Calculating the elapsed time between two dates is a core task in Excel, whether you’re tracking project deadlines, analyzing employee work periods, or managing invoices. Without the right approach, it’s easy to get incorrect results, especially when switching between days, months, or hours.
In this article, we’ll show you multiple proven methods to calculate elapsed time between two dates. You’ll learn simple subtraction for total days, how to convert durations into hours, minutes, or seconds, and how to use the DATEDIF, NETWORKDAYS, and month-based formulas. Let’s begin.
Steps to calculate elapsed time between two dates in Excel:
➤ Enter your start dates in column B and end dates in column C.
➤ Go to a blank cell like D2.
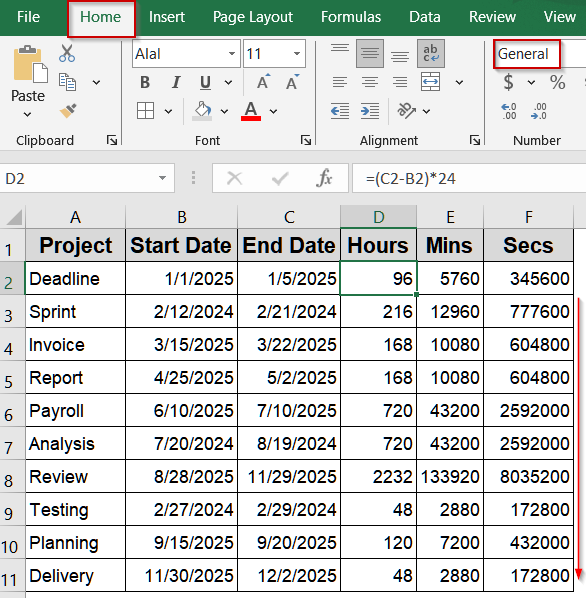
➤ To avoid the result appearing as a date instead of a number, select the cell, go to the Home tab >> Number group >> choose General.
➤ Type the formula: =C2-B2
➤ Press Enter.
➤ Drag the fill handle down to apply to other rows.
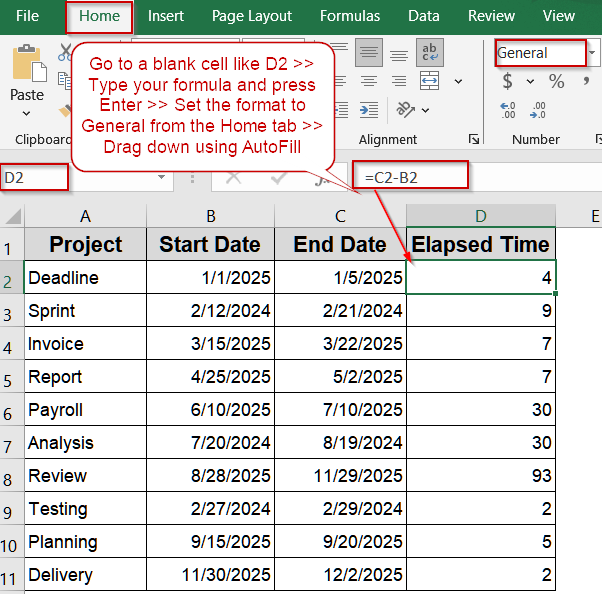
Subtract Dates Directly to Calculate Days Between Two Dates
Subtracting one date from another is the simplest way to calculate elapsed days in Excel. Excel stores dates as serial numbers, so subtracting the start date from the end date instantly gives the number of days between them. This is ideal when you need a fast calculation without extra functions or formatting.
