When managing data across multiple worksheets, copying specific ranges between sheets is a common task. Whether you’re consolidating reports, archiving data, or preparing summaries, VBA can help automate this process with speed and accuracy.
In this article, you’ll learn several practical VBA methods to copy ranges from one sheet to another in Excel. Each method is tied to a real-world scenario such as copying fixed ranges, transferring based on conditions, or working with dynamic selections, so you can choose the solution that best fits your workflow.
Steps to copy a fixed range from one sheet to another using VBA:
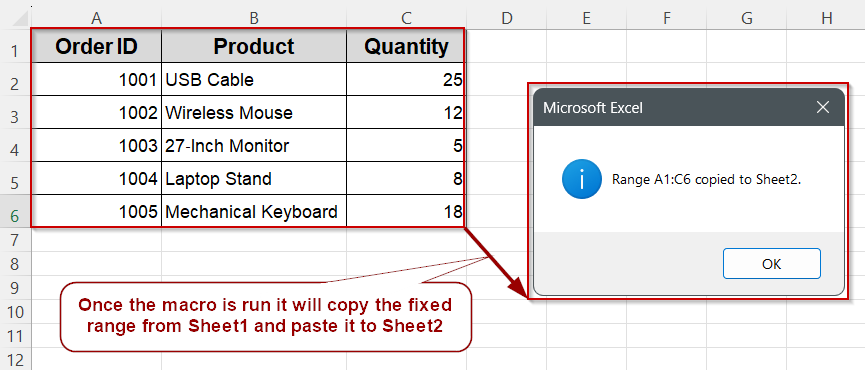
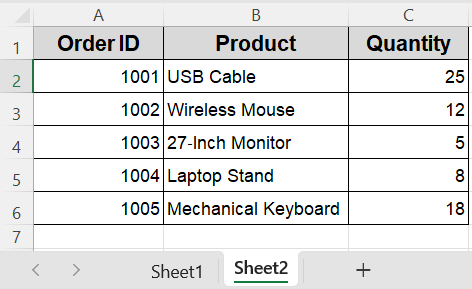
➤ In Sheet1, ensure the data you want to copy is in cells A1:C6 (headers plus five rows).
➤ Press Alt + F11 , go to Insert >> Module, and paste the code below:
Sub CopyFixedRange()
Dim sourceWS As Worksheet
Dim targetWS As Worksheet
Dim copyRange As Range
Set sourceWS = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1") ' Source sheet
Set targetWS = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet2") ' Destination sheet (must exist)
Set copyRange = sourceWS.Range("A1:C6") ' Exact range to copy
copyRange.Copy Destination:=targetWS.Range("A1") ' Paste to A1 in Sheet2
MsgBox "Range A1:C6 copied to Sheet2.", vbInformation
End Sub➤ The macro defines sourceWS (Sheet1) and targetWS (Sheet2).
➤ copyRange is explicitly set to A1:C6, so only that block is copied.
➤ .Copy Destination:=… pastes the block into cell A1 on Sheet2, preserving data and formatting.
➤ A message box confirms success when the copy operation finishes.
➤ To run: press Alt + F8 , select CopyFixedRange, and click Run. The block from Sheet1!A1:C6 appears at Sheet2!A1.
Copy a Fixed Range to Another Sheet Using Excel VBA
Sometimes, you want to copy a specific block of data, like the first few rows of a report, to a new sheet for presentation or backup. This method demonstrates how to use VBA to copy a defined range from one worksheet to another.
