When we work with an Excel dataset, we often need to repeat actions many times. That is where the For Next loop is used. It is a VBA statement that lets you run a set of instructions repeatedly. Moreover, you can control how many times you want the task to run.
This makes it easy to automate repetitive jobs like calculations, data entry, or formatting. That’s even without writing the same code again and again. In this article, we will learn what For Next is, its syntax, how it works, and simple examples to help you start using it in your Excel tasks.
➤ The For Next loop repeats a task in VBA for a fixed number of times.
➤ You can control the loop with start, end, and Step values.
➤ Positive Step moves forward and negative Step loops backward.
➤ Single loops handle simple ranges, and nested loops work for rows and columns.
➤ Use Exit For to stop the loop early if needed.
➤ For next loop is perfect for tasks like calculations, data checks, and formatting.
What is For Next Loop in Excel VBA?
For Next Loop in Excel VBA is used to create a For loop so you can repeat an action for a fixed number of times. It repeats a group of statements while the loop counter moves from a starting value and approaches its final value.
That means here you set a starting value and an end value. You also specify what action you want to repeat. The VBA will run the action step by step until it reaches the ending value.
You can think control structure as counting. For example, let’s say you want to add numbers from 1 to 10. The loop will start at 1, add 2, then 3, and so on, until it reaches 10. Here For Next loop makes it easy to repeat tasks without writing the same code over and over again.
Syntax of the For Next Loop
The basic syntax of the For Next Loop in Microsoft Excel is:
For counter = start To end [Step increment]
{...statements...}
Next [counter]Below is what each arguments mean:
➥ counter: A variable used to count the loop.
➥ start: The number where the loop starts.
➥ end: The number where the loop ends.
➥ Step increment: Tells VBA how much to increase or decrease the counter each time. It is optional.
➥ Next – Moves to the next loop cycle.
Here is a simple example for a For Next Loop:
For i = 1 To 10
MsgBox i
Next iIt starts with i = 1 and keeps going until i = 10. The loop runs 10 times—one time for each number.
Examples of For…Next Loop in Excel VBA
The For…Next loop in Excel VBA lets you repeat actions a set number of times. It’s perfect for automating tasks like calculating totals or checking values in a range.
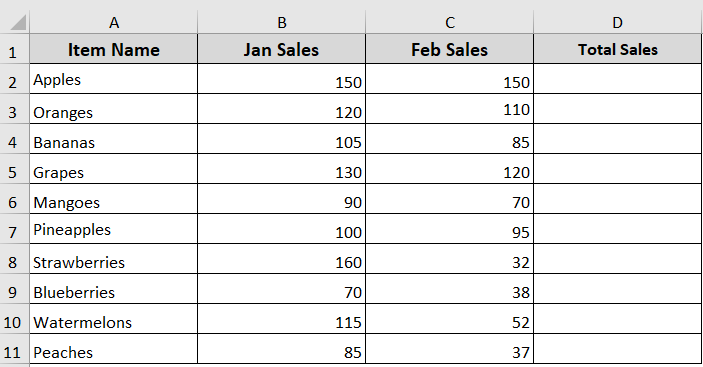
In the below dataset, we’ve Sales data for January and February of different items. Now we are going to use a For…Next loop to calculate the total sales for each item and enter the result in the “Total Sales” column.
Single loop
It is the simplest implementation of the for…next loop. It creates a single loop and repeats an action a set number of times.
For example:
Sub Single_Loop_Example()
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To 4
MsgBox i
Next i
End SubHere, the For loop is controlled by the variable i. It starts at 1 and ends at 4, looping a total of 4 times.
Let’s now use a single loop to calculate total sales from an Excel table.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
➤ Right click on you sheet name >> Insert >> Module.
➤ Insert the below VBA code in the module.