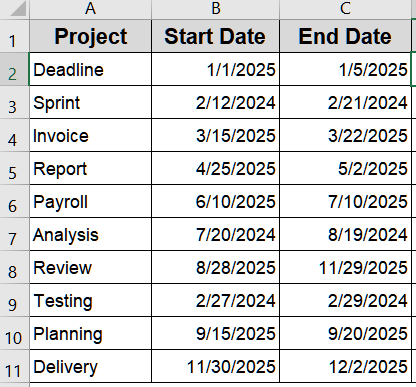
We’ll use the following sample dataset:
Steps:
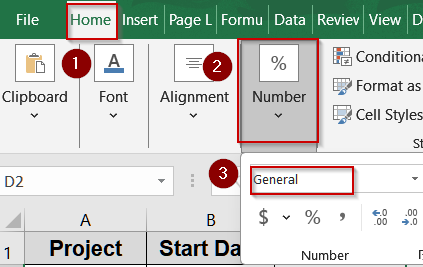
➤ Enter your start dates in column B and end dates in column C.
➤ Go to a blank cell like D2.
➤ To avoid the result appearing as a date instead of a number, select the cell, go to the Home tab >> Number group >> choose General.
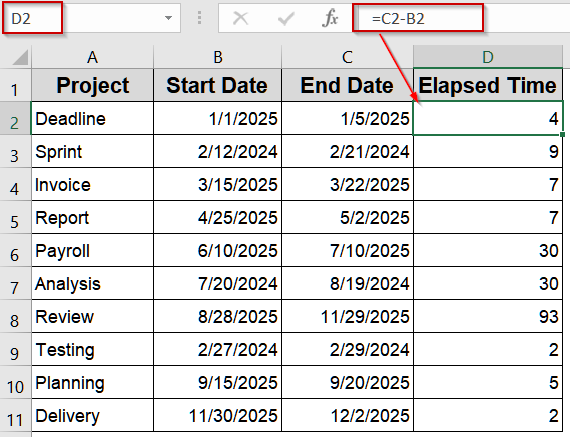
➤ Type the formula:
=C2-B2
➤ Press Enter.
➤ Drag the fill handle down to apply to other rows.
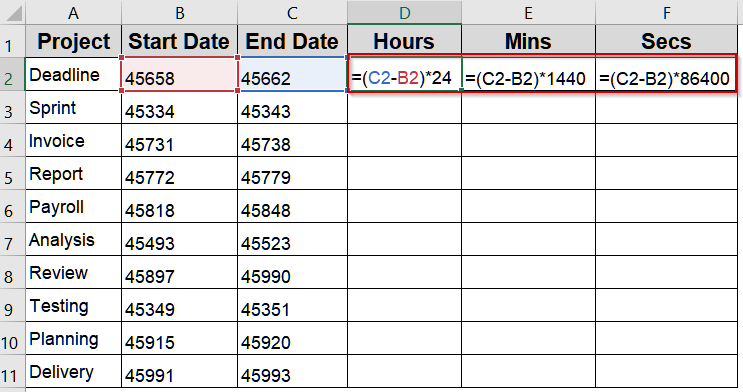
Multiply Subtracted Days to Get Total Hours, Minutes, or Seconds
Once you have the difference in days, multiplying by conversion factors can convert it to hours, minutes, or seconds. This is essential for performance metrics or process timing where finer units matter.
Steps:
➤ Enter your start dates in column B and end dates in column C.
➤ Go to a blank cell like D2.
➤ To calculate hours, type this formula:
=(C2-B2)*24
➤ For minutes, use this formula in E2 cell:
=(C2-B2)*1440
➤ For seconds, use this formula in F2 cell:
=(C2-B2)*86400
➤ Format the result cell as General from the Home tab.
➤ Press Enter and drag the fill handle down for all rows.
