In Excel, most of the time, we work with lots of data. But practicing advanced features and functions in Excel makes it quite easier to extract information from such a huge datasets. And the VLOOKUP function is one of the most useful and powerful functions in Excel. But by default, it only returns one value per match.
So, what if your data has multiple values for the same lookup key? Well, with a little trick like combining different functions as TEXTJOIN + IF, we can simply vlookup multiple values in one cell. Let’s see how this works at a glance.
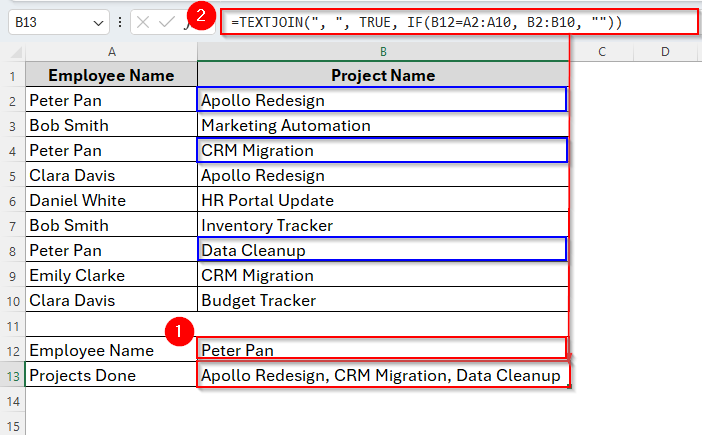
➤ Firstly, insert the employee name Peter Pan in cell B12.
➤ Then apply the following formula in cell B13:
=TEXTJOIN(“, “, TRUE, IF(B12=A2:A10, B2:B10, “”)
➤ Press Enter and the result is ready to go.
➤ If you’re not using Microsoft 365 or Excel 2019, press Ctrl + Shift + Enter instead.
Fortunately, there are also some other ways to choose from while searching multiple values in one in Excel. Throughout this article, we’ll explain each of them gradually with some real world examples. So, let’s dive in.
Using TEXTJOIN & IF Functions to Vlookup Multiple Values in One Cell
When we combine the functions TEXTJOIN and IF together, the IF basically checks the data on each row and see if it matches the lookup key. If it does, it returns the result in the required cell. At the same time, the TEXTJOIN function joins those matches into one line separated by commas.
So, this method is incredibly useful to check and vlookup multiple values into a cell. For example, let’s assume that we have a dataset of a company including their employee name and their projects. Here, each employee is working on multiple projects and these are listed in different cells randomly. But we have to find out all the projects done by a particular employee.
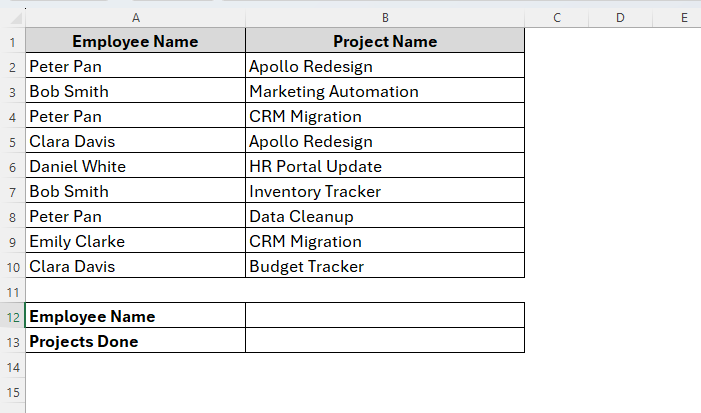
To do so, we’ll be using the TEXTJOIN and IF functions. Let’s say here we want to look up the employee named Bob Smith and return all the projects associated with him in one single cell. So, here we go.
Steps:
➤ In cell B12, type the employee name Bob Smith.