We’ll use the sample dataset on Sheet1 (Order ID, Product, Quantity, etc.) and copy the first 5 rows (including headers) from columns A to C into Sheet2, starting at cell A1.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 , go to Insert >> Module
➤ Paste this code:
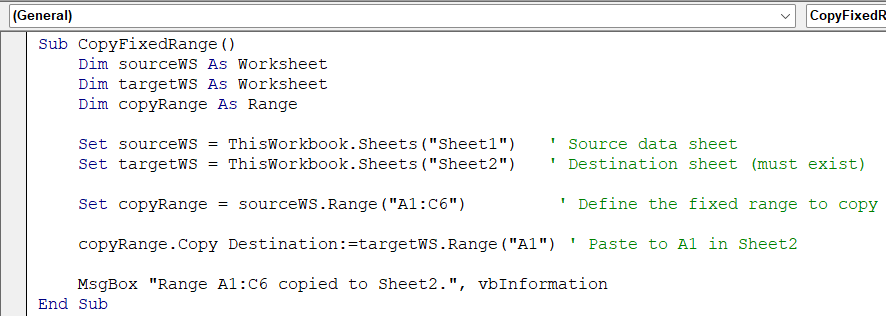
Sub CopyFixedRange()
Dim sourceWS As Worksheet
Dim targetWS As Worksheet
Dim copyRange As Range
Set sourceWS = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1") ' Source data sheet
Set targetWS = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet2") ' Destination sheet (must exist)
Set copyRange = sourceWS.Range("A1:C6") ' Define the fixed range to copy
copyRange.Copy Destination:=targetWS.Range("A1") ' Paste to A1 in Sheet2
MsgBox "Range A1:C6 copied to Sheet2.", vbInformation
End Sub
➧ copyRange = sourceWS.Range("A1:C6") selects the exact range to copy.
➧ .Copy Destination:=... pastes it into Sheet2, starting at cell A1.
➧ A confirmation message appears when the process is complete.
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select CopyFixedRange, and click Run.
➤ The block from A1 to C6 on Sheet1 will be copied to Sheet2, cell A1.
Filter and Copy Rows That Meet a Condition To Another Sheet Using VBA
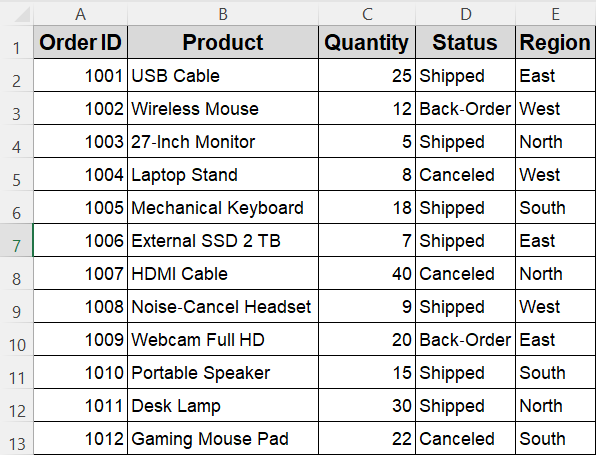
When you need to move only certain records, such as orders that are canceled, to another sheet, VBA can loop through each row, test a condition, and copy matching rows to a designated location.
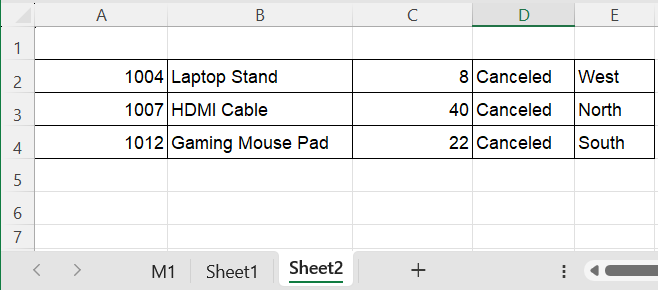
In this example, we will copy rows from Sheet1 to Sheet2 where Status (column D) equals “Canceled”. The data will be appended to the next empty row in Sheet2, so you can run the macro repeatedly without overwriting previous results.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 , choose Insert >> Module, and paste the code below:
