Microsoft Excel continues to be one of the most dependable and adaptable tools for organizing and analyzing time data. Knowing the number of hours worked, spent, or allocated for an employee is crucial for handling payroll, charging clients, organizing projects, and assessing productivity.
However, managing time in Excel isn’t always simple. Formatting or formula errors might produce confusing results since Excel records time as a fraction of a 24-hour day. So, we need to learn the correct procedure of doing this.
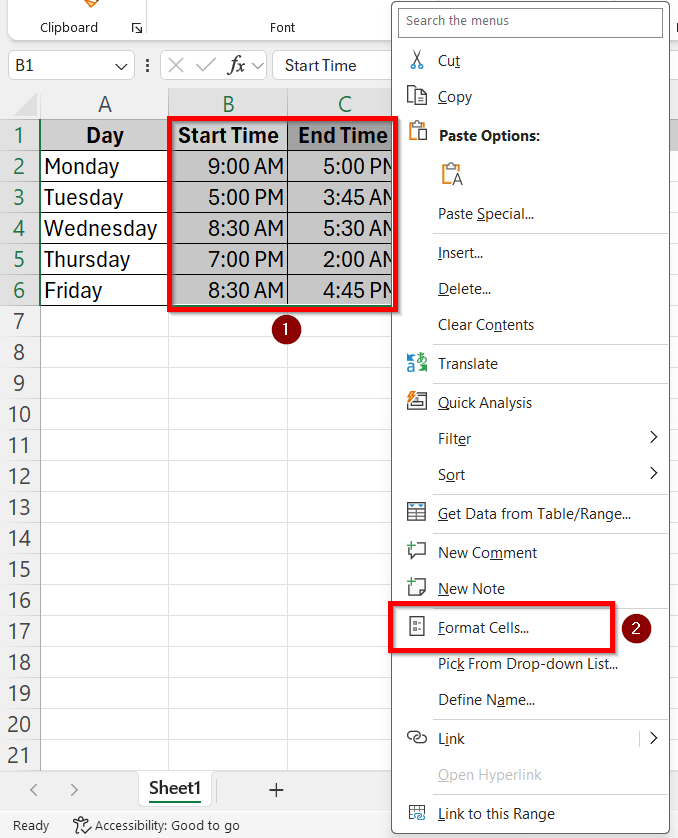
➤ Firstly, select all the columns containing the time values and right click on it.
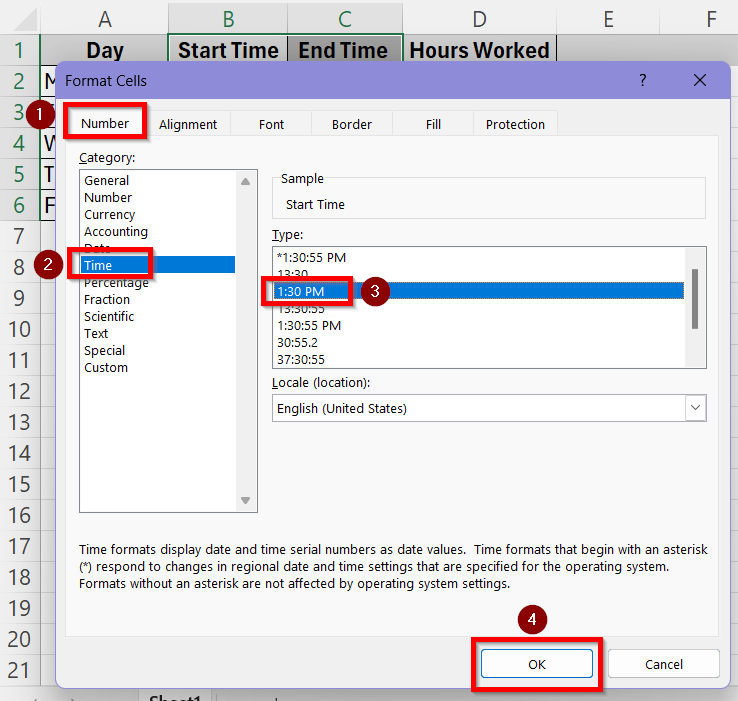
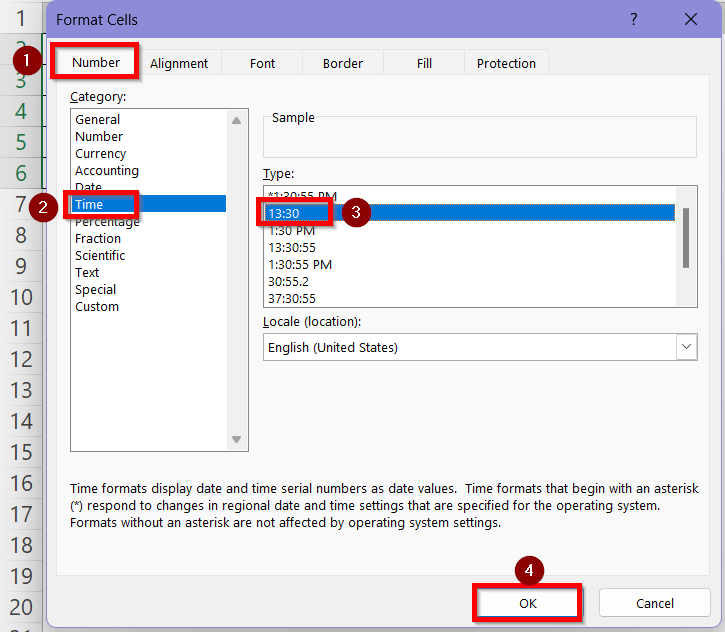
➤ Go to Format Cells > Number > Time and select the 1:30 or 13:30 option to show the time as HH:MM format.
