When working with dated records in Excel, you often need to count entries that match a specific time window and meet a related text condition. The COUNTIFS function lets you do exactly that, allowing you to filter based on date ranges and criteria like product name, status, or region.
In this article, you’ll learn how to combine date filters and text filters in COUNTIFS using dynamic references, partial text matching, EOMONTH function and live updates with functions like TODAY. Each example returns a specific count, helping you quickly summarize and analyze key data patterns.
Steps to use COUNTIFS with date range and text in Excel:
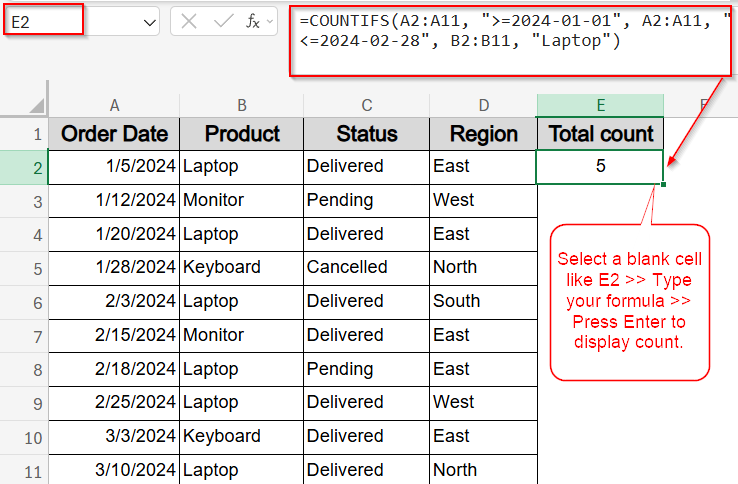
➤ Select a blank cell like E2.
➤ Type this formula:
=COUNTIFS(A2:A11, “>=2024-01-01”, A2:A11, “<=2024-02-28”, B2:B11, “Laptop”)
➤ Press Enter for output.
Count Dates Falling Between Two Dates and Text Value
This method counts how many times a specific product appears between two fixed dates. It’s helpful when you want to filter historical data like how many “Laptop” orders were placed in January and February.
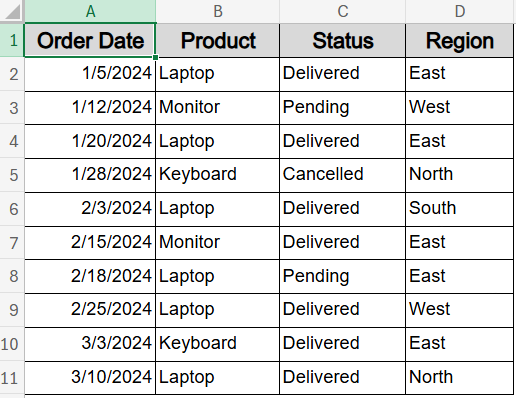
We’ll use a dataset containing order details with columns for Order Date, Product, Status, and Region. This structure lets us apply COUNTIFS logic using a mix of dates and text-based criteria for clear, real-world filtering.
Steps:
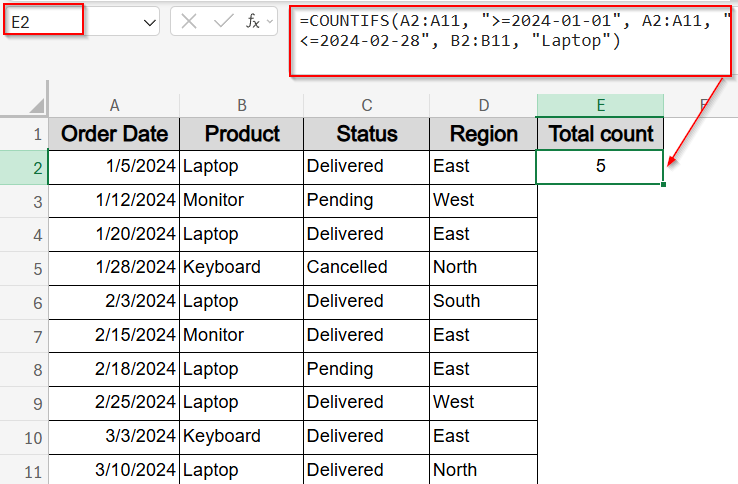
➤ Select a blank cell like E2.
