When planning finances or solving business problems, you often need to find the exact input that leads to a desired result. That’s where Goal Seek in Excel becomes useful. It allows you to work backward by setting a target value and letting Excel calculate the input needed to reach that goal. In this tutorial, we will walk you through how to use Goal Seek in Excel with three examples.
To use Goal Seek in Excel:
➤ Go to the Data tab, click What-If Analysis, and choose Goal Seek.
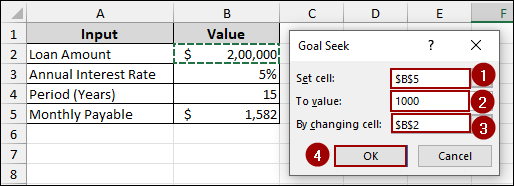
➤ In the Goal Seek dialog box, choose the cell with the formula (like Monthly Payable) in the Set cell field.
➤ Enter the target value you want (e.g., $1,000).
➤ Choose the input cell you want to change (like Loan Amount) in the By changing cell field.
➤ Click OK, and Excel will calculate the loan amount needed according to the monthly payment $1000.
What Is Goal Seek in Excel and How Does It Work?
Goal Seek is a built-in what-if analysis tool that finds the input value needed to reach a specific output. Instead of manually guessing different inputs, Goal Seek allows you to work backward from a desired result. You define the goal (target value), and Excel automatically adjusts one input cell until the formula returns that exact result.
The following are the steps on how Goal Seek works in Excel:
- Start with a formula: First, make sure you have a formula in your sheet, something that calculates a result based on an input, like total sales or loan payment.
- Decide your goal: Next, put your desired result you want. For example, maybe you want your loan payment to be exactly $500.
- Pick the input to change: Choose which cell Excel should change to reach your goal, like adjusting the interest rate or number of items sold.
- Let Excel do the work: Finally, run Goal Seek, and Excel will automatically test different values until the formula gives you the result you wanted.
3 Examples to Use Goal Seek in Excel
In this guide, we will show you how to use Goal Seek through three real-life examples: calculating a loan amount, estimating time to reach a profit goal, and finding the minimum score needed on a final exam.
Suppose we have a dataset containing Loan Amount, Annual Interest Rate, and Period (Years) as inputs. Now, we will calculate the Monthly payable amount and use Goal Seek to find the exact Loan Amount needed to match a specific monthly payment.
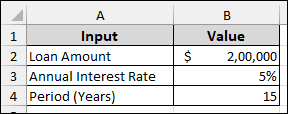
Example 1: Loan Amount Calculation
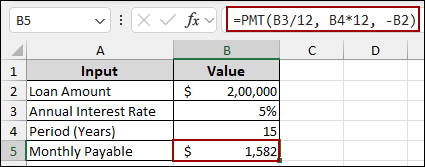
First, we will calculate the monthly payable amount using the PMT function.
➤ Choose cell B5 and input the formula below.
=PMT(B3/12,B4*12,-B2)
This formula calculates the monthly payment based on the Loan Amount in B2, Annual Interest Rate in B3, and Period (Years) in B4.
To apply Goal Seek and determine the loan amount:
➤ Click on the Data tab from the menu bar.
➤ In the Forecast group, click What-If Analysis.
➤ From the dropdown menu, choose Goal Seek.
In the Goal Seek dialog box, you will define your target and the cell that Goal Seek should change to reach that target.
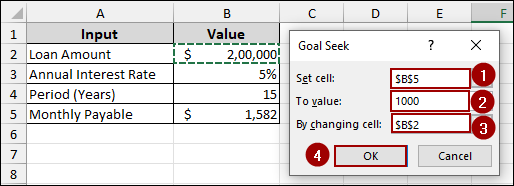
➤ In the Set cell field, enter B5, as this is the cell containing the formula for our Monthly Payable.
➤ In the To value field, enter 1000, which is our desired monthly payment.
➤ In the By changing cell field, enter B2, as we want to find the Loan Amount that results in a $1,000 monthly payment.
➤ Finally, click OK.
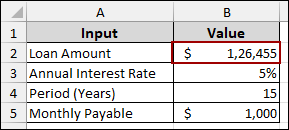
This way, the Loan Amount in cell B2 will change to $1,26,455, indicating that this is the loan amount required for a monthly payment of $1,000.
Example 2: Calculating Time to Get Desired Profit
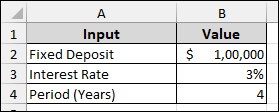
Goal Seek can also be used to determine the investment period required to reach a specific return. Imagine a dataset containing the Fixed Deposit in B2, Interest Rate in B3, and Period (Years) in B4. Here, we will use Goal Seek to find out the Period (Years) needed to achieve a specific return on investment.
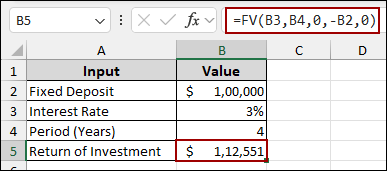
Starting with, we will calculate the return on investment using the FV function.