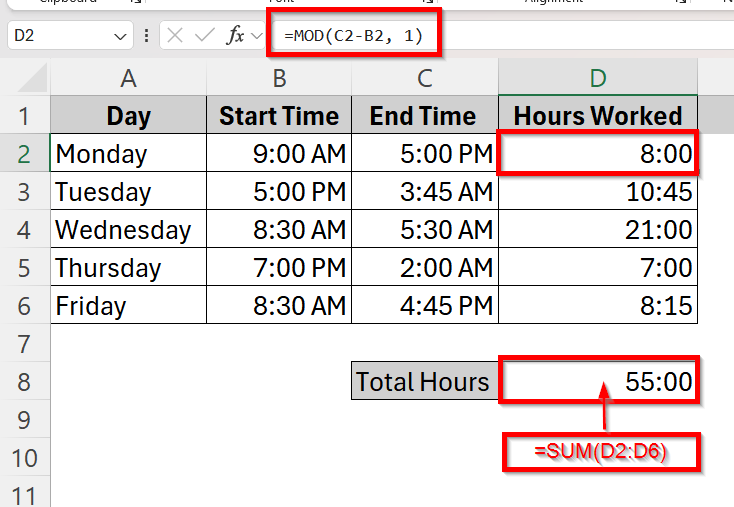
➤ In the cell D2, type the formula =MOD(C2-B2, 1) and drag it to apply to the whole column.
➤ Use =SUM(D2:D6) formula in the Total Hours cell to complete the summation of all the hours worked.
Quick Video Tutorial: Calculate Total Hours in Excel
Prerequisite Task: Enter Time in The Correct Format in Excel
First and foremost, to ensure that Excel handles your time data properly, the time should be entered in the correct format. The time data in Excel should always be entered in HH:MM format.
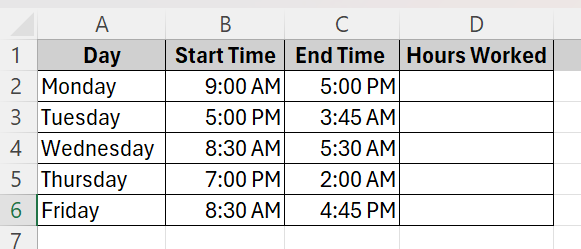
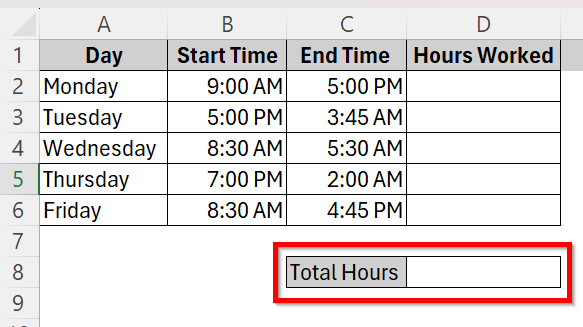
This is our sample dataset where an employee’s working hours throughout a week is documented. We need to calculate the total hours this employee has worked using Excel.