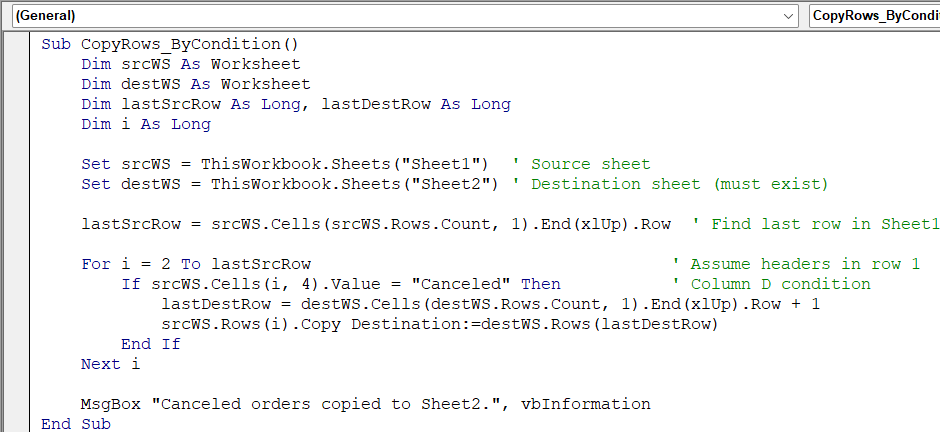
Sub CopyRows_ByCondition()
Dim srcWS As Worksheet
Dim destWS As Worksheet
Dim lastSrcRow As Long, lastDestRow As Long
Dim i As Long
Set srcWS = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1") ' Source sheet
Set destWS = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet2") ' Destination sheet (must exist)
lastSrcRow = srcWS.Cells(srcWS.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row ' Find last row in Sheet1
For i = 2 To lastSrcRow ' Assume headers in row 1
If srcWS.Cells(i, 4).Value = "Canceled" Then ' Column D condition
lastDestRow = destWS.Cells(destWS.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row + 1
srcWS.Rows(i).Copy Destination:=destWS.Rows(lastDestRow)
End If
Next i
MsgBox "Canceled orders copied to Sheet2.", vbInformation
End Sub➧ lastSrcRow identifies the last used row in Sheet1.
➧ The loop starts at row 2 to skip headers and checks each row’s Status in column D.
➧ When the Status equals "Canceled", the row is copied to the next empty row in Sheet2 (lastDestRow).
➧ A message box confirms that all matching rows have been copied.
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select CopyRows_ByCondition, and click Run.
➤ Rows with “Canceled” in column D will be copied from Sheet1 and appended to Sheet2, while other rows remain in place.
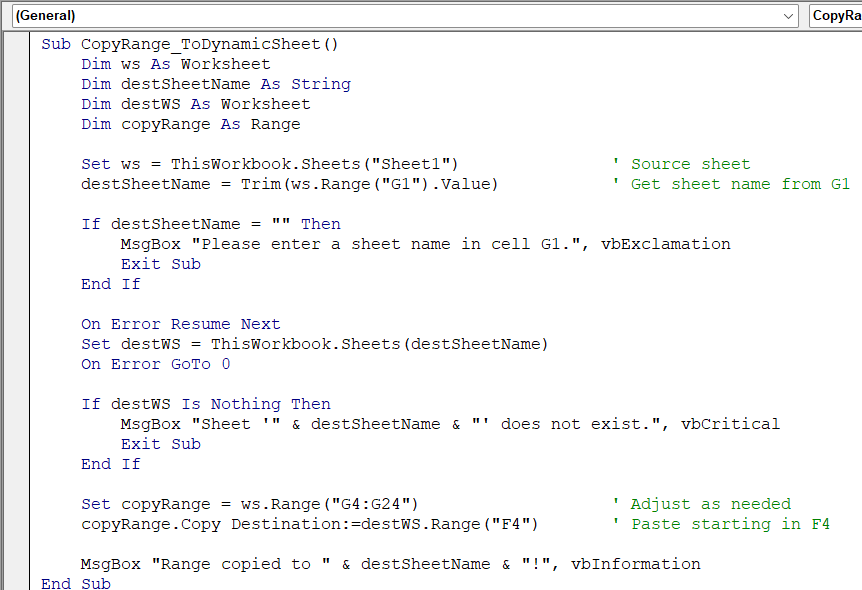
Copy a Range to a Sheet Specified by the User
When building flexible reports or dashboards, it’s useful to copy a specific range to a target sheet that the user can choose at runtime. This method uses a cell (e.g., G1) to determine the destination sheet name and then performs the copy operation.