➤ Type this formula:
=COUNTIFS(A2:A11, “>=2024-01-01”, A2:A11, “<=2024-02-28”, B2:B11, “Laptop”)
➤ Press Enter for output.
This formula returns the number of rows where the product is “Laptop” and the order date is within January and February.
Use Cell References for Dynamic Date Range and Text Filters
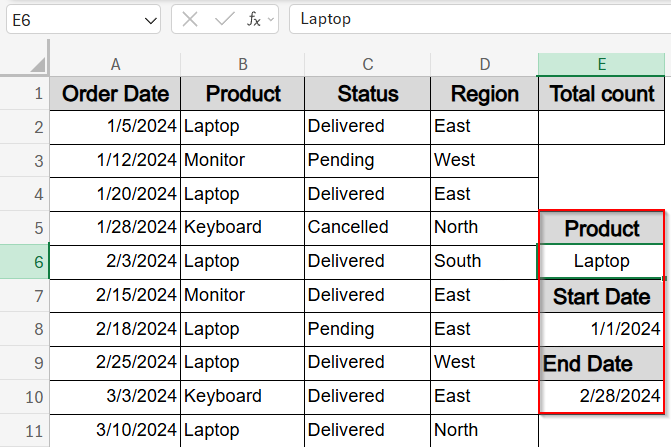
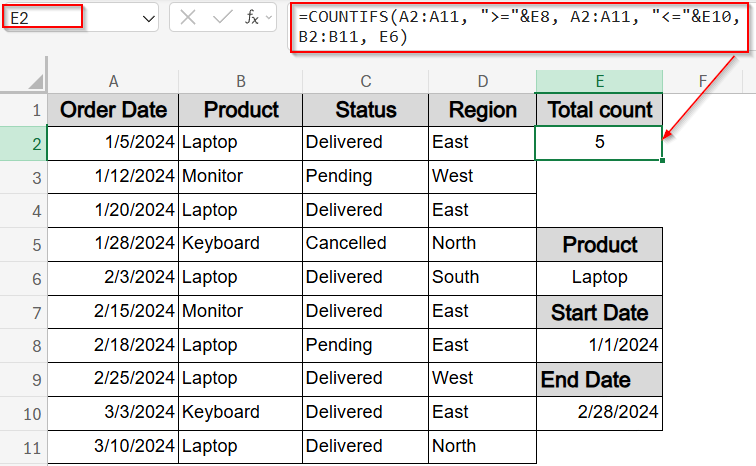
This method lets you count how many entries fall within a specific date range and match a product name without hardcoding anything. For example, you’ll type your criteria into three reference cells, and select an output cell like E2. If cell E6 contains a product name like Laptop, E8 and E10 has the date range 1/1/2024 and 2/28/2024, the total count in E2 will be 5.
Steps:
➤ In cell E6, type the product name to filter (e.g., Laptop).
➤ In cell E8, enter the start date for your filter range (e.g., 1/1/2024).
➤ In cell E10, enter the end date (e.g., 2/28/2024).
➤ In the result cell E2, enter this formula:
=COUNTIFS(A2:A11, “>=”&E8, A2:A11, “<=”&E10, B2:B11, E6)
➤ Press Enter.
This formula counts how many orders were placed between the two dates and matches the product name provided in E6. For instance, if E6 contains “Laptop” and the date range spans January through February, it will return 5, since there are five matching records in that period.