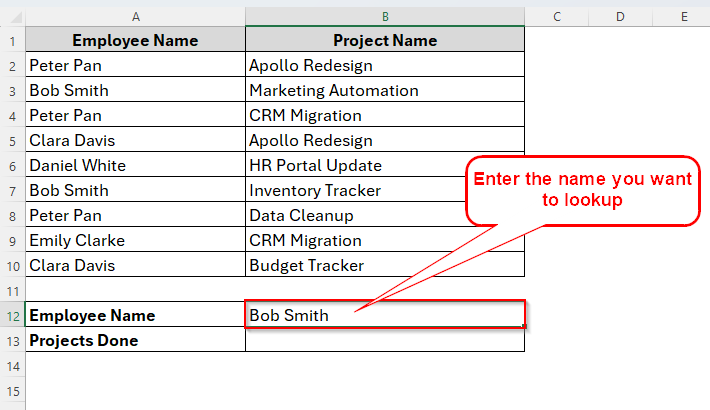
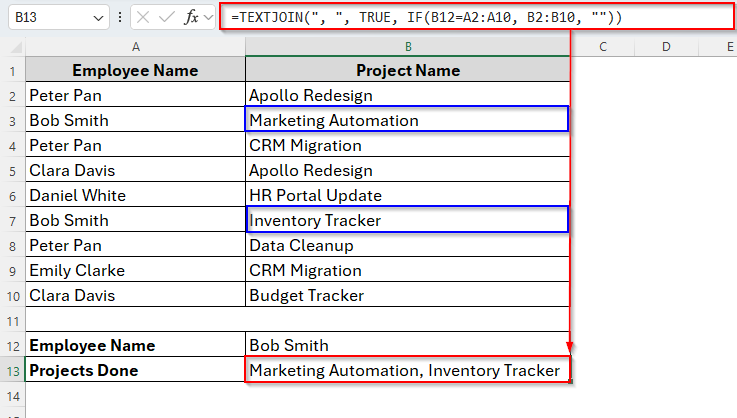
➤ Now in cell B13, use the formula as follows:
=TEXTJOIN(", ", TRUE, IF(B12=A2:A10, B2:B10, ""))
➤ Hit the Enter key and all the project names related to Bob Smith will appear in the cell B13 as we can see in the image below.
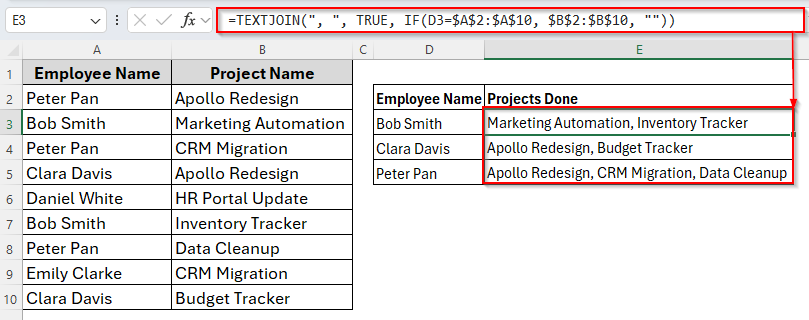
If you want the result for more than one employee at the same time, there’s also a way to do so. All we need to do is just make a small change in the formula. We’ll add dollar signs ($) as follows.
=TEXTJOIN(", ", TRUE, IF(B12=$A$2:$A$10, $B$2:$B$10, ""))
➤ Press Enter and drag the AutoFill Handle down to E5.
Note:
We can do this with any formula. All we need to do is just add a dollar sign in cell ranges.
Using TEXTJOIN & FILTER Functions to Vlookup Multiple Values in One Cell
By combining TEXTJOIN and FILTER, it allows simple lookups and summarizes related data cleanly in one cell. It’s a great tool for dashboards, reports, or any scenario where you need a quick overview of multiple matches.
If you have Excel 365 or Excel 2019+, you can absolutely use FILTER inside TEXTJOIN. It’s clean and more efficient than the IF array trick. Below are the steps to follow.