➤ Select cell B5, and write the following formula.
=FV(B3,B4,0,-B2,0)
This function provides you with the future amount that you will get after 4 years with 3% interest, according to your fixed deposit amount.
To start the Goal Seek process and find the required investment period:
➤ Click on the Data > Forecast > What-If Analysis > Goal Seek.
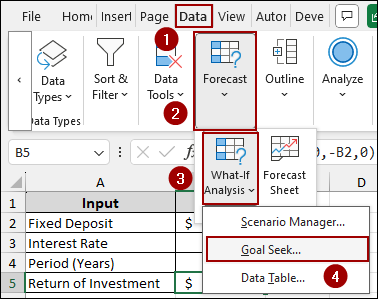
In the Goal Seek dialog box, you will define your target return and the cell that Goal Seek should adjust to achieve that return.
➤ In the Set cell field, enter B5, as this cell contains the formula for our Return on Investment.
➤ In the To value field, enter 130000, which is our desired return.
➤ In the By changing cell field, enter B4, as we want to find the Period (Years) that yields the desired return.
➤ Finally, click OK.
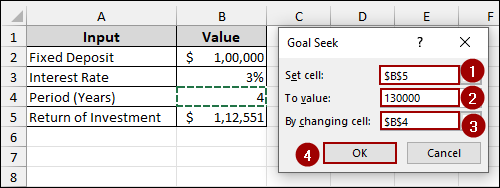
As a result, the Period (Years) in cell B4 will change to 9, indicating that it will take 9 years to achieve a return on investment of $1,30,000.
Example 3: Computing Minimum Number for Final Exam
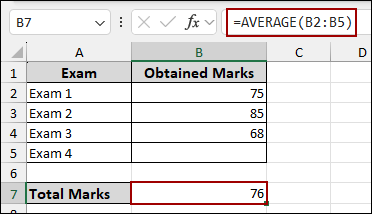
In this example, we will determine what score is needed in one particular exam to reach a desired overall average. Suppose we have a dataset containing four exams and their obtained marks. In Exam 4, the marks cell is blank, as we will use Goal Seek to find out the score for Exam 4 needed to achieve a Total Marks (average) of 80.
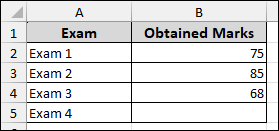
First, we will calculate the average of all marks using the AVERAGE function.
➤ Choose cell B7, and put the formula in the cell.
=AVERAGE(B2:B5)
To begin the Goal Seek process and find the required exam score:
➤ Click on the Data > Forecast > What-If Analysis > Goal Seek.
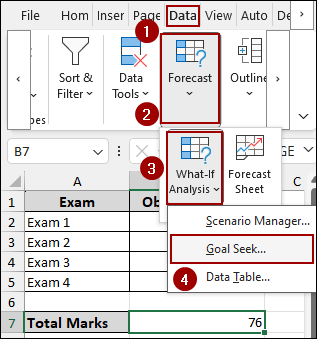
In the Goal Seek dialog box, you will specify your target average and the cell that Goal Seek should modify to reach that target.
➤ In the Set cell field, enter B7, as this cell contains the formula for our Total Marks (average).
➤ In the To value field, enter 80, which is our desired average score.
➤ In the By changing cell field, enter B5, as we want to find the score for Exam 4 that achieves the desired average.
➤ Finally, click OK.
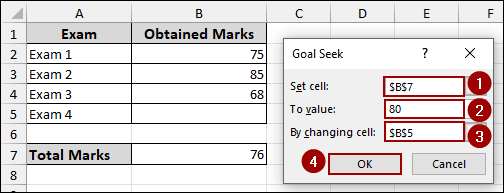
As a result, the score for Exam 4 in cell B5 will change to 92, indicating that you need to score 92 in Exam 4 to achieve an overall average of 80.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get more precise results using Goal Seek?
By default, Goal Seek uses Excel’s standard calculation precision. To improve accuracy, go to File > Options > Formulas. Under Calculation options, reduce the Maximum Change value (e.g., 0.0000001). This ensures Excel iterates with greater precision when running Goal Seek.
Why is Goal Seek not working in my Excel sheet?
There are two common reasons. First one is, you need to set the cell that contain a valid formula. If it’s a static number, Goal Seek won’t work. The second one is a circular reference (when a formula refers back to itself) that can block Goal Seek. Check for and remove any circular references.
Why does Goal Seek give a negative number sometimes?
If you are using financial functions like PMT, Excel shows cash outflows as negative. The result is still correct, just interpret the negative sign as a payment.
Concluding Words
Above, we have explored how to use Goal Seek in Excel to work backward from a desired outcome and find the exact input needed. This feature is especially useful in scenarios like loan planning, profit targeting, or grade forecasting. If you have any questions, feel free to leave them in the comments below.