Count Rows Based on Date Range and Partial Text Match
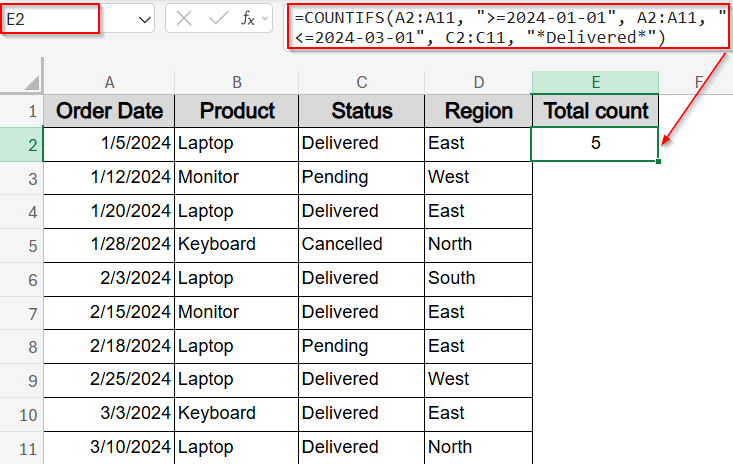
Sometimes, your text column might include variations like “Delivered Today“, “Delivered Late“, or simply “Delivered“. If you want to capture all of them in one count, using wildcards inside your COUNTIFS formula allows for flexible text matching. In this example, we’ll count how many orders were marked with any form of “Delivered” status between January 1, 2024 and March 1, 2024.
Steps:
➤ Select a blank cell like E2.
➤ Type this formula:
=COUNTIFS(A2:A11, “>=2024-01-01”, A2:A11, “<=2024-03-01”, C2:C11, “*Delivered*”)
➤ Press Enter for output.
This returns the count of all orders within the date range that include the word “Delivered” anywhere in the Status column.
Count Multiple Texts within Date Range Using SUM and COUNTIFS Functions
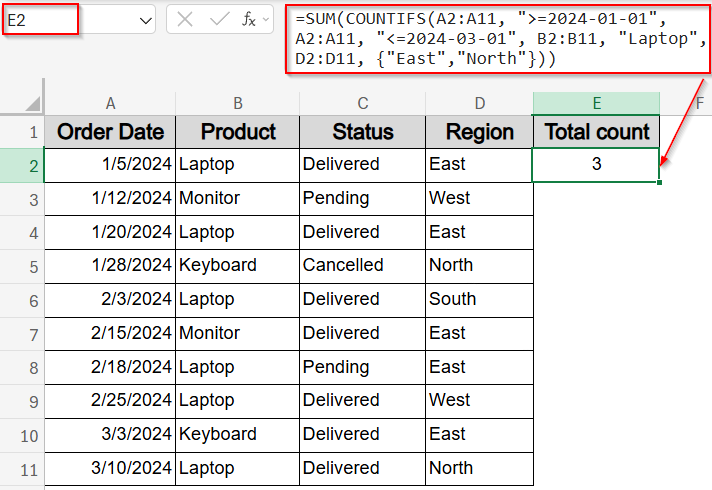
When you want to count rows within a date range that match a product like “Laptop” and also match multiple text values in another column (like “East” or “North”), combining COUNTIFS with SUM allows you to apply OR logic while keeping the date and product filters intact. This method returns a total count across all matching conditions.
Steps:
➤ Select a blank cell like E2.
➤ Type this formula:
=SUM(COUNTIFS(A2:A11, “>=2024-01-01”, A2:A11, “<=2024-03-01”, B2:B11, “Laptop”, D2:D11, {“East”,”North”}))
➤ Press Enter for output.
Now this formula returns the total number of rows that match the specific date range, product, and region from the set criterias.
Count Entries for a Specific Month Using COUNTIFS and EOMONTH Functions
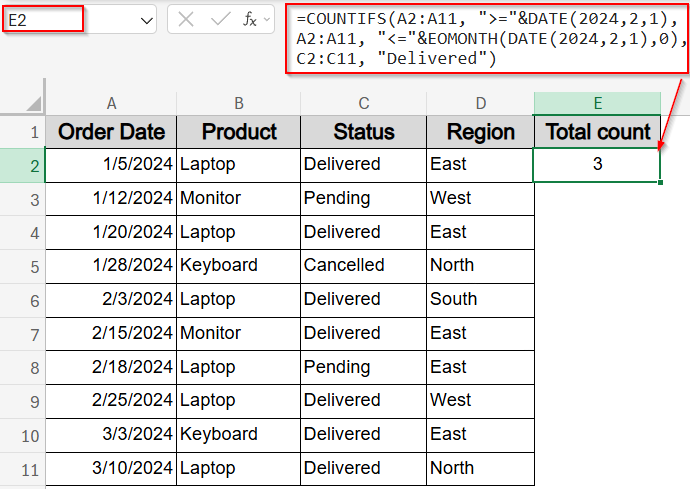
This method uses the EOMONTH function to dynamically set the end date of a month, allowing you to count rows that fall within a full calendar month without manually typing dates. For example, you can count how many orders were marked “Delivered” in February 2024 by specifying the first day of the month and calculating the month’s end automatically. This technique makes your formulas flexible and ideal for monthly reports.