Steps:
➤ Insert the lookup key in cell B12. Here we enter the employee name Peter Pan.
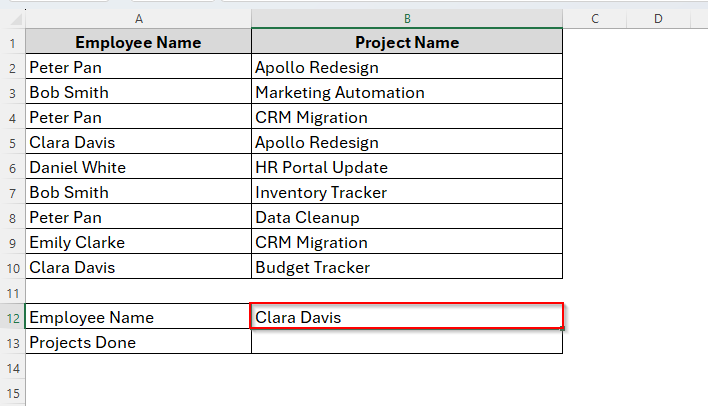
➤ Then type the following array formula in cell B13.
=TEXTJOIN(", ", TRUE, FILTER(B2:B10, A2:A10=B12, "No projects found"))
➤ Press Enter. The result will appear in the cell as follows.
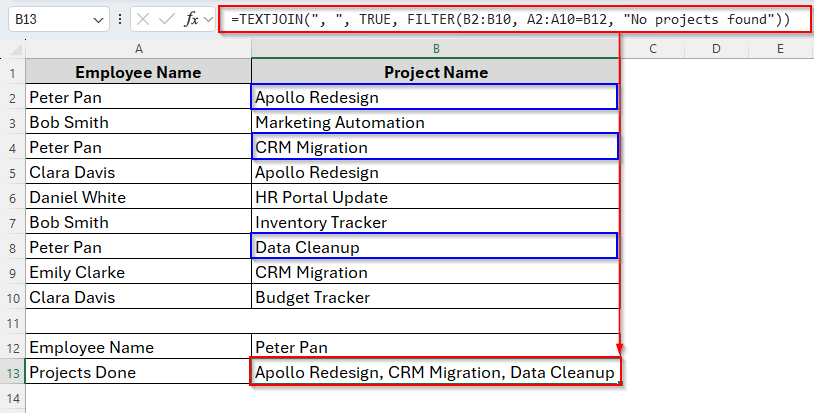
Here, we can see that Peter Pan has done a total of three projects and all the project names are listed in the cell B13 after applying the formula.
Vlookup Multiple Values in One Cell Without Duplicates
Undoubtedly, the previous two methods were the simplest and fastest ways to get your result. But here, you’ll also notice that we’re getting the repeated results too.
For example, here in the following dataset, you can see that an employee has taken the same project multiple times.
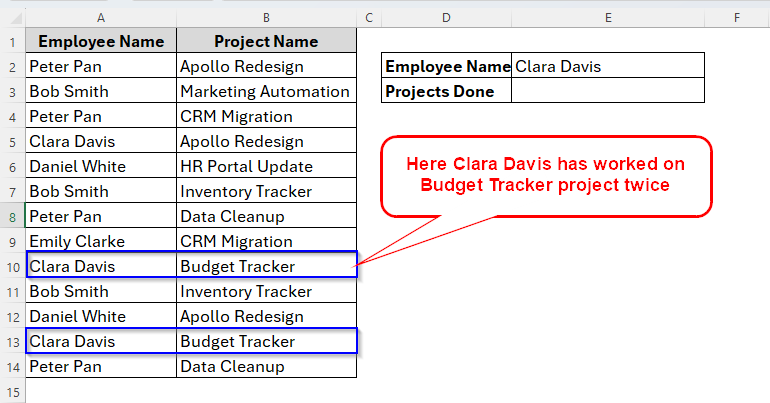
If you apply any of the previous methods, we’ll get repeated results as the following images shows.