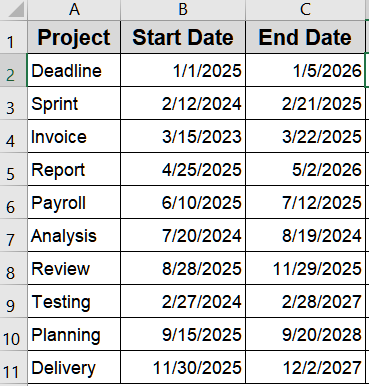
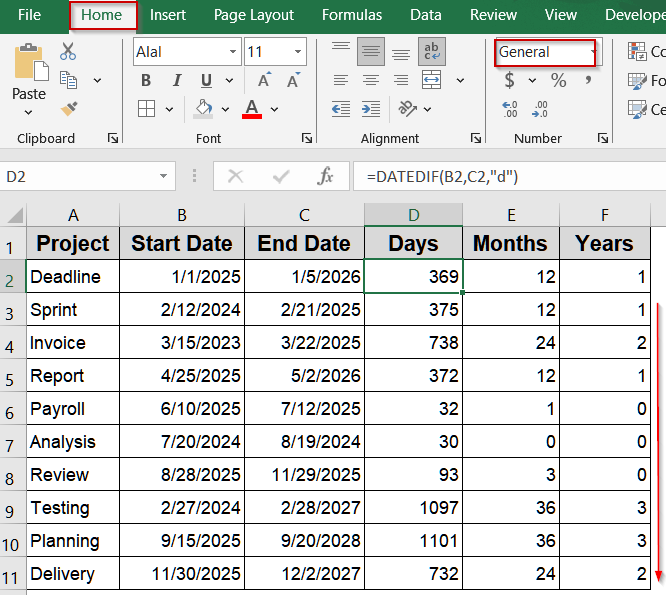
Use DATEDIF Function for Full Days, Months, or Years
The DATEDIF function provides elapsed time directly in specific units such as days, months, or years. This method is particularly useful for calculating ages, project phases, or HR data where full units are needed. We’ll use this modified dataset for demonstration:
Steps:
➤ Place start dates in column B and end dates in column C.
➤ Click a blank cell like D2.
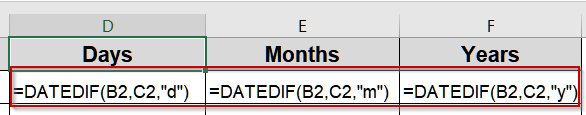
➤ To calculate days, type this formula:
=DATEDIF(B2,C2,"d")
➤ For months, use this formula in E2 cell:
=DATEDIF(B2,C2,"m")
➤ For years, use this formula in F2 cell:
=DATEDIF(B2,C2,"y")
➤ Press Enter and copy down.
➤ Format the result cell as General from the Home tab.
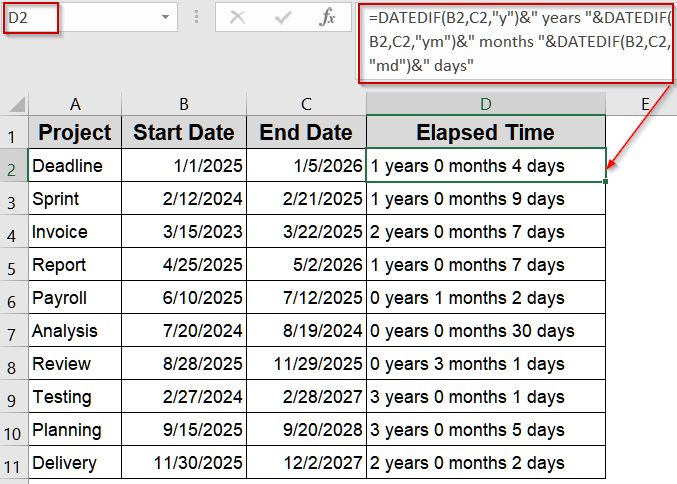
Combine DATEDIF Units to Display Years, Months, and Days Together
You can merge multiple DATEDIF function calculations to show elapsed time in a single readable string like “2 years 5 months 3 days”. This is especially handy for service anniversaries or detailed timeline reports.
Steps:
➤ Enter start dates in B2 and end dates in C2.
➤ Select a blank cell such as D2.