To ensure all the time data is set in the right format, we need to-
➤ Select the Start Time and End time column. Right click and select the Format Cells option from the drop-down box.
➤ In the Format Cells box, go to Number > Time and select the third 1:30 PM option to ensure the time is in HH:MM AM/PM format. You can select the second 13:30 option if you want to use the 24 hour format too. Press OK.
Calculate Total Hours Using MOD Function and Time Difference formula
Calculating the time difference between the start time and the end time is the simplest way of finding out total hours worked. However, simply using time difference is not enough to calculate the hours when the shift has crossed a 24 hour day and into the next day.
So, we use the MOD function to deal with the calculator when the end time goes past midnight. Let’s take a look at how we can utilize this below:
➤ First, create a new row where we will show the result of total hours worked. Here, go to cell C8 and type Total Hours and cell D8 will show us our calculated result.
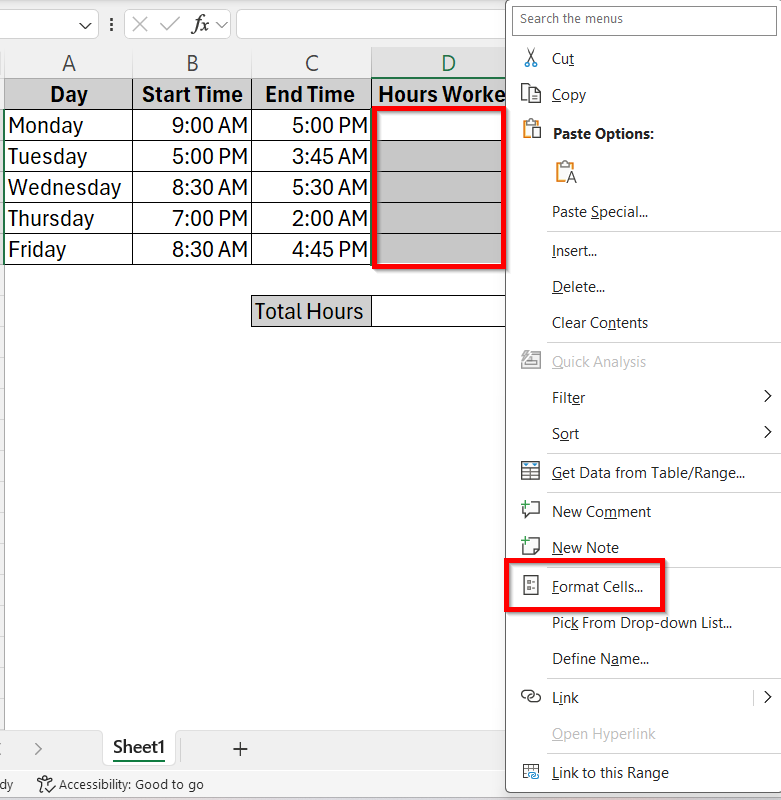
➤ Now, to fix the formatting in the Hours Worked column by selecting the cells from D2 to D6. Right click and go to Format Cells from the options.
➤ In the Format Cells box, go to Number > Time and select the second 13:30 PM option to show the time difference in hours. Press OK.
