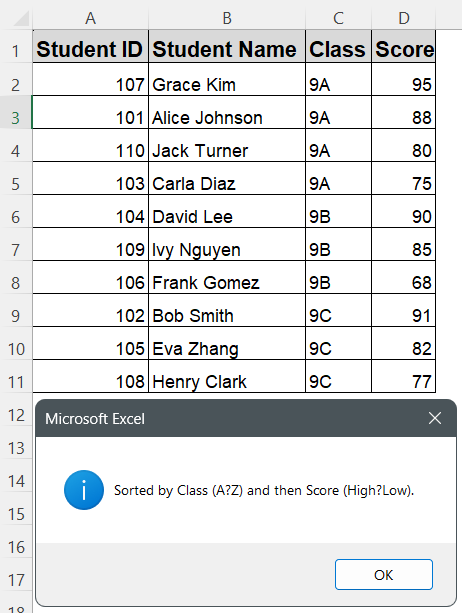
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select SortByMultipleColumns, and click Run to sort the dataset instantly by two columns.
➤ Your data will now be neatly sorted first by Class (A to Z), and within each class, students will be sorted by Score (highest to lowest).
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you sort multiple columns using VBA without errors?
Make sure all SortFields keys are within the specified Range. Always use full sheet references (e.g., ws.Range) and clear existing sort rules before adding new ones.
Can VBA sort dynamic data without knowing the row count?
Yes. Use UsedRange or .End(xlUp) to find the last row, then apply SortFields on a range like “I2:I” & lastRow to sort variable-length data.
Is it possible to sort tables (ListObjects) instead of ranges?
Yes. Use the table’s Sort object and specify columns by ListColumns(“ColumnName”).Range. It works just like sorting a normal range.
How can I sort two or more columns when a workbook opens?
Use Worksheet_Open() in the ThisWorkbook module. Inside it, call Columns.Sort Key1:=… , Key2:=…, so your multi-column sort runs automatically on open.
Wrapping Up
Sorting multiple columns in Excel manually can be time-consuming and error-prone—especially when dealing with large datasets. With VBA, you can automate multi-level sorts with precision and flexibility. In this article, we covered how to sort data by two columns (e.g., Class and Score) using just a few lines of code