LOOKUP and VLOOKUP are Excel’s built-in functions, used to search for values and return related results. These functions work differently and are suited for different situations.
LOOKUP is an older function that works well for simple searches in a single row or column, but it requires sorted data. VLOOKUP is a more flexible function, as it can search across full tables and doesn’t always need the data to be sorted.
In this article, we’ll show how LOOKUP and VLOOKUP functions work, compare their results, and explain when you should use each one.
Here’s how to use LOOKUP and VLOOKUP functions in Excel:
➤ Open your dataset in Excel where you want to apply the LOOKUP and VLOOKUP functions.
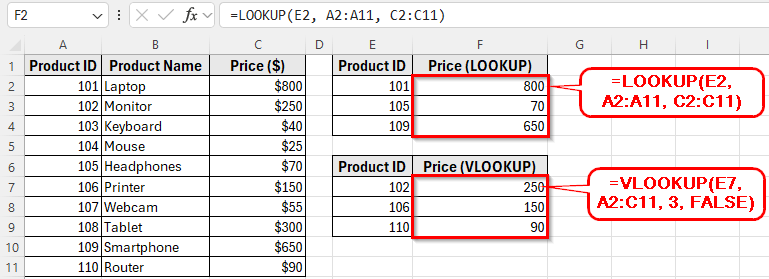
➤ Enter the formula in cell F2: =LOOKUP(E2, A2:A11, C2:C11)
➤ Press Enter. Excel will find the Product ID in column A and return the matching Price from column C.
➤ Drag the fill handle down to F4 to apply the formula for the rest of the Products.
➤ Enter the formula in cell F7: =VLOOKUP(E7, A2:C11, 3, FALSE)
➤ Excel will return the exact Price for the Product ID entered in F7.
➤ Drag the formulas down to find the prices for all products in your lookup table.
What is the LOOKUP Function?
The LOOKUP function in Excel is used to search for a value in a single row or column and return a corresponding value from another row or column. It’s best suited for simple lookups where the data is sorted in ascending order.
LOOKUP can be used in two different ways. The vector form searches for a value in a single column or row and returns a value from another column or row of the same size. The array form searches within an array and returns a value from the same position in another array.
Example: To find the price of a product with ID 101 in a sorted list:
=LOOKUP(101, A2:A11, C2:C11)
Here, Excel searches for 101 in column A (Product IDs) and returns the corresponding value from column C (Prices).
What is the VLOOKUP Function?
The VLOOKUP function in Excel searches for a value in the first column of a table and returns a value from another column in the same row. Unlike the LOOKUP function, it does not require the data to be sorted when you use an exact match.
VLOOKUP has four main parts: the value to find, the table to search in, the column number to get the result from, and whether you want an exact or approximate match.
Example: To find the price of Product ID 101:
=VLOOKUP(101, A2:C11, 3, FALSE)
Here, Excel looks for 101 in the first column of the table A2:C11 and returns the value from the third column (Price). The FALSE ensures it finds an exact match.
Using the LOOKUP Function in Excel
In the following dataset, we have a simple product list that contains item details. Column A lists the Product IDs, Column B shows the Product Names, and Column C contains the Prices.
On the right, we’ve created two separate lookup tables to compare the functions. The first table in Columns E and F will use the LOOKUP function to return prices based on given Product IDs.
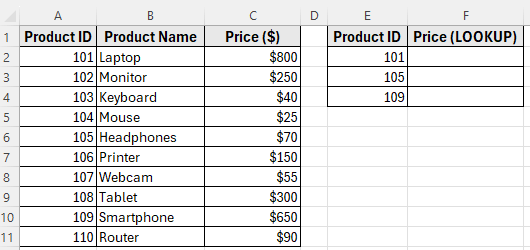
We’ll use this dataset throughout the article to demonstrate how both functions work side by side.
The LOOKUP function is a simple way to find values in a sorted list. It searches for a lookup value in one column and returns the matching result from another column.
In this method, we want to find the prices for certain listed in the LOOKUP table. The results will appear in Column F.
Here’s how to do it:
➤ Open your dataset in Excel.
➤ Click on cell F2 and enter the following formula:
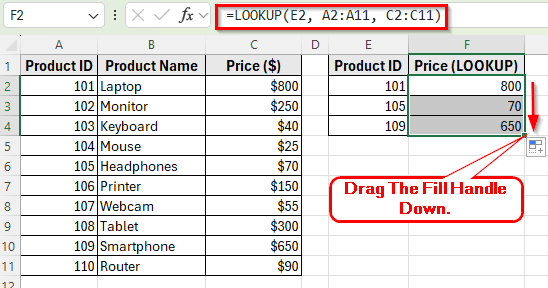
=LOOKUP(E2, A2:A11, C2:C11)
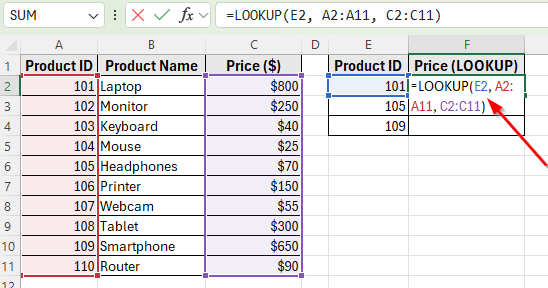
➤ Press Enter. Excel will return 800, which is the price of Product ID 101 (Laptop).