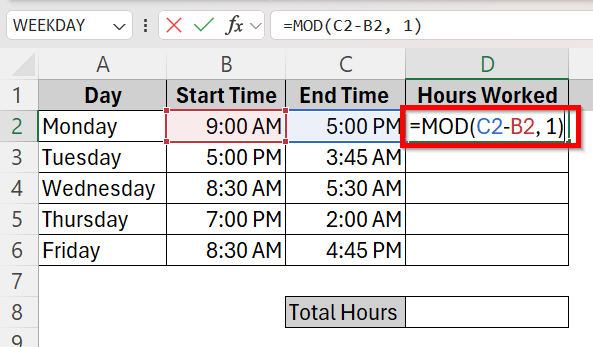
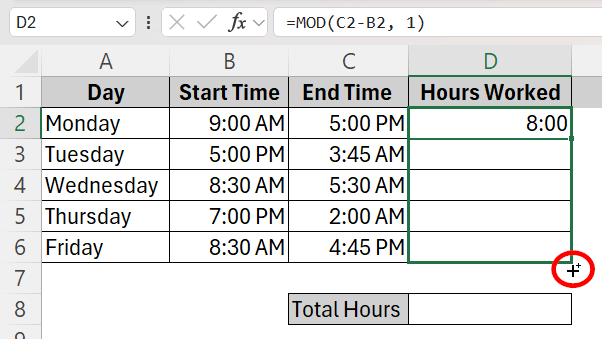
➤ Click on cell D2 and type the formula =MOD(C2-B2, 1). This calculates the total hours of work on that day (Monday).
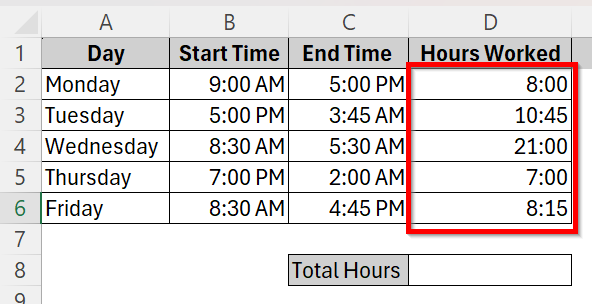
➤ Click the plus sign at the bottom right corner of cell D2 and drag it down to cell D6 to apply the formula to all the cells in the column.
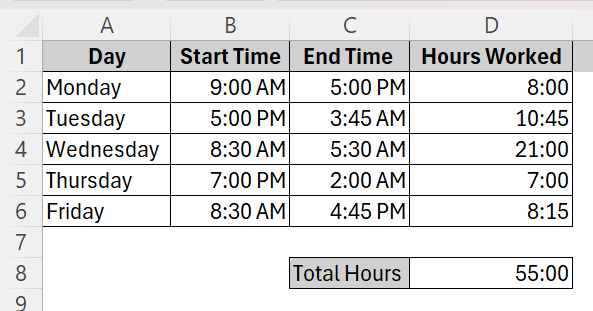
➤ This will be our resultant column where you can see the total hours of work done every single day of the week.
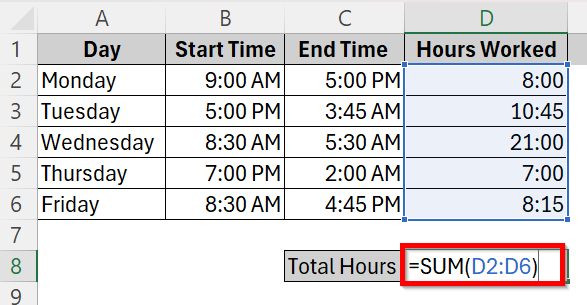
➤ Now, in order to calculate the total hours of work done in the whole week, click on cell D8 and type in the addition formula
=SUM(D2:D6).
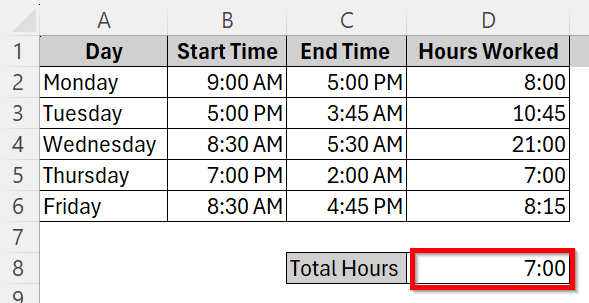
➤ The result will show like this- 7 hours which is clearly incorrect. Now, to show total hours correctly over 24 hours, we must use a custom format.