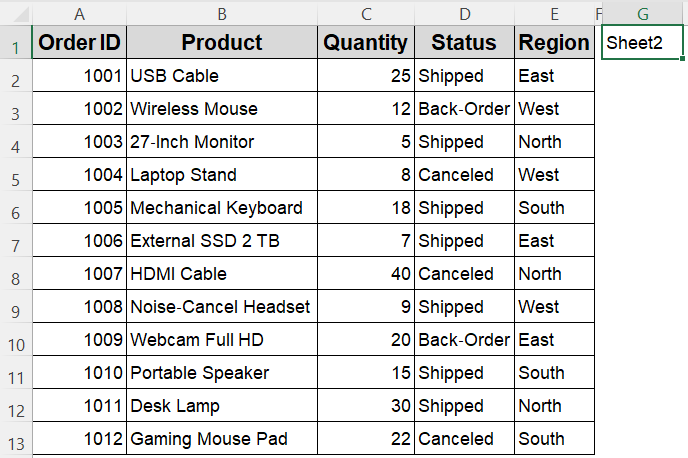
In this example, we’ll copy a range from Sheet1!A2:E5 to the A1 cell of the sheet whose name is typed in G1 of the same sheet.
Steps:
➤ In Sheet1, type the target sheet name in cell G1.
➤ Press Alt + F11 , choose Insert >> Module, and paste this code:
Sub CopyRange_ToDynamicSheet()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim destSheetName As String
Dim destWS As Worksheet
Dim copyRange As Range
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1") ' Source sheet
destSheetName = Trim(ws.Range("G1").Value) ' Get sheet name from G1
If destSheetName = "" Then
MsgBox "Please enter a sheet name in cell G1.", vbExclamation
Exit Sub
End If
On Error Resume Next
Set destWS = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(destSheetName)
On Error GoTo 0
If destWS Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "Sheet '" & destSheetName & "' does not exist.", vbCritical
Exit Sub
End If
Set copyRange = ws.Range("A2:E5") ' Adjust as needed
copyRange.Copy Destination:=destWS.Range("A1") ' Paste starting in F4
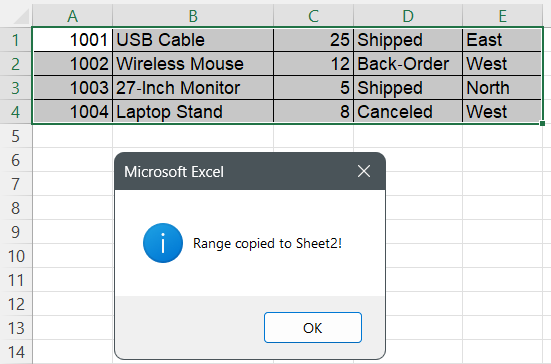
MsgBox "Range copied to " & destSheetName & "!", vbInformation
End Sub
➧ copyRange defines what to copy, in this case, G4:G24 in Sheet1.
➧ The macro verifies that the sheet exists before attempting to copy.
➧ copyRange.Copy Destination:=... sends the data to F4 of the specified sheet.
➧ A message box confirms that the copy operation was successful.
➤ Press Alt + F8 , select CopyRange_ToDynamicSheet, and click Run.
➤ Your selected range will be pasted into the appropriate sheet at the target location.
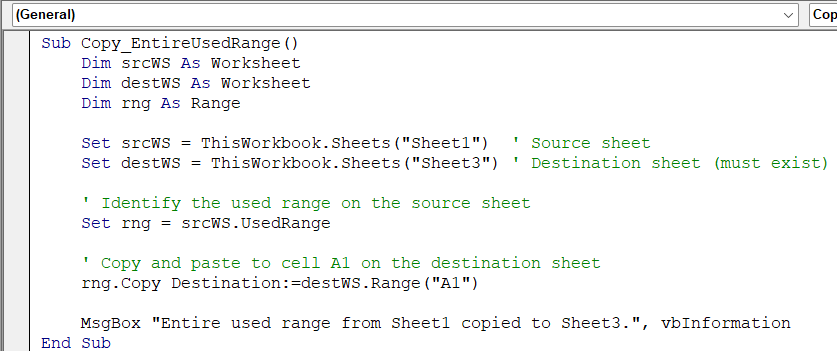
Move the Entire Used Range to Another Sheet with VBA
When you need to transfer all data from one worksheet to another,perhaps to create an archive or consolidate monthly reports, you can copy the entire used range in a single step. This method copies every populated cell from the source sheet and pastes it to the top‑left corner of the destination sheet.