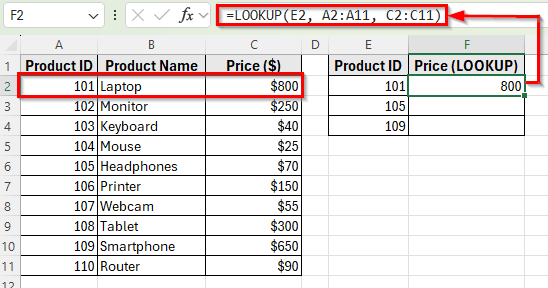
➤ Drag the fill handle down to F4 to apply the formula for Product IDs 105 and 109. Excel will return 70 for Headphones and 650 for Smartphone.
Using the VLOOKUP Function in Excel
The VLOOKUP function is one of the most common ways to search data in Excel. It looks for a value in the first column of a table and then returns a result from another column in the same row. Unlike LOOKUP, VLOOKUP does not require the data to be sorted when you use an exact match.
In our dataset, we’ll use the VLOOKUP table in Columns E and F. The Product IDs are listed in Column E, and we want to return their Prices in Column F.
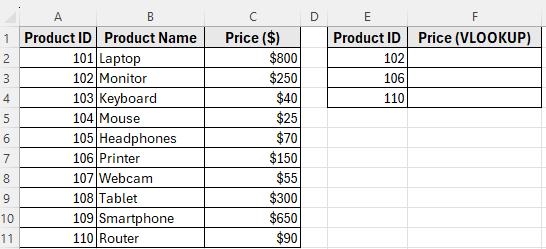
Here’s how to do it:
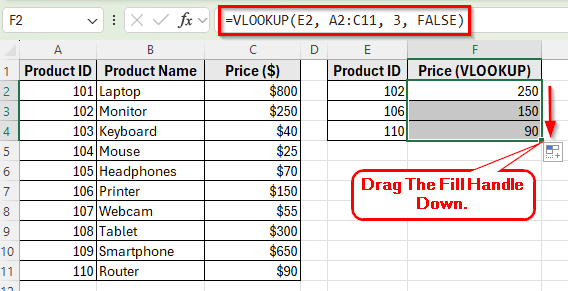
➤ Open your dataset in Excel.
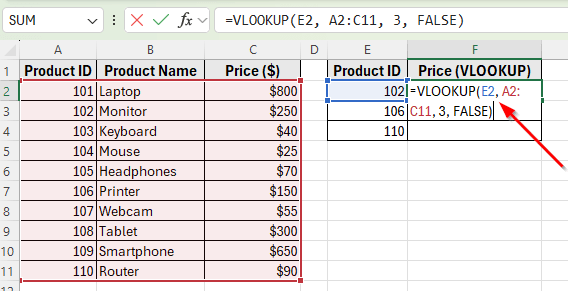
➤ Click on cell F2 and enter the following formula:
=VLOOKUP(E2, A2:C11, 3, FALSE)
➤ Press Enter. Excel will return 250, which is the price of Product ID 102 (Monitor).
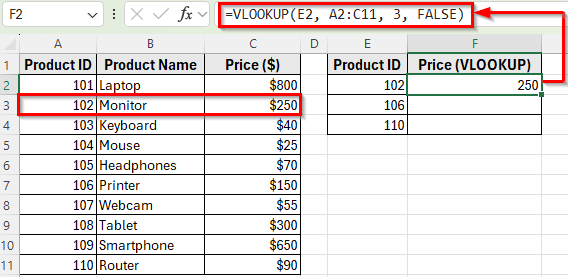
➤ Drag the fill handle down to F4 to apply the formula for Product IDs 106 and 110. Excel will return 150 for Printer and 90 for Router.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between LOOKUP and VLOOKUP functions?
LOOKUP function is an older function that searches in a single row or column and requires the data to be sorted in ascending order. The VLOOKUP function is more flexible because it works with full tables and can find exact matches even when the data is not sorted.
Why does the LOOKUP function sometimes return the wrong result?
The LOOKUP function assumes that your data is sorted. If the lookup column is not in ascending order, it may return an incorrect value or the last available match instead of the exact one you want.
Which function should I use in modern Excel?
VLOOKUP function is generally better than LOOKUP function for most tasks, but in the latest versions of Excel, XLOOKUP function is the best option because it replaces both and provides more flexibility.
Wrapping Up
LOOKUP and VLOOKUP functions both help you find values in Excel, but they work in different ways. LOOKUP function is simple but only works with sorted lists, while VLOOKUP function is more reliable for table data and can return exact results even when the data isn’t sorted.
For most modern Excel tasks, VLOOKUP function is the better choice, but understanding LOOKUP function gives you a solid foundation and helps you recognize its limitations.





