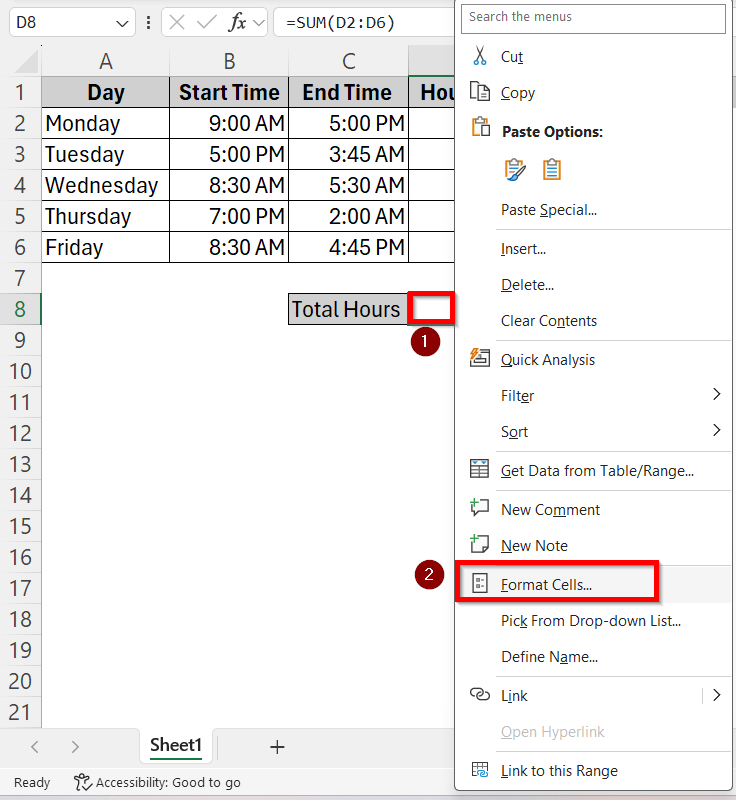
➤ Right click on cell D8 and select the Format Cells option.
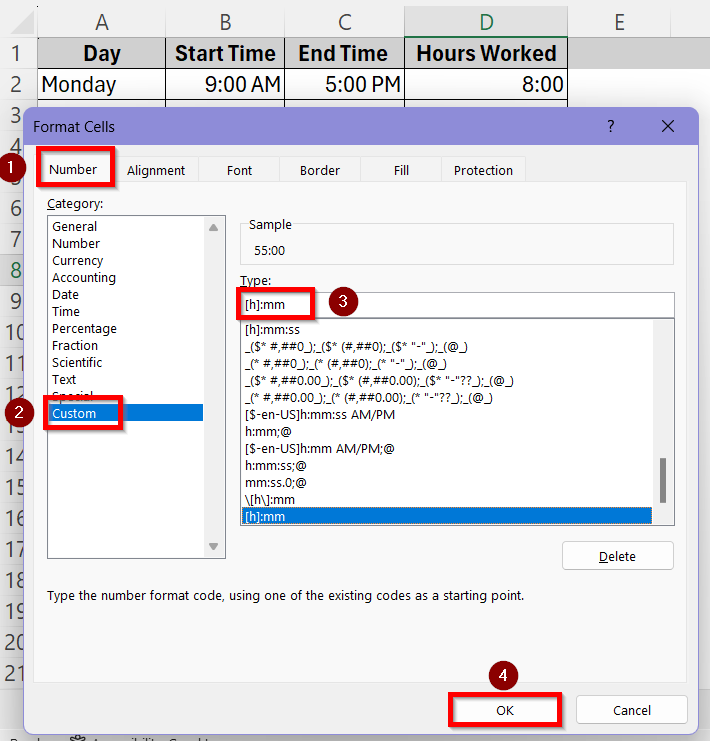
➤ In the Number tab, go to Custom. Type a custom format [h]:mm under the Type box and press OK.