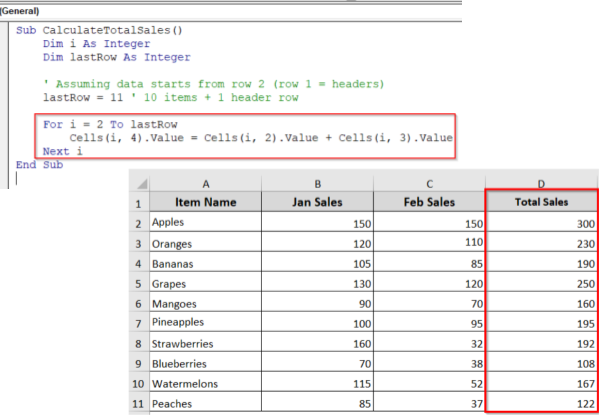
Sub CalculateTotalSales()
Dim i As Integer
Dim lastRow As Integer
' Assuming data starts from row 2 (row 1 = headers)
lastRow = 11 ' 10 items + 1 header row
For i = 2 To lastRow
Cells(i, 4).Value = Cells(i, 2).Value + Cells(i, 3).Value
Next i
End Sub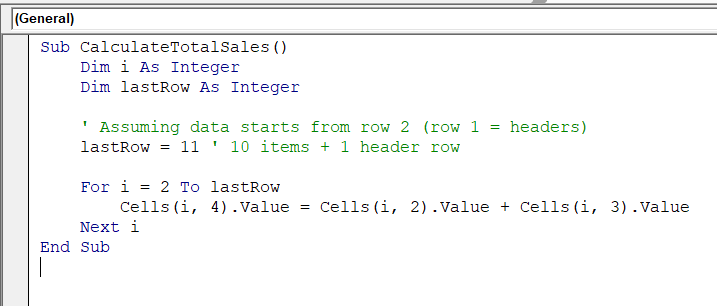
➤ Press F5 to run the code.
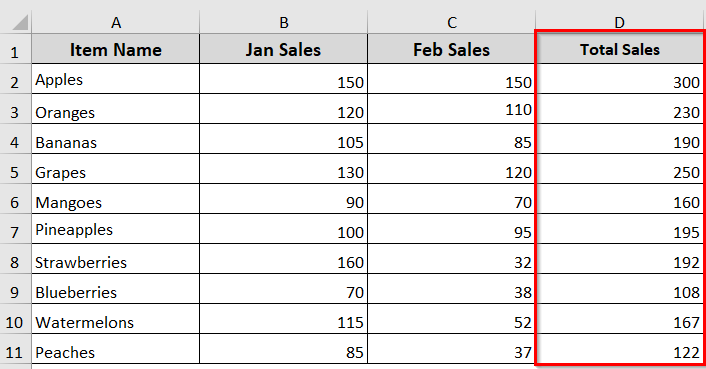
➥ The loop counter i starts at 2. That is because row 1 contains headers.
For i = 2 To lastRow
➥ It loops through each row down to row 11.
lastRow = 11
➥ For each row, it adds the values in columns 2 (Jan Sales) and 3 (Feb Sales).
Cells(i, 2).Value + Cells(i, 3).Value
➥ The result is placed in column 4 (Total Sales)
Cells(i, 4).Value = Cells(i, 2).Value + Cells(i, 3).Value
➥ The loop repeats until all rows are processed.
Next i
Changing Increment
The FOR loop will increment its loop counter by 1 by default. However, you can change how the loop counter increases by using the Step keyword to increment the counter. The increment can be
- Either a positive to skip rows or columns, or
- Negative value to loop in reverse
For example:
Positive increment
Sub Step_Loop_Example()
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To 7 Step 2
MsgBox i
Next i
End SubIn this example, the loop starts at 1 and ends at 7. It increases by 2 each time instead of 1. So it shows message boxes with:
1, 3, 5, and 7
Now, we’ll use a Step Loop to calculate Total Sales only for alternate rows.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA Editor
➤ Right-click on your sheet name >> Insert >> Module
➤ Insert the following VBA code in the module.