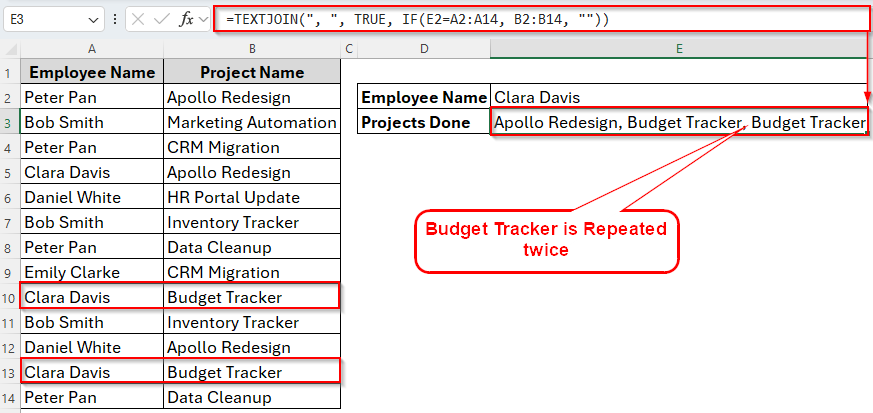
So, we have made a small change in the formula to fix this issue. Let’s find it out.
Steps:
➤ Type the following formula in cell E3.
=TEXTJOIN(", ",TRUE,UNIQUE(IF(E2=A2:A14,B2:B14,"")))
➤ Hit Enter and the results are here without any duplicates. Though Clara Davis has done the Budget Tracker project twice, here the project name appeared once.
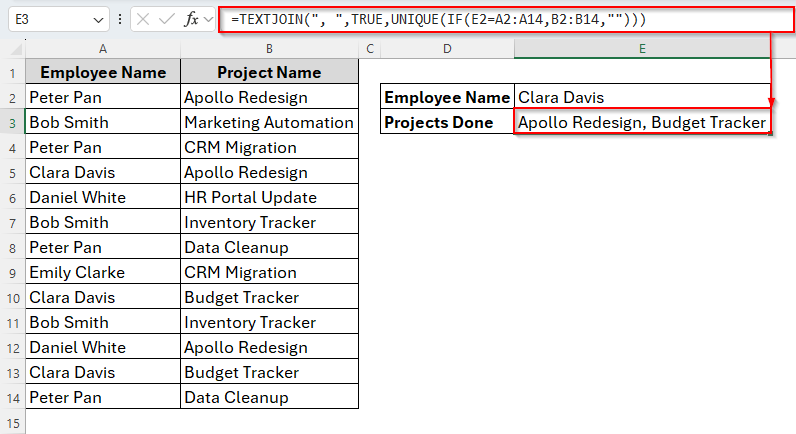
And, as you can see that here we just applied the IF function within the UNIQUE function.
Using VBA Codes to Vlookup Multiple Values in One Cell
Till now, we used the TEXTJOIN function and got multiple lookup values in a cell. But if you’re using older Excel versions like 2016 or prior, unfortunately this function is not available for you.
Therefore, we’ve got a solution to this problem too. We can simply create a VBA code and it will vlookup the values in nearly no time. So, let’s see how this works.
Steps:
➤ To begin with, open the VBA Editor window by pressing Alt + F11 .
➤ Go to Insert > Module.
➤ Now copy and paste the following VBA Code:
Function MultiVlookupConcat(LookupValue As String, LookupRange As Range, ReturnRange As Range, Optional Delimiter As String = ", ") As String
Dim i As Long
Dim Result As String
Dim LR As Variant, RR As Variant
If LookupRange.Rows.Count <> ReturnRange.Rows.Count Then
MultiVlookupConcat = "Error: Ranges not the same size!"
Exit Function
End If
LR = LookupRange.Value
RR = ReturnRange.Value
For i = 1 To UBound(LR, 1)
If Trim(LR(i, 1)) = Trim(LookupValue) Then
Result = Result & RR(i, 1) & Delimiter
End If
Next i
If Result <> "" Then
MultiVlookupConcat = Left(Result, Len(Result) - Len(Delimiter)) ' remove trailing delimiter
Else
MultiVlookupConcat = "No matches found"
End If
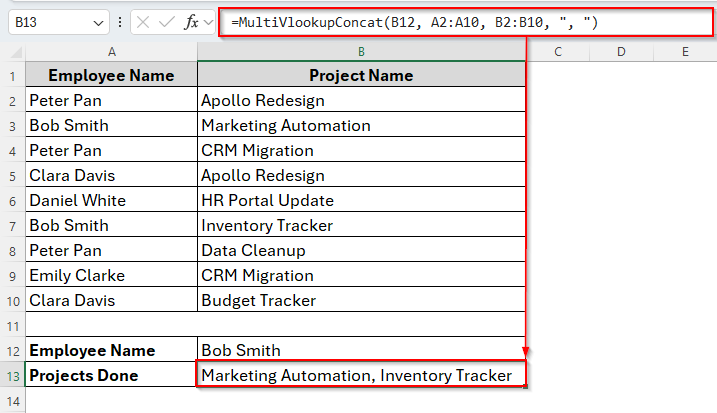
End Function➤ Then run the code. Typically there are many ways to run a VBA code. Here we’ll use the default MultiVlookupConcat function. To do so, close the VBA Editor and insert the following formula in cell B13.
=MultiVlookupConcat(B12, A2:A10, B2:B10, ", ")
➤ Tap the Enter key and you’ll see the projects done by Bob Smith.
Using VBA Codes to Vlookup Multiple Values in One Cell Without Duplicates
The key benefit of this approach is its ability to eliminate duplicate values, ensuring a clean and concise result. It’s a reliable method that works across all versions of Excel and doesn’t depend on specific functions like FILTER, which are only available in newer versions. Let’s see how it works.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the Basic VBA Editor.
➤ Same as the previous method, choose Insert > Module.
➤ Now copy and paste the following code inside the new module.
Sub VLOOKUP_Multiple_Values()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim employeeName As String
Dim projectList As String
Dim i As Long
Dim lastRow As Long
' Set the worksheet to be active
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet
' Get the employee name from cell E2
employeeName = ws.Range("E2").Value
' Find the last row of data in column A
lastRow = ws.Cells(ws.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
' Clear the previous project list in cell E3
ws.Range("E3").ClearContents
' Loop through each row of the data
For i = 2 To lastRow
' Check if the employee name in column A matches the search value
If ws.Cells(i, 1).Value = employeeName Then
' Check if the project name is not already in our list
If InStr(projectList, ws.Cells(i, 2).Value) = 0 Then
' If the project list is not empty, add a comma and space before the new project
If projectList <> "" Then
projectList = projectList & ", "
End If
' Add the new project to the list
projectList = projectList & ws.Cells(i, 2).Value
End If
End If
Next i
' Put the final list of projects into cell E3
ws.Range("E3").Value = projectList
' Optional: Provide a message box to show it's done
MsgBox "Projects for " & employeeName & " have been compiled.", vbInformation
End Sub➤ Now let’s run this code. This time we’ll learn an alternative way to do so. Firstly, go to View > Macros > View Macros.
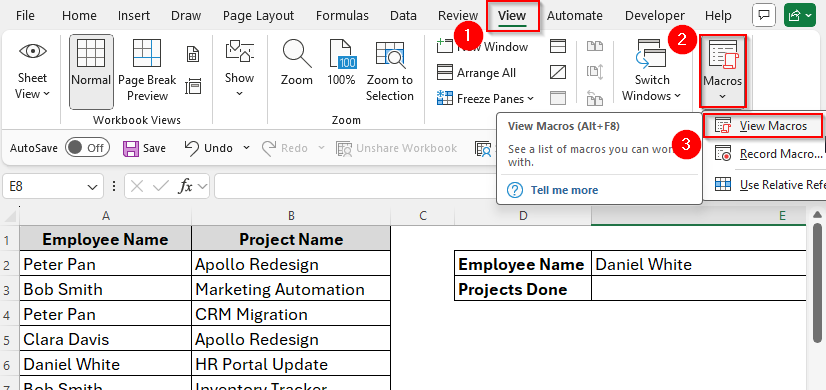
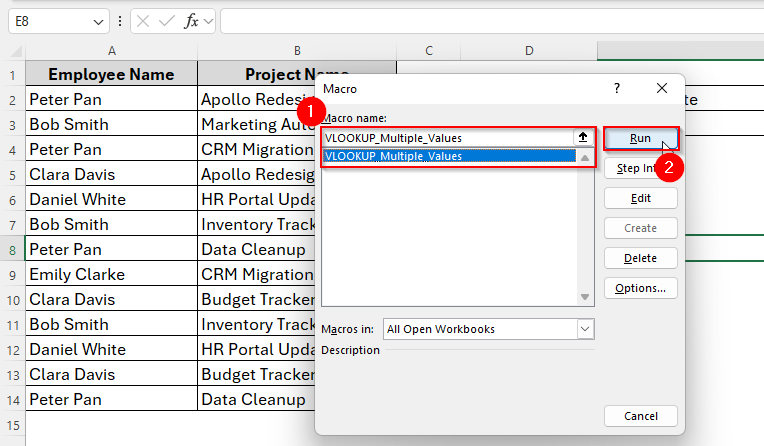
➤ Select VLOOKUP_Multiple_Values and click Run.
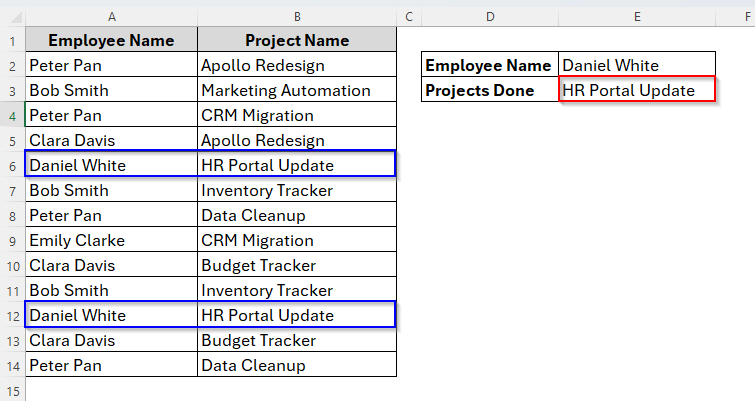
➤ Once you choose Run, the result will be already generated. And as we can see in the image below, the project name has not been repeated though Daniel White completed the same project twice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can VLOOKUP Return Multiple Values in Sheets?
No, the VLOOKUP function, by default, cannot return multiple values from multiple matches. It can only match and return the first value.
What is Better than VLOOKUP for Multiple Values in One Cell?
TEXTJOIN and IF combination is a better alternative to VLOOKUP when it comes to returning multiple values in a cell. But remember that it is only available on Excel 2019 and later versions. You won’t get it on Excel 2016, 2013 or prior.
Concluding Words
Finding multiple values for the same lookup key in Excel doesn’t have to be hard. With the tricks we learned using TEXTJOIN with IF, FILTER, or UNIQUE, you can easily join multiple results into one cell, even without duplicates. And if you’re using an older version of Excel, VBA provides a smart way to get the same outcome. We hope these techniques help you save time and work smarter in Excel.




