In this example, we will copy the full used range from Sheet1 and paste it into Sheet3, starting at cell A1. Any existing data in Sheet3 will be overwritten in that area.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 , choose Insert >> Module, and paste this code:
Sub Copy_EntireUsedRange()
Dim srcWS As Worksheet
Dim destWS As Worksheet
Dim rng As Range
Set srcWS = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1") ' Source sheet
Set destWS = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet3") ' Destination sheet (must exist)
' Identify the used range on the source sheet
Set rng = srcWS.UsedRange
' Copy and paste to cell A1 on the destination sheet
rng.Copy Destination:=destWS.Range("A1")
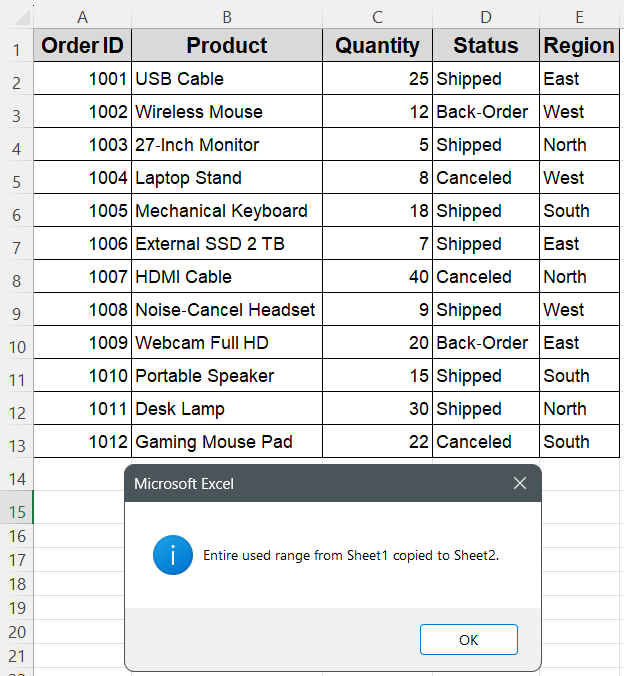
MsgBox "Entire used range from Sheet1 copied to Sheet3.", vbInformation
End Sub
➧ rng.Copy Destination:=destWS.Range("A1") pastes the entire range to the top‑left corner of the destination sheet.
➧ Any data already occupying that destination area will be replaced.
➧ A message box confirms the operation’s completion so you know the copy succeeded.
➤ Return to Excel, press Alt + F8 , select Copy_EntireUsedRange, and click Run.
➤ All cells in the used range on Sheet1 will be copied to Sheet2 starting at cell A1, creating an exact duplicate of the original data block.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I copy a range without selecting it first?
Use Worksheets(“Sheet1”).Range(“A1:C5”).Copy Destination:=Worksheets(“Sheet2”).Range(“D1”). This method avoids using .Select, making your VBA cleaner and faster.
How do I copy a range to the first empty row in another sheet?
Find the last row using .End(xlUp) on the destination, then offset and paste.
Example: src.Range(…).Copy Destination:=dest.Cells(dest.Rows.Count,1).End(xlUp).Offset(1)
Can I copy both cell contents and column widths?
Yes. Use .Copy followed by .PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteColumnWidths.
This preserves data, formatting, and column widths in the destination.
How do I copy data without bringing formatting?
You can copy data without bringing formatting by using direct value assignment:
Worksheets(“Sheet2”).Range(“A1:C5”).Value = Worksheets(“Sheet1”).Range(“A1:C5”).Value.
This transfers only raw data.
Wrapping Up
Copying ranges between sheets is a common task in Excel automation, and VBA offers flexible ways to do it. Whether you need to copy a single range, filter and copy rows based on conditions, or dynamically choose the destination sheet, these methods help you save time and reduce errors.