➤ Format the result cell as General from the Home tab under the Number group.
➤ Type this formula:
=DATEDIF(B2,C2,"y")&" years "&DATEDIF(B2,C2,"ym")&" months "&DATEDIF(B2,C2,"md")&" days"
➤ Press Enter.
➤ Drag the fill handle to fill down.
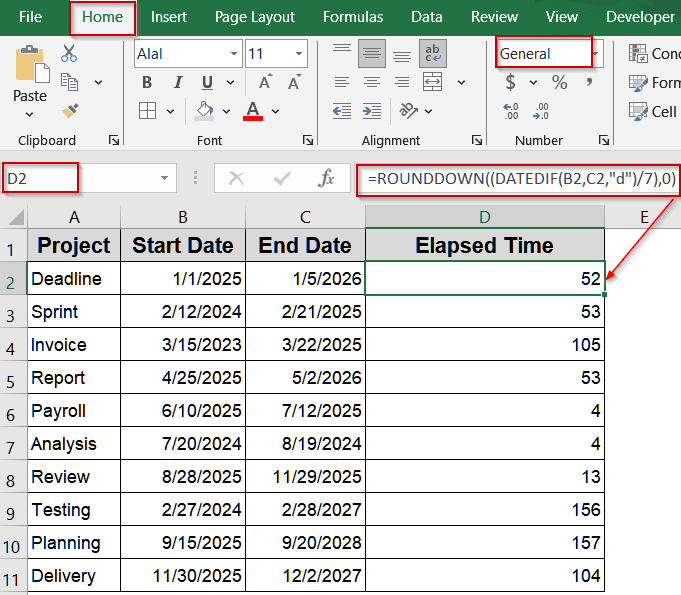
Calculate Date Difference in Weeks Using DATEDIF and ROUNDDOWN Functions
When you need the elapsed time in weeks, dividing the day difference by seven and rounding down gives whole weeks. This is useful for tracking weekly sprints or schedules.
Steps:
➤ Enter start dates in B2 and end dates in C2.
➤ Click an empty cell like D2.
➤ Type this formula:
=ROUNDDOWN((DATEDIF(B2,C2,"d")/7),0)
➤ Press Enter.
➤ Format the cell as General and drag down.
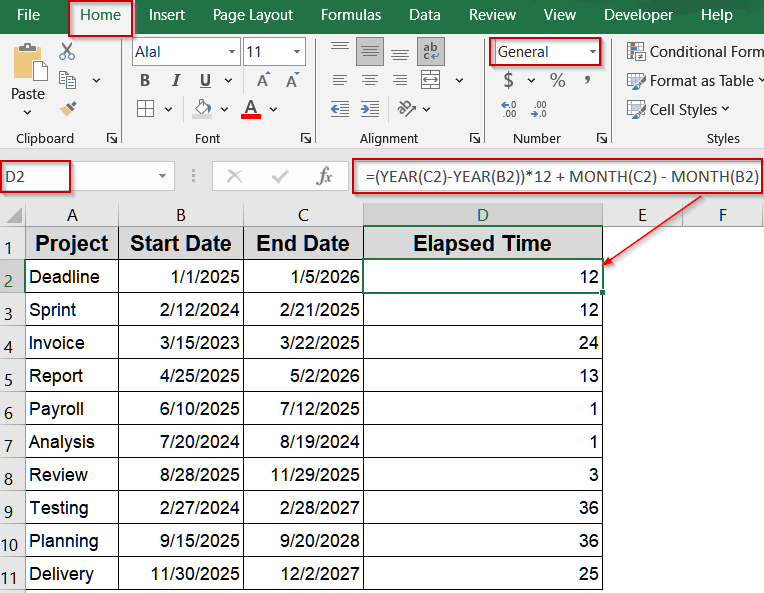
Compute Months Between Two Dates Using YEAR and MONTH Functions
This approach calculates total months across years, making it perfect for finance or subscription data where you need to count calendar months rather than partial periods.