Sub Step_Loop_Positive()
Dim i As Integer
For i = 2 To 11 Step 2
Cells(i, 4).Value = Cells(i, 2).Value + Cells(i, 3).Value
Next i
End Sub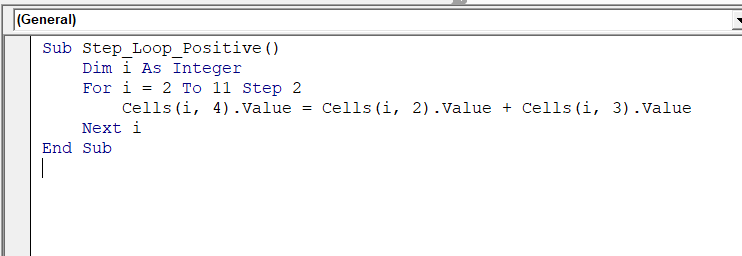
➤ Press F5 to run the code.
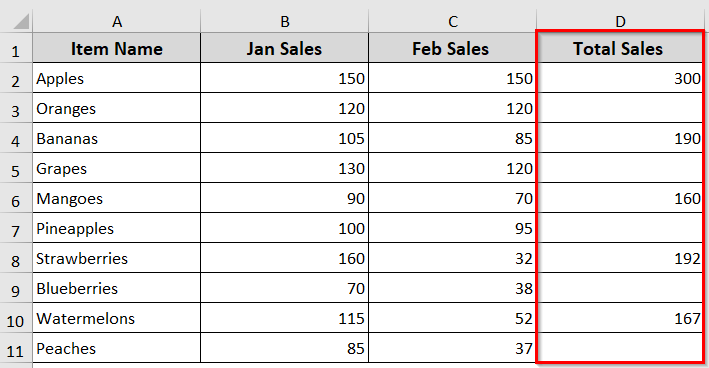
➥ It calculates total sales only for alternate rows: 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10
➥ It adds values from Column B and Column C for each of those rows
➥ The result is placed in Column D.
Negative Increment
Sub Step_Negative_Example()
Dim i As Integer
For i = 10 To 4 Step -2
MsgBox i
Next i
End SubWhen the increment value is negative, you need the starting value to be the higher number and the ending value to be the lower number, as the FOR loop will be counting down.
In this example, the loop starts at 10, increments by -2, and ends at 4. The code would display 4 message boxes with the following values: 10, 8, 6, and 4
Here are the steps for using the Step loop for a negative increment.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA Editor
➤ Right-click on your sheet name >> Insert >> Module
➤ Insert the following VBA code in the module.
Sub Step_Loop_Negative()
Dim i As Integer
For i = 11 To 2 Step -2
Cells(i, 4).Value = Cells(i, 2).Value + Cells(i, 3).Value
Next i
End Sub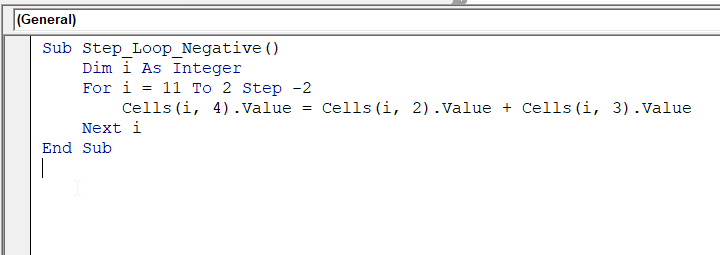
➤ Press F5 to run the code.
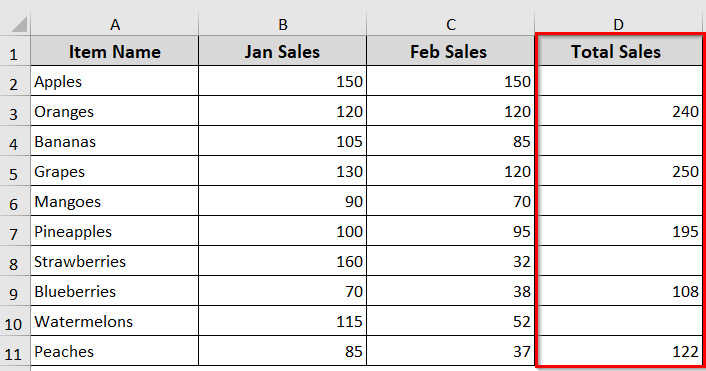
➥ It updates rows 11, 9, 7, 5, and 3
➥ Again, it adds Column B and Column C sales and shows the total in Column D
Double Loop
A Double Loop uses one loop inside another. Now, let’s see how to create a Double For loop in Excel. This is helpful when you’re working with rows and columns.