Steps:
➤ Select a blank cell like E2.
➤ Enter this formula:
=COUNTIFS(A2:A11, “>=”&DATE(2024,2,1), A2:A11, “<=”&EOMONTH(DATE(2024,2,1),0), C2:C11, “Delivered”)
➤ Press Enter.
This formula returns the number of orders with status “Delivered” placed during February 2024, using the EOMONTH function to set the date range dynamically.
Combine COUNTIFS with DATE Functions for Rolling Filters
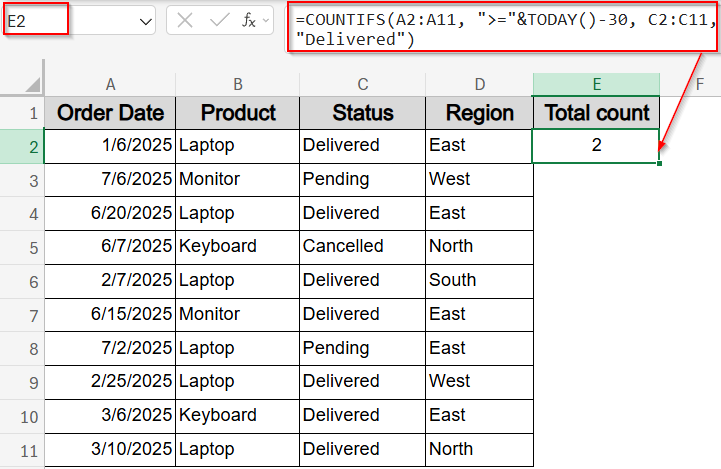
If you’re building a dashboard or working with live reports, it’s helpful to calculate how many recent entries meet certain criteria like counting how many orders were “Delivered” in the last 30 days starting from the present date. By combining COUNTIFS with the TODAY functions, you can build a rolling date filter that always stays current.
Steps:
➤ Select a blank cell like E2.
➤ Type this formula:
=COUNTIFS(A2:A11, “>=”&TODAY()-30, C2:C11, “Delivered”)
➤ Press Enter.
This formula shows how many orders marked “Delivered” were placed in the last 30 days.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I count rows with a date range and a text condition in Excel?
Use the COUNTIFS function with conditions for both date and text columns. For example, you can apply formula: =COUNTIFS(DateRange, “>=start”, DateRange, “<=end”, TextRange, “Product”) to count all matching rows.
Can COUNTIFS match partial text like “Delivered” inside a longer status?
Yes. By surrounding your keyword with asterisks like *Delivered*, COUNTIFS function searches for that text anywhere within a cell, enabling you to capture variations such as “Delivered Today” or “Late Delivery” effectively.
Can I make the dates and text values dynamic?
Yes. Instead of hardcoding dates or text in the formula, you can use cell references like “>=”&A1 or B1. This lets you change criteria easily without modifying the formula, making your worksheet more flexible and user-friendly.
Can COUNTIFS work with TODAY() and other date formulas?
Yes. You can incorporate dynamic date functions like TODAY or EOMONTH within the COUNTIFS function to automatically update date ranges. This is especially useful for creating rolling windows, dashboards, or real-time data filters.
Does COUNTIFS work for ranges with blank cells?
Yes, the COUNTIFS function processes blank cells, but blanks don’t match text or date criteria by default. To exclude blank entries, add a condition like “<>” in one of the criteria ranges to ensure only populated cells are counted.
Wrapping Up
In this tutorial, you learned how to use the COUNTIFS function to count rows based on both dates and text. We covered filtering with exact product names, using wildcards for partial matches, applying region-based filters, setting up dynamic inputs with cell references, using EOMONTH function and creating rolling date windows using the TODAY function. Feel free to download the practice file and share your feedback.