Extracting the first number from a text string in Excel is a common challenge when working with mixed data like product codes, IDs, or SKU lists. Whether you’re cleaning imported datasets or preparing reports, identifying the first numeric character can save significant time during analysis or transformation. Excel doesn’t have a direct “find first number” function, but with a mix of formulas, array tricks, and even VBA, you can accomplish this reliably.
In this article, we’ll explore multiple ways to locate the first number in a string. You’ll learn several formula-based approaches and even a simple VBA script for automation. Let’s get started.
Steps to find first number in string in Excel:
➤ In B2, enter: =MID(A2,MIN(FIND({0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9},A2&”0123456789″)),1)
➤ Drag the formula down through C11.
➤ Column B will now display only the first number found in each string.
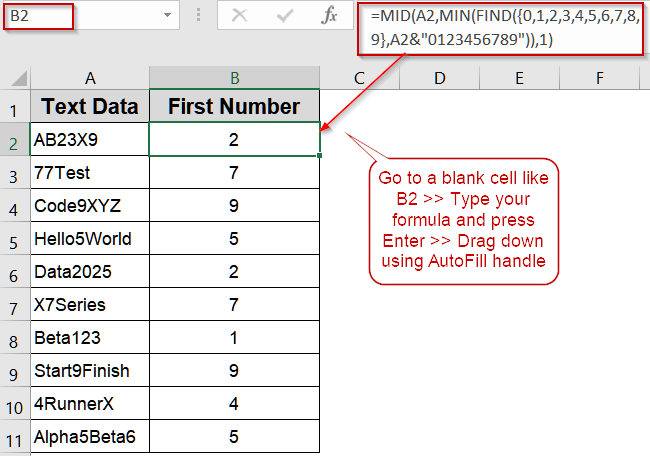
Extract the First Number Using the MID Function
Once you know the position of the first digit, you can use the MID function to extract that character directly. This approach works well for a full extraction workflow and is reliable for strings containing both letters and digits.
We’ll use the following dataset:
Steps:
➤ In B2, enter:
=MID(A2,MIN(FIND({0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9},A2&"0123456789")),1)
➤ Drag the formula down through C11.
➤ Column B will now display only the first number found in each string.
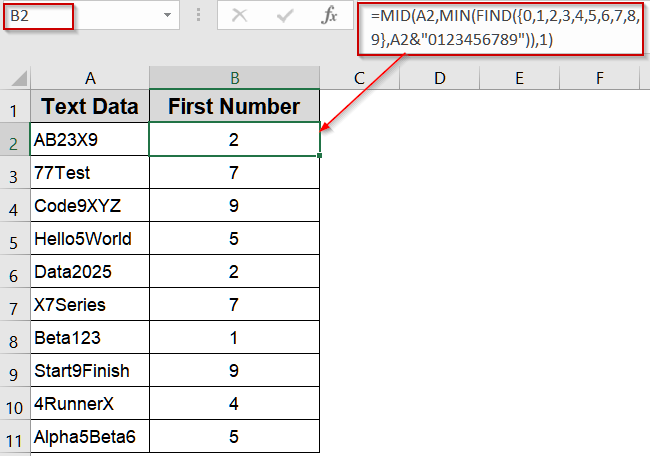
Use the FIND Function with an Array for Quick Detection
When you need a straightforward way to locate the first digit within a text string, combining the FIND function with an array of digits is fast and reliable. FIND function searches for each digit (0–9) and returns their positions. By wrapping it with MIN function, you extract the position of the first number. This is ideal for datasets where the string structure varies.
Steps:
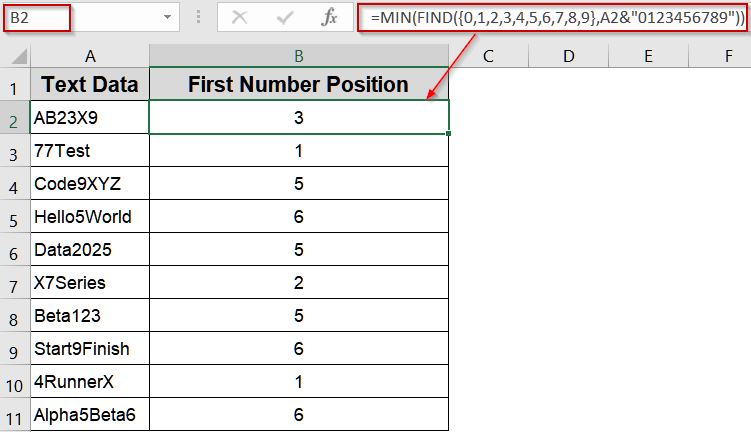
➤ Select cell B2 and type:
=MIN(FIND({0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9},A2&"0123456789"))
➤ Press Ctrl + Shift + Enter if using older Excel versions (Excel 365 handles arrays automatically).