Sub Double_Loop_Example()
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
For i = 2 To 4
For j = 5 To 6
MsgBox "Row: " & i & ", Column: " & j
Next j
Next i
End SubHere we have two for loops. The outer loop (i) runs from 2 to 4, and the inner loop (j) runs from 5 to 6. The outer FOR loop runs 3 times, starting at 2 and ending at 4. The inner FOR loop runs 2 times, starting at 5 and ending at 6. So this code displays 6 message boxes with the following values:
2-5, 2-6, 3-5, 3-6, 4-5, and 4-6.
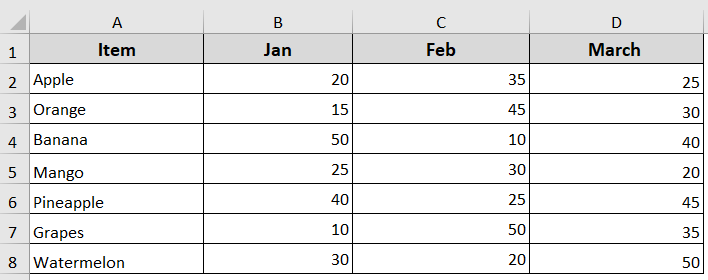
For example, in this dataset, we have fruit items and their sales for three months: Jan, Feb, and March. Now we’re going to use a double loop to find and highlight the highest sales value for each fruit in those three months.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA Editor
➤ Right-click on your sheet name >> Insert >> Module
➤ Insert the following VBA code in the module.
Sub HighlightMaxInEachRow()
Dim i As Integer, j As Integer
Dim maxVal As Double, maxCol As Integer
For i = 2 To 8 'Rows 2 to 8 (7 fruits)
maxVal = Cells(i, 2).Value
maxCol = 2
For j = 3 To 4 'Columns 3 (Feb) to 4 (March)
If Cells(i, j).Value > maxVal Then
maxVal = Cells(i, j).Value
maxCol = j
End If
Next j
Cells(i, maxCol).Interior.Color = RGB(255, 255, 0) 'Highlight in Yellow
Next i
End Sub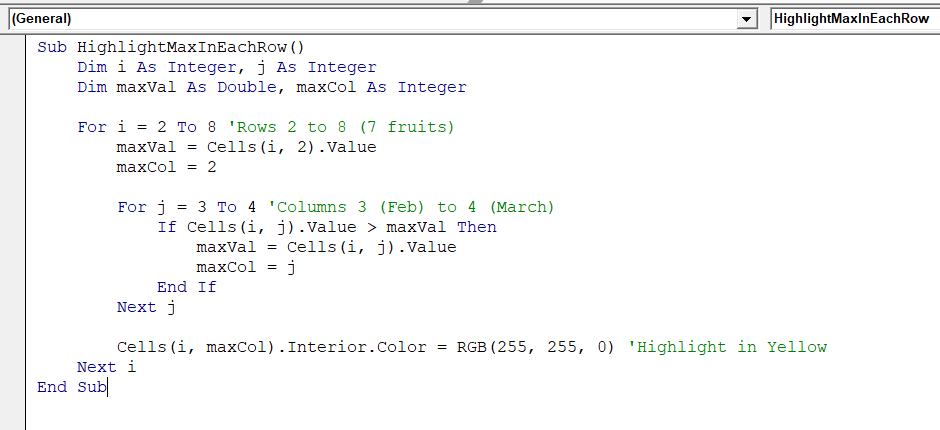
➤ Press F5 to run the code.
➤ It will highlight the highest value for each fruit.