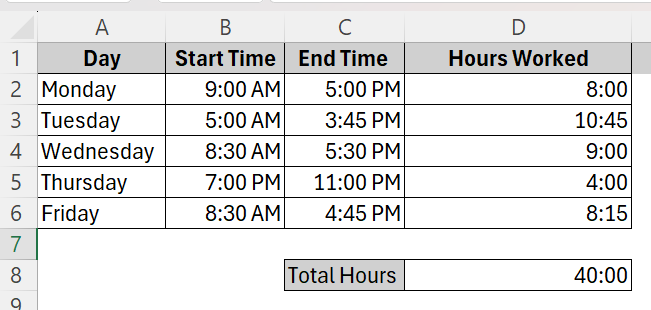
➤ Now, the total hours will show up accurately which is 55 hours.
Calculate Total Hours Using TEXT Function
You can simply use the TEXT function to calculate total hours as well. But in this method, shifts that cross midnight can not be calculated. The TEXT function shows an error if it has to calculate over 24 hours. So, it is recommended to use this method only if all the shifts end on the same day.
The process of using the TEXT function is described below:
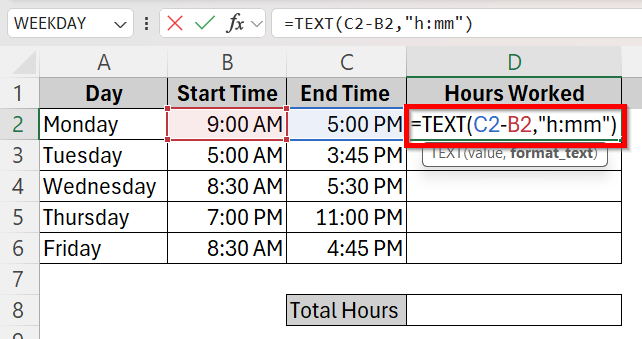
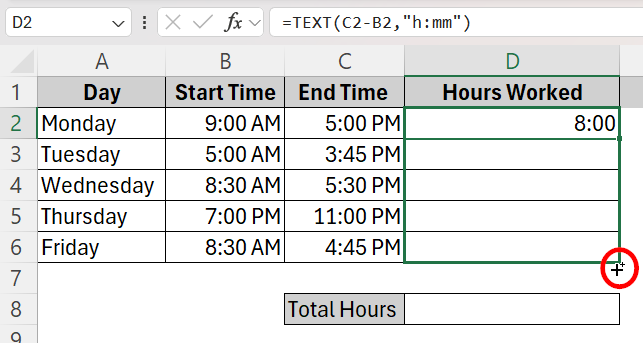
➤ Click on cell D2 and type in the TEXT formula
=TEXT(C2-B2,”h:mm”)
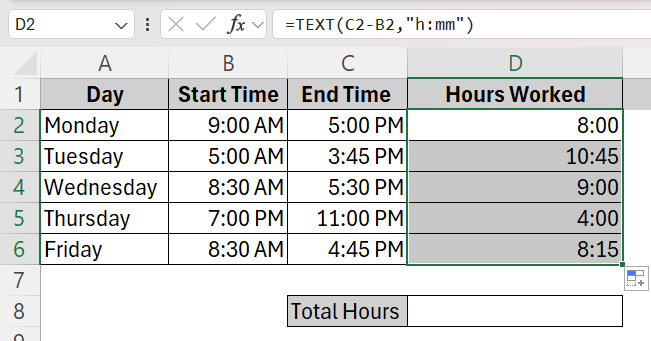
➤ Click the plus sign at the bottom right corner of cell D2 and drag it down to cell D6 to apply the formula to all the cells in the column.
➤ This will be our resultant column where you can see the total hours of work done every single day of the week.
➤ Follow the same steps for the Total Hours of the week using the =SUM(D2:D6) formula as mentioned above to get the results below.