Steps:
➤ Put start dates in B2 and end dates in C2.
➤ Select a blank cell like D2.
➤ Type this formula:
=(YEAR(C2)-YEAR(B2))*12 + MONTH(C2) - MONTH(B2)
➤ Press Enter and drag the fill handle down.
➤ Format the cell as General for correct display.
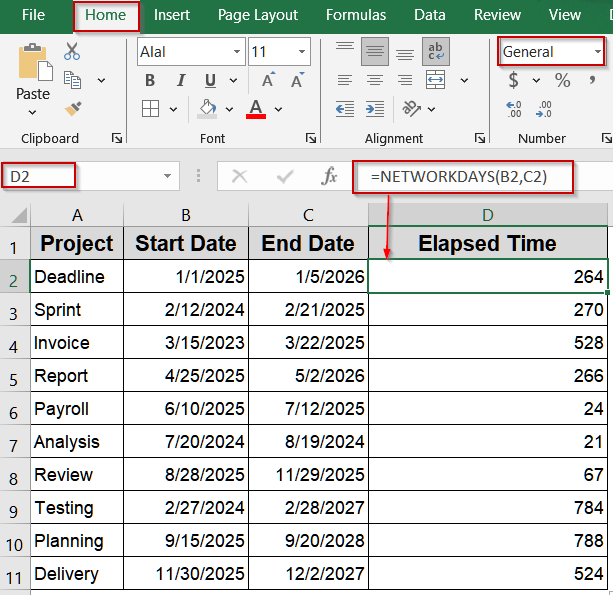
Use NETWORKDAYS to Calculate Duration in Working Days
If you only need to count Monday to Friday workdays between two dates, NETWORKDAYS function is the correct choice. It’s frequently used in project planning or payroll to exclude weekends automatically.
Steps:
➤ Enter your start dates in B2 and end dates in C2.
➤ In a blank cell like D2, type this formula:
=NETWORKDAYS(B2,C2)
➤ Press Enter.
➤ Drag the fill handle to copy for all rows.
➤ Format as General for a clean numeric result.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Excel’s date arithmetic accurate with leap years?
Yes. Excel date serial numbers automatically account for leap years. Subtraction, DATEDIF, and NETWORKDAYS functions include February 29 when applicable, so calculations spanning leap years remain accurate without requiring manual adjustments or additional formulas.
How do I calculate elapsed time in days between two dates in Excel?
Use a simple subtraction formula such as =End_Date-Start_Date (e.g., =C2-B2). If the result displays as a date, format the cell as General or Number to view the total elapsed days accurately.
What is the DATEDIF function used for when calculating elapsed time?
The DATEDIF function directly calculates differences in chosen units. For example, use =DATEDIF(A2,B2,”d”) for days, “m” for months, or “y” for years. It’s ideal for precise elapsed calculations spanning multiple months or years effectively.
How can I calculate elapsed time in weeks between two dates?
Use the formula =ROUNDDOWN(DATEDIF(A2,B2,”d”)/7,0) to convert total days into full weeks. This divides the day difference by seven, then rounds down. It’s perfect for schedules, timelines, or weekly reporting in Excel.
What formula should I use for business or working days only?
Use =NETWORKDAYS(Start_Date,End_Date) to count weekdays, excluding Saturdays and Sundays. To exclude specific holidays as well, include a holiday range such as =NETWORKDAYS(Start_Date,End_Date,Holiday_Range).
Wrapping Up
In this tutorial, we explored several reliable ways to calculate elapsed time between two dates in Excel, including direct subtraction for days, multiplying by 24, 1440, or 86400 for hours, minutes, or seconds, and using DATEDIF function for years, months, and days. We also covered NETWORKDAYS function for business days and a combined DATEDIF formula for detailed differences. Feel free to download the practice file and share your feedback.

