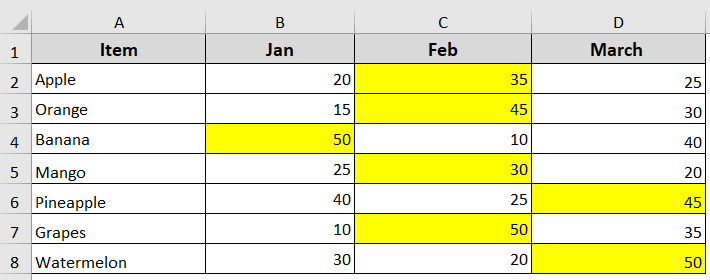
➥ For i = 2 To 8: It is the outer loop and goes by row from 2 to the last 8 for the fruit row. It excludes row 1 as it is our header.
➥ For j = 3 To 4: It is the inner loop and checks sales in those months.
➥ Now, for every row (i), the inner loop (j) checks fruits and months, and highlights the row with the highest value.
Triple Loop
You can nest a third FOR loop inside a double loop to create a triple loop. Here is how it works.
Sub Triple_Loop_Example()
Dim i As Integer
Dim j As Integer
Dim k As Integer
For i = 1 To 2
For j = 5 To 6
For k = 7 to 8
MsgBox i & "-" & j & "-" & k
Next k
Next j
Next i
End SubHere, the example has 3 FOR loops. The outer-most FOR loop would loop 2 times, starting at 1 and ending at 2. The next FOR loop would loop 2 times, starting at 5 and ending at 6. At last, the inner-most FOR loop would loop 2 times, starting at 7 and ending at 8.
Within the inner-most loop, the code would display a message box each time with the value of the i-j-k counters. This code would display 8 message boxes with the following values:
1-5-7, 1-5-8, 1-6-7, 1-6-8, 2-5-7, 2-5-8, 2-6-7, and 2-6-8.
That means, you can use the triple loop when you are working with a dataset containing three category values. For example, in the following dataset, we have T-shirt orders with three categories: Color, Size, and Sleeve type. Now, we will use a triple loop to count how many times each unique combination of these categories appears.
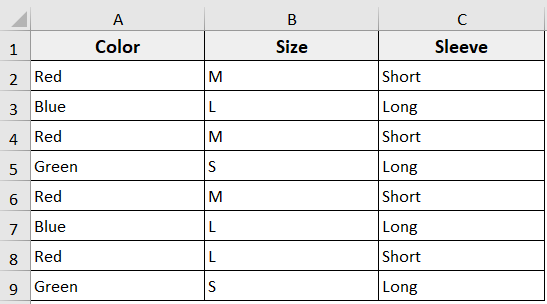
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA Editor
➤ Right-click on your sheet name >> Insert >> Module
➤ Insert the following VBA code in the module.
Sub CountTShirtCombos()
Dim colorList As Variant
Dim sizeList As Variant
Dim sleeveList As Variant
Dim i As Integer, j As Integer, k As Integer
Dim r As Long, lastRow As Long
Dim count As Long
colorList = Array("Red", "Blue", "Green")
sizeList = Array("S", "M", "L")
sleeveList = Array("Short", "Long")
lastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
For i = 0 To UBound(colorList)
For j = 0 To UBound(sizeList)
For k = 0 To UBound(sleeveList)
count = 0
For r = 2 To lastRow
If Trim(Cells(r, 1).Value) = colorList(i) And _
Trim(Cells(r, 2).Value) = sizeList(j) And _
Trim(Cells(r, 3).Value) = sleeveList(k) Then
count = count + 1
End If
Next r
If count > 0 Then