Use Conditional Formula to Calculate Total Hours In Overnight Shifts
We can’t use the direct time difference formula =C2-B2 or the TEXT function when the shift has crossed midnight. Apart from MOD function, another method in this case would be constructing a custom formula for the calculation. We have described the proper steps below:
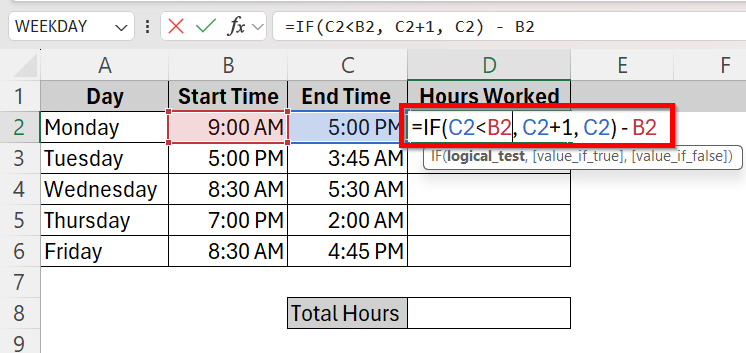
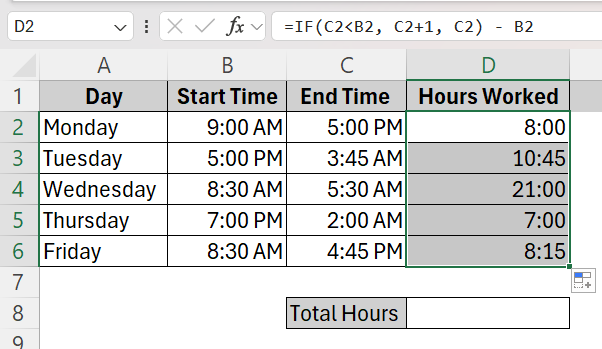
➤ Click on cell D2 and type the formula =IF(C2<B2, C2+1, C2) – B2. This checks if the end time is technically earlier (next day) and adjusts accordingly to give the correct total hour output.
➤ Click and drag to apply the formula to all the cells and get the total hours result.
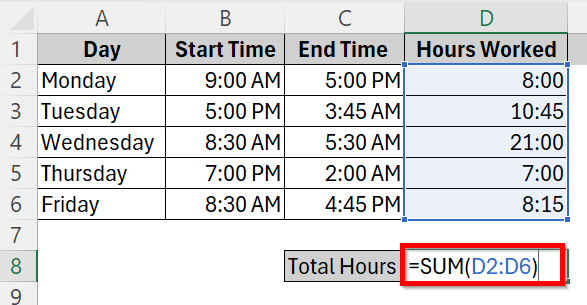
➤ In order to calculate the total hours of work done in the whole week, click on cell D8 and type in the addition formula
=SUM(D2:D6)
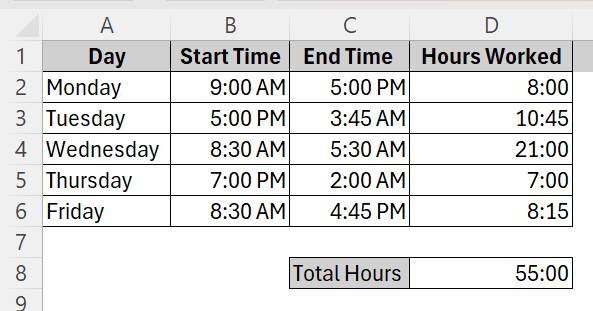
➤ Now, the total hours of the entire week will show up which is 55 hours.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why isn’t my SUM of time values adding up correctly?
You have to make sure the column you are applying the SUM function in, has all time formats instead of text formats for it to work. If they are not already in real time values, format the column with [h]:mm using the Format Cells > Custom box.
What Formula Should I Use if the Workshift Goes Past Midnight?
When the workshift begins at PM and goes past 12 AM on the same day, Excel messes up the calculation in the typical time difference formula. To fix this error, use this general formula =IF(EndTime<StartTime, EndTime+1, EndTime) – StartTime.
Can I See The Total Time in Decimals Instead of Time Format?
Sure, you can convert the total hours column to decimals from its usual time format if you want to. Go to Format Cells > Number and select up to 2 decimal places. For instance, the results will show up as 8.5 hours instead of 8:30 now.
Wrapping Up
Excel provides a range of versatile tools to make time tracking precise and effective. From managing overnight shifts to presenting totals beyond 24 hours using formats like [h]:mm, you have all the options to choose what you want to use. You can stay clear of typical errors and make efficient use of functions and formulas like MOD, TEXT, and SUM by being aware of how Excel saves and manages time now.
Choose whichever method works the best for you and let us know your feedback!