➤ Drag the formula down to B11.
➤ The formula returns the position of the first digit in each text string.
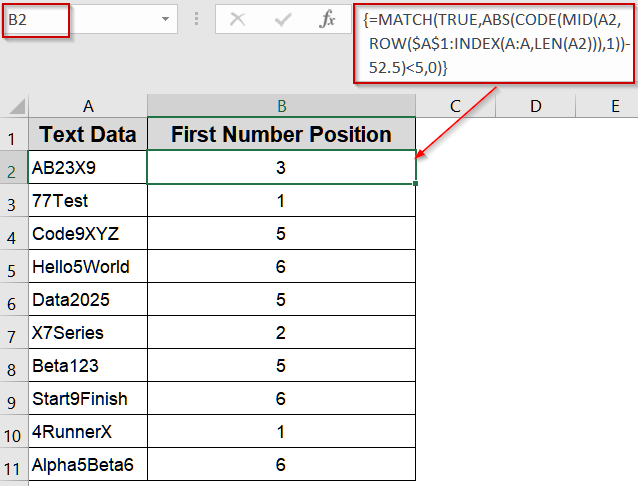
Apply MATCH and CODE Functions for an Advanced Array Solution
For advanced users, the MATCH and CODE functions can detect the first digit based on ASCII codes. This method is especially useful when working with special characters or ensuring compatibility across different locales.
Steps:
➤ In B2, enter:
=MATCH(TRUE,ABS(CODE(MID(A2,ROW($A$1:INDEX(A:A,LEN(A2))),1))-52.5)<5,0)
➤ Press Ctrl + Shift + Enter for older Excel versions.
➤ Drag down to B11 to find the numeric character’s position.
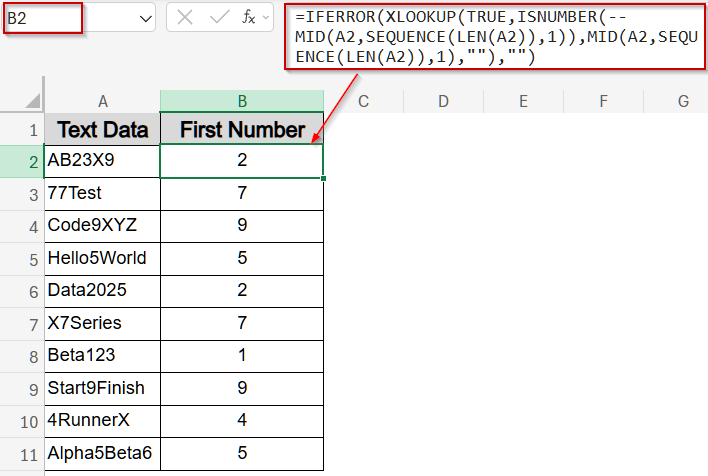
Insert XLOOKUP Function for Modern Excel Versions
XLOOKUP function offers a clean, dynamic array solution for Excel 365 or 2021. It searches through characters and retrieves the first number it encounters, simplifying the formula-building process.
Steps:
➤ Select B2 and type:
=IFERROR(XLOOKUP(TRUE,ISNUMBER(--MID(A2,SEQUENCE(LEN(A2)),1)),MID(A2,SEQUENCE(LEN(A2)),1),""),"")
➤ Press Enter.
➤ Drag the formula down to apply to all rows.
➤ This returns the first digit only, even if multiple numbers are present.
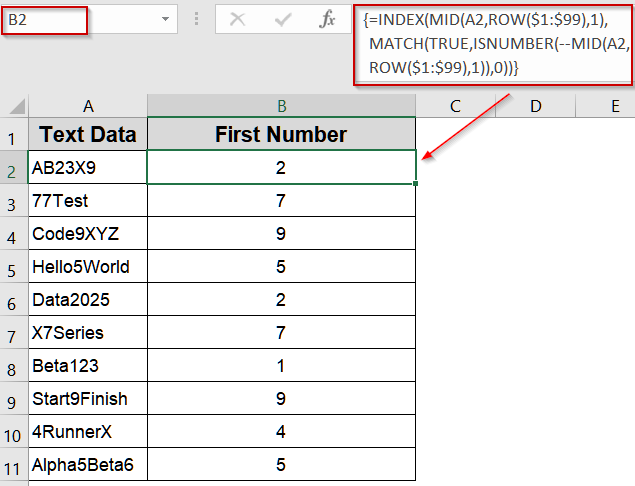
Use INDEX and MATCH Functions for Versatile Lookups
INDEX and MATCH functions can be combined to pinpoint the first numeric value within a string. MATCH function locates the first TRUE condition where a character is numeric, and INDEX function retrieves that character. This is efficient for users familiar with these core functions.
Steps:
➤ Select B2 and type:
=INDEX(MID(A2,ROW($1:$99),1),MATCH(TRUE,ISNUMBER(--MID(A2,ROW($1:$99),1)),0))
➤ Confirm with Ctrl + Shift + Enter in legacy Excel (just Enter in modern versions).
➤ Drag the formula down.
➤ The first numeric digit is displayed for each string.
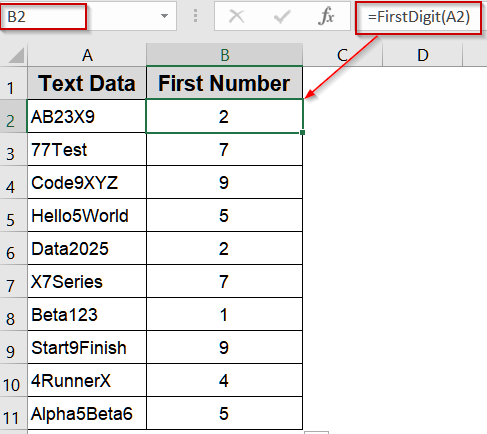
Automate Extraction Using VBA Code
If you regularly process strings and need to extract the first number without writing formulas every time, a VBA macro is the best option. VBA allows you to automate this process for multiple worksheets or files effortlessly.
Steps:
➤ Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
➤ Go to Insert >> Module and paste the following code:
Function FirstDigit(cell As String) As String
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To Len(cell)
If Mid(cell, i, 1) Like "[0-9]" Then
FirstDigit = Mid(cell, i, 1)
Exit Function
End If
Next i
FirstDigit = ""
End Function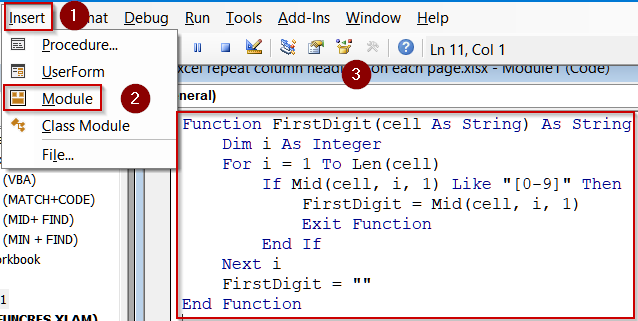
➤ Close the VBA editor and return to Excel.
➤ In B2, type:
=FirstDigit(A2)
➤ Drag down through B11.
➤ The first digit from each string will be displayed automatically.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why use formulas like FIND or SEARCH function to locate the first number in a string?
These formulas allow you to automatically detect the first numeric character within a mixed string without manual inspection, making large datasets easier to manage, validate, or parse for reporting and analysis.
When should I use array formulas or Ctrl + Shift + Enter for finding numbers?
Array formulas process multiple values simultaneously, which is essential when testing multiple digits (0–9) in one formula. Pressing Ctrl + Shift + Enter confirms the array calculation, enabling Excel to scan the entire string for the first numeric character.
Why might VBA be preferable for extracting the first number in a string?
VBA allows greater flexibility, automation, and performance on large datasets. It can extract the first number directly, handle errors gracefully, and process many cells at once without using complex formulas or array calculations.
What’s the main difference between FIND and SEARCH in Excel for this task?
FIND function is case-sensitive and works with exact matches, whereas SEARCH function is not case-sensitive. For detecting numbers specifically, either function works well, but SEARCH function is generally more forgiving with variations in text formatting.
Can I adapt these methods for multiple numbers within a string or for different character types?
Yes. By adjusting the formulas or modifying VBA code, you can locate subsequent numbers, extract all numbers, or search for other specific characters such as letters, symbols, or delimiters according to your data requirements.
Wrapping Up
Finding the first number in a string in Excel can be achieved in several ways, depending on your version and needs. From simple FIND-MID function combinations to advanced VBA automation solutions, each approach offers unique advantages for data cleaning and reporting tasks. Feel free to download the practice file and share your feedback.