Debug.Print "Color: " & colorList(i) & ", Size: " & sizeList(j) & _
", Sleeve: " & sleeveList(k) & " -> Count: " & count
End If
Next k
Next j
Next i
End Sub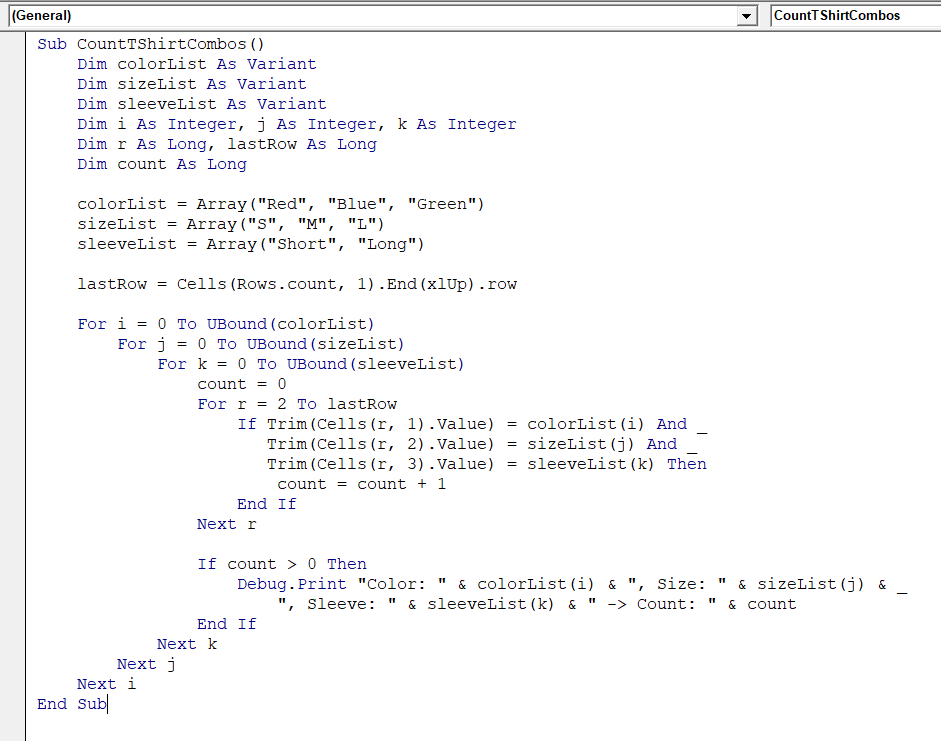
➤ Press F5 or click Run >> Run Sub/UserForm.
➤ Now press Ctrl + G to open the Immediate Window. Here, the results will show.
➤ In the Immediate Window, you will see the counts of how many times each unique combination of Color, Size, and Sleeve has appeared in the dataset.
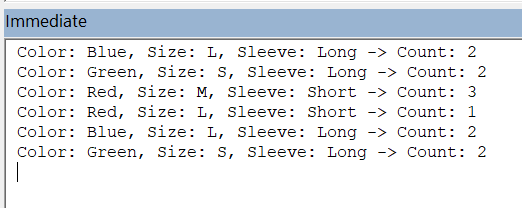
➥ For i = 0 To UBound(colorList): It is the outer loop, going through each Color in the list.
➥ For j = 0 To UBound(sizeList): It is the middle loop, going through each Size for the current Color.
➥ For k = 0 To UBound(sleeveList): It is the inner loop, going through each Sleeve type for the current Color and Size.
➥ Now, for every combination of Color (i), Size (j), and Sleeve (k), the code loops through all rows to count how many times this combo appears.
➥ If the combo appears at least once, it shows the Color, Size, Sleeve, and the count in the Immediate Window.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to exit a for next loop in VBA?
You can exit the For Next loop in VBA using the Exit For statement. This Exit For statement stops the loop and continues the code after the loop. For example:
For i = 1 To 10
If i = 5 Then Exit For
MsgBox i
Next iHere, it starts with i = 1 and keeps going until i = 10. But the loop stops when i reach 5 for the Exit For statement.
What is a nested For Loop?
In simple words, it means one loop under another loop. It contains one outer loop and one inner loop. For example:
For i = 1 To 3
For j = 1 To 2
Cells(i, j).Value = "Row " & i & ", Col " & j
Next j
Next iHere, the outer loop runs from 1 to 3 and the inner loop runs from 1 to 2. It is called a nested For loop.
What is next in VBA?
In VBA, Next is used to specify the end of a For loop. For example:
For i = 1 To 5
MsgBox i
Next iHere, Next i increases the value of i by 1 and repeats the loop until i reaches 5.
Wrapping Up
In this guide, we have learnt how to use the For…Next loop in Excel VBA to automate repetitive tasks. You can apply this loop to automate many Excel tasks once you understand the basics. For instance, calculations, data checks, or even formatting. You can also download the sample Excel dataset to practice the code examples shared in this article and see how exactly they